Still downloading templates?
There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Ever wondered what Y=f(x) means in project management? This powerful concept isn’t just for mathematicians. It’s a game-changer for project success, helping you map out how inputs affect outcomes.
Y=f(x) is more than just a formula; it’s a way to understand and control your project’s variables, improve efficiency, and make smarter decisions.
In this article, you’ll learn how to implement Y=f(x) in your projects. We’ll break down the DMAIC framework and show you how it ties in with this concept. You’ll also learn some best practices to make the most of Y=f(x) in your projects.
Whether you’re new to Six Sigma tools or a seasoned pro, these insights will help you be a more effective project manager.
Y=f(x) is a cornerstone of the Six Sigma methodology, helping us express desired outcomes in measurable terms.
In project management, the equation Y=f(x) is a mathematical representation of the functional relationship between a project’s inputs (x) and its outputs (Y). Essentially, it means that a project’s outcome is a function of its input variables and the factors that influence them.
In other words, the results you achieve (Y) depend on the elements you put into the project (x) and how they are combined (f).
When setting up a project, it can be challenging to formulate the initial problem statement and specify the desired outcomes. By using Y=f(x) at the outset, you’re pushed to clearly understand ‘Y,’ which represents the desired results you’re working to achieve.
This approach forces you and your project team to view outcomes as measurable terms, setting a solid foundation for your project’s success regardless of your chosen project management methodology.
To harness the power of Y=f(x) in your projects, you need to understand its core components:

The mathematical function Y=f(x) describes a relationship between a dependent variable (Y) and one or more independent variables (x). It shows how changes in the independent variables lead to changes in the dependent variable.
Let’s understand the concept with a practical example.
Consider a software development project:
Y: A fully functional, bug-free software application
f: The development process, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment
x: Inputs such as the development team’s skills, the project’s budget, the chosen programming language, and the project’s timeline
In this example, the quality and success of the software application (Y) depend on the effectiveness of the development process (f) and the availability and quality of the inputs (x).
Implementing Y=f(x) in your project management approach offers several key benefits:
While Y=f(x) offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges. Some of these are:
🎉Bonus Resource: The playbook for keeping your project on track!
DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is a structured problem-solving methodology often used in Six Sigma projects. It provides a systematic approach to identifying and addressing the root causes of defects or inefficiencies. The Y=f(x) concept can be seamlessly integrated into the DMAIC framework to enhance problem-solving and process improvement.
Here’s how you can use DMAIC to put Y=f(x) into action.
The first step toward a successful project is identifying what you wish to achieve. This is where the Define stage comes in handy. It’s all about grasping the ‘Y’ in your Y=f(x) equation—your desired outcome.
Start by asking yourself if your project has a specific, defined business or process problem to solve.
Sometimes, the answer is clear, but often, you’ll need to dig deeper. If it’s not obvious, work on getting a clear picture of your ‘Y’—the process problem you’re trying to solve—in measurable terms that align with your project goals.
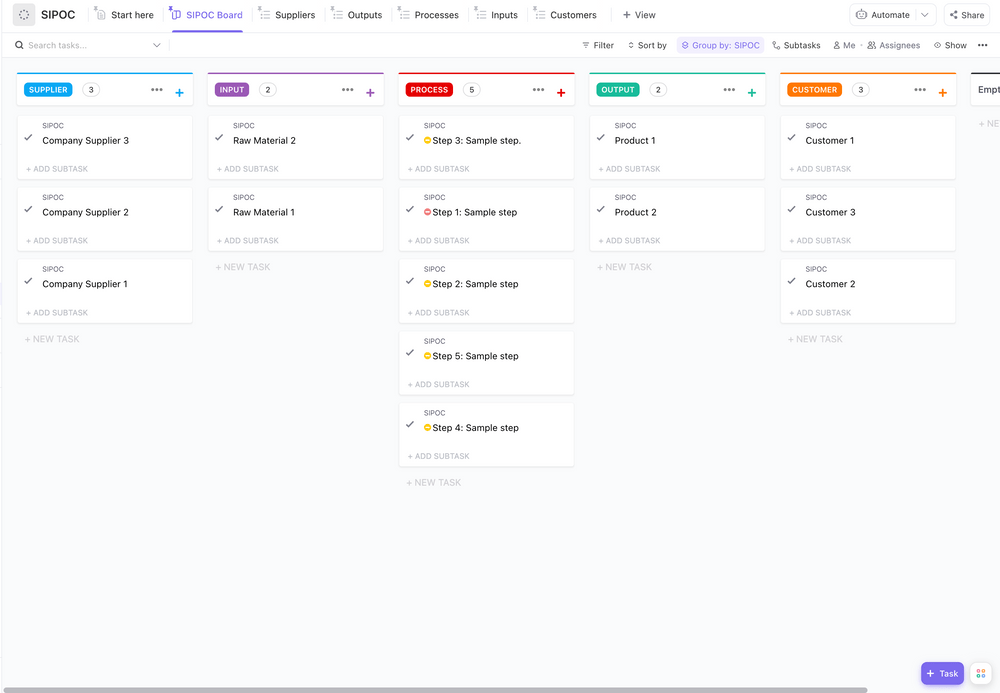
A helpful tool at this stage is the SIPOC (Supplier, Input, Process, Output, Customer) diagram. This can help you:
By using SIPOC, you’re setting the stage for Y=f(x) thinking right from the start.
Once you’ve defined your ‘Y,’ it’s time to move into the Measure stage. In this stage, the focus is on collecting and analyzing data. In this stage, you must:
This is a critical stage since the lack of significant data can often lead to failure ahead. Avoid making decisions based on gut feelings or anecdotes. Instead, focus on gathering solid data to inform your choices.
Also Read: Free Six Sigma templates
Moving into the Analyze stage, your goal is to verify and quantify the relationship between ‘x’ and ‘Y.’ This is where the Y=f(x) formula really comes into play. Use statistical and graphical tools to:
This stage is all about gathering clues for improvement