Still downloading templates?
There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Ever felt like you’re running a marathon but unsure if you’re on pace to finish?
In project management, keeping track of your progress and ensuring you’re heading toward successful completion can feel just as challenging.
That’s where Earned Value (EV) comes into play—a powerful metric that helps project managers gauge the financial performance of their projects against the timeline and budget.
In this blog, we’ll talk about how to calculate Earned Value, providing you with a clear roadmap to understand where your project stands and how to steer it toward success.
Earned Value (EV) in project management is a metric that measures the actual work completed against the planned cost, providing a snapshot of project financial performance.
It helps project managers determine how much of the budget should have been spent, considering the amount of work done at any point in the project’s timeline.
By comparing this figure with the actual costs, managers can assess whether a project is under or over budget. This critical insight allows for effective tracking of financial progress and facilitates proactive decision-making to keep projects aligned with their budgetary and timeline objectives.
Earned value management (EVM) is a tried-and-tested method that provides real, quantifiable insights into your project’s health. By combining measurements of the project schedule, budget, and actual work completed, EVM gives you a comprehensive snapshot of project performance and progress.
Earned value management in project management:
EVM offers a three-dimensional view of project performance, enabling project managers to make informed decisions, anticipate problems, and adjust plans proactively.
It transcends traditional measures like the cost performance index (CPI) and schedule performance index (SPI), providing a comprehensive framework to:
Whether you’re overseeing a small team or managing a sprawling, complex project, integrating EVM with project management tools like ClickUp can transform your approach to tracking progress and ensuring project success.
Let’s get down to brass tacks with the core concepts of Earned Value Management (EVM), a framework that might seem daunting initially but is really about keeping your project on track and within budget.
Here’s a brief rundown of the key terms you must know:
Now, let’s connect the dots with some other crucial terms:
Earned Value (EV) is the linchpin in earned value management, providing a snapshot of the project’s financial health and progress.
Imagine you’re managing a project to upgrade a business’s IT infrastructure.
Your Planned Value (PV) by month three is $150,000, signaling what you aimed to spend for the work scheduled.
By this time, your Actual Cost (AC) is $120,000.
But here’s where EV comes in: if the work you’ve actually completed is valued at $130,000, EV reveals you’re under budget and getting more done for your dollar.
This shows EV’s role in gauging cost efficiency and work progress, offering a clear, quantifiable measure of how well the project performs against its plan.
Calculating Earned Value (EV) lets you measure, in real time, how your project performs against your plan.
Let’s break it down step by step.
The first step is to establish your project’s baseline, which is a detailed version of your project plan that includes the project scope, schedule, and total budget (Budget at Completion, BAC). This baseline serves as your project’s financial and scheduling benchmark.
Let’s say you’re launching a new software module. Your total budget (Budget at Completion, BAC) is $200,000, planned over five months.
Planned Value (PV) is a snapshot of your expected progress, allowing you to measure what the project should have accomplished financially up to any point in its timeline.
Three months into the project, you planned to complete 60% of the work. For our software project, that’s 60% of $200,000, equaling a PV of $120,000.
Next, you need to figure out the Actual Cost (AC), which is the total cost incurred for the work performed on the project up to a specific time. This includes all expenses related to the project, giving you a clear view of the financial resources you’ve actually spent.
So, if, by month three, you’ve spent $100,000, then AC = $100,000.
Earned Value (EV) is where you assess the value of the work actually completed to date, compared to the original budget. EV helps you understand whether you are ahead, on, or behind schedule and budget by putting a dollar value on the amount of work done.
If you’ve finished only 50% of the software module, then EV = 50% of $200,000 = $100,000.
After calculating EV, you perform variance analysis to identify differences between planned and actual performance. This involves calculating Cost Variance (CV) and Schedule Variance (SV), which indicate how far off you are from your budget and schedule, respectively.
Finally, to understand the efficiency and productivity of your project, you calculate the Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI). These indexes help you predict the project’s cost and time to completion, enabling strategic decision-making.
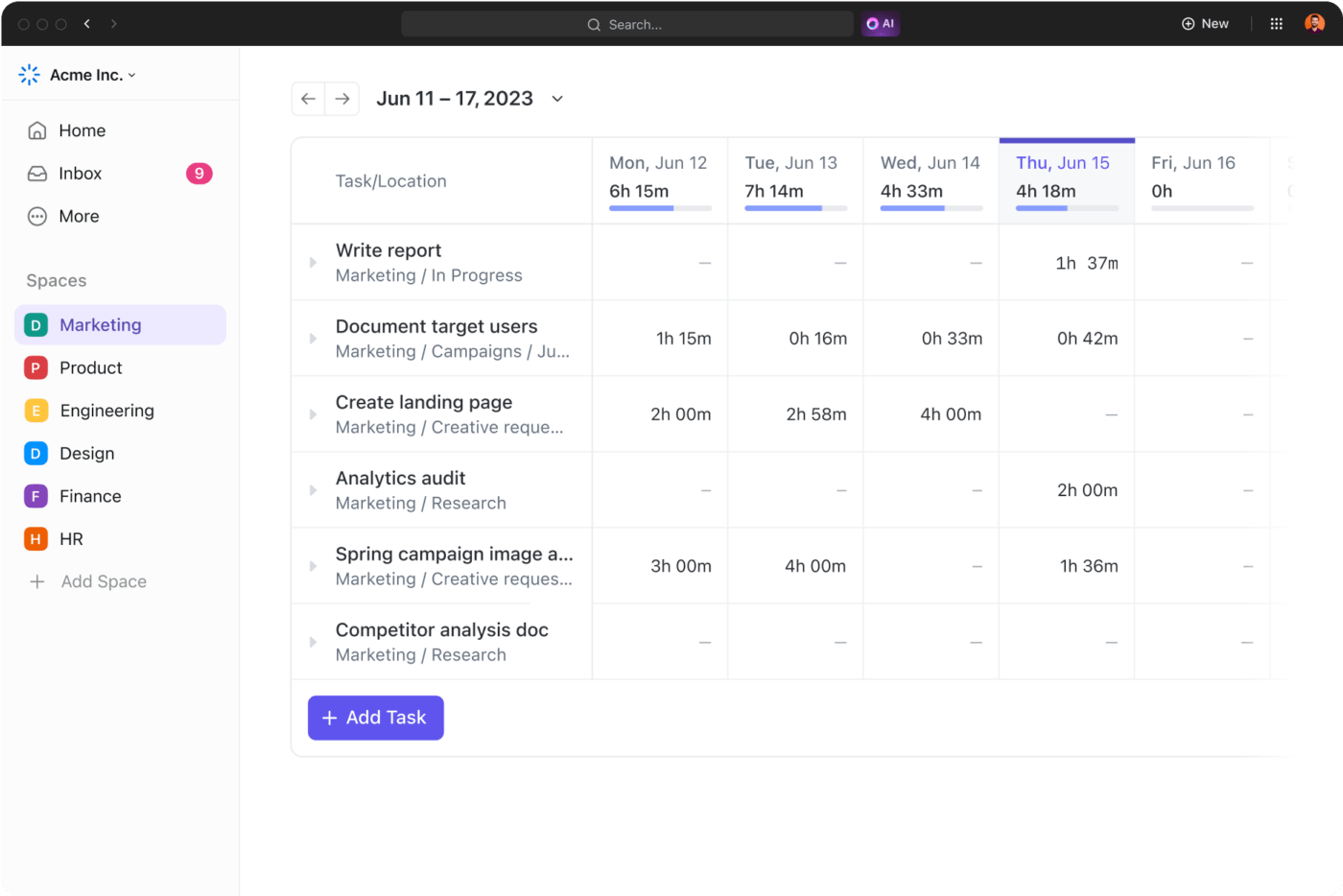
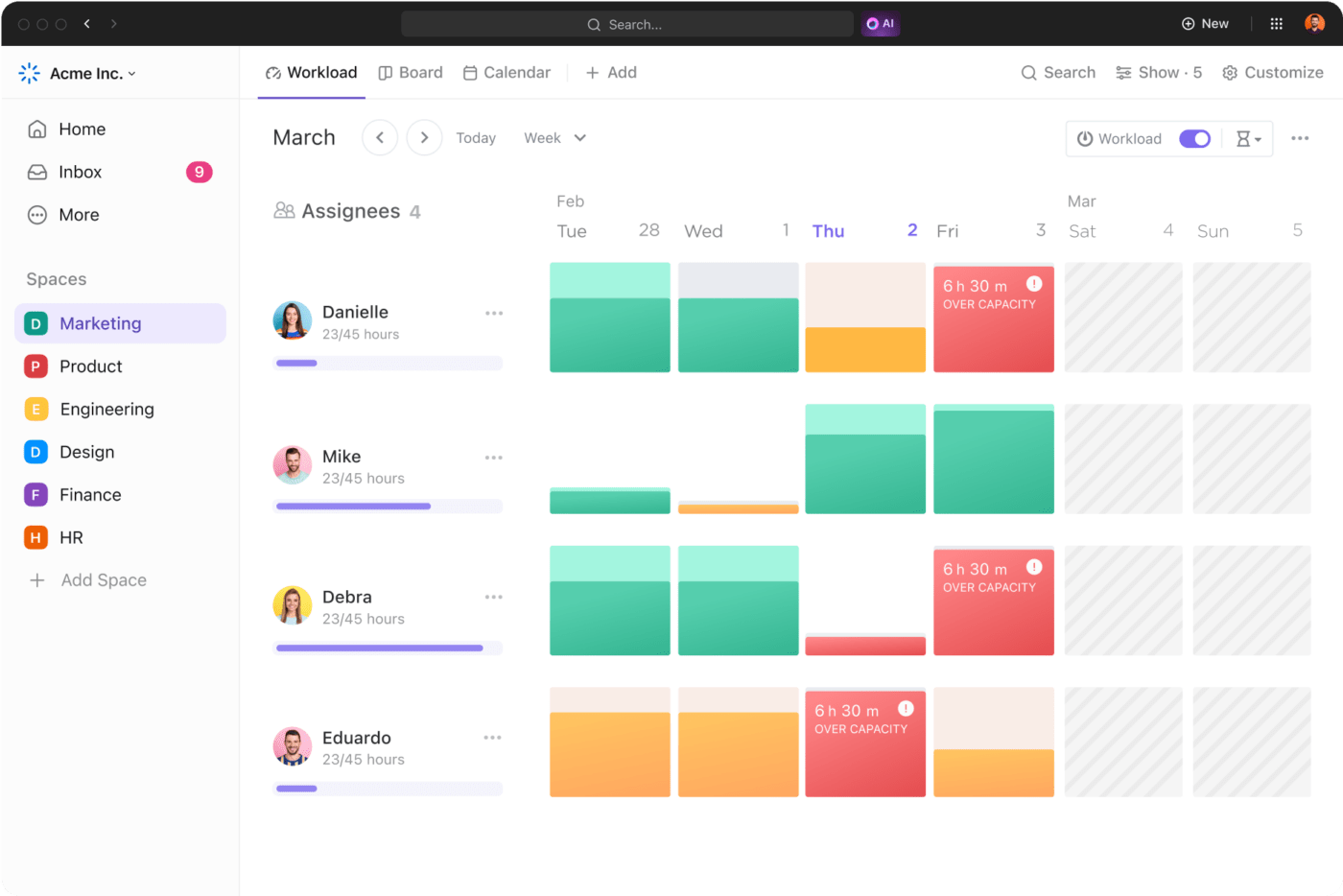
Project management software plays a pivotal role in implementing earned value management (EVM), especially when you’re juggling multiple complex projects. Integrating EVM tools allows you to effortlessly track your project’s performance against its budget and schedule.
Think of having a dashboard that does all the earned value analysis and shows your project’s actual progress, planned value, and actual costs—all without you drowning in spreadsheets.
Project management software calculates schedule variance and cost variance in real time, enabling project managers to make informed decisions swiftly. Whether it’s adjusting the project budget or reevaluating the work breakdown structure, having a project management tool equipped with EVM capabilities means you’re prepared to tackle any discrepancies head-on.
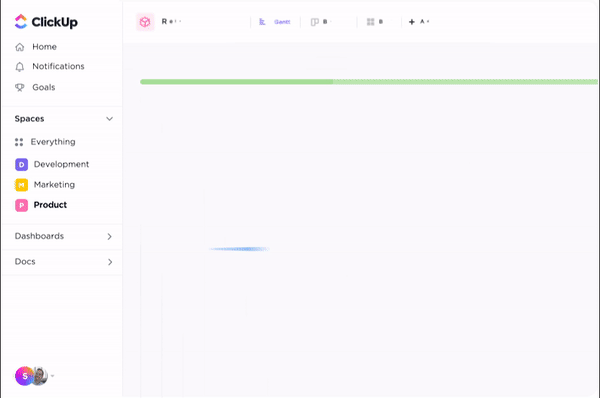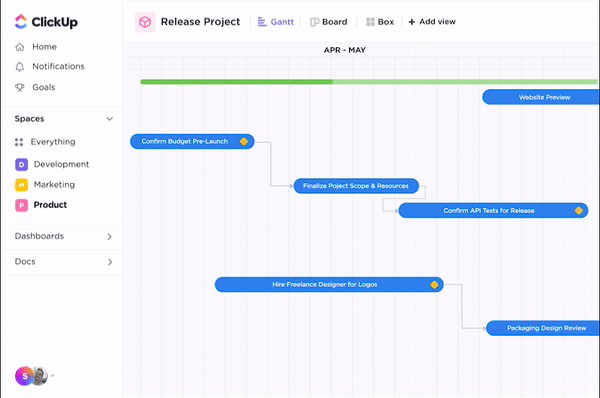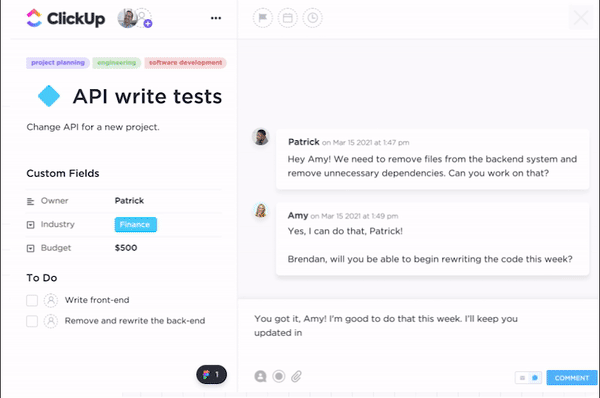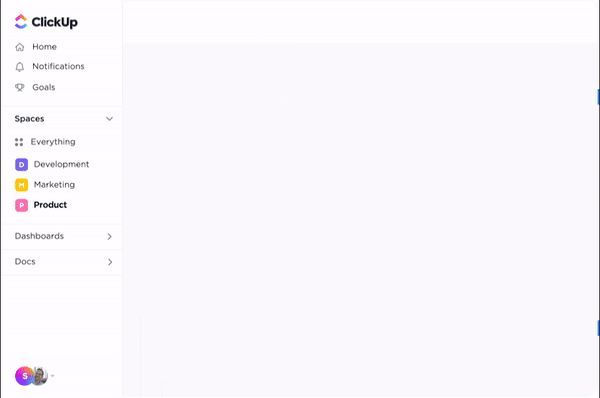
ClickUp is one of the best project management tools for implementing earned value management (EVM) effectively within your projects. Through a suite of features tailored for detailed tracking and analysis, ClickUp enables project managers to integrate EVM principles into their workflow seamlessly.
Whether you’re aiming to keep a close eye on your project scope, costs, hours, or budget, ClickUp offers a robust platform for all your EVM needs. Let’s look into its specific features:






Even the most robust frameworks have their Achilles’ heel, and earned value management (EVM) is no exception. Let’s break down its limitations, dive into risk management within EVM, and explore strategies to navigate common pitfalls:
While EVM excels at tracking cost and schedule performance, it doesn’t directly address risk management. However, you can integrate risk analysis by monitoring variances and performance indices, which can signal potential risks. For example, consistent cost overruns might indicate underestimated project complexity, requiring a risk reassessment.
To overcome EVM’s limitations, consider the following approaches:
Earned value management is your roadmap and reality check rolled into one, ensuring you’re not just spending time and money but investing them wisely.
The magic, however, isn’t just in knowing EVM exists but in using it effectively. That’s where your skills and experience come into play. Expert project managers understand the need to dive deep into the numbers, understand what they’re indicating, and act.
EVM can become smoother and more intuitive with tools like ClickUp.
Bridging the gap between complexity and usability, ClickUp transforms the implementation of EVM from a task into an advantage. With ClickUp, applying key project management principles becomes an integral, effortless part of managing your projects.
So why wait? Make every decision an informed one! Get started with ClickUp today!
The earned value of a project is like taking a snapshot of what your team has accomplished, but in dollars and cents. It measures the value of the work completed compared to the original budget. Let’s say you planned to spend $50,000 on a part of your project, and you’ve completed that portion. If it was supposed to cost $50,000 according to your plan, then your earned value is $50,000. It’s a way to see if your project’s spending and progress are on track, blending scope, schedule, and cost into one clear number.
In project management techniques, the earned value gives you a real-deal look at your project’s health beyond just deadlines and dollar signs. Earned value ties together how much work you’ve completed, how much you planned to do, and how much you’ve spent doing it. It’s part of a larger strategy called Earned Value Management (EVM), helping project managers predict project outcomes, control costs, and ensure schedules are met. It turns complex project data into actionable insights so you can steer your project to success with confidence.
The earned value formula goes like this:
EV = (The percentage of completed work) x (The project’s total budget).
If you’re halfway through a project budgeted at $100,000, your earned value (EV) is 50% of $100,000, which equals $50,000.
This simple formula helps you figure out if your project is on the right financial and progress track. It’s a cornerstone of assessing where your project stands today and predicting where it will end up, enabling smarter decisions along the way.

© 2026 ClickUp

There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.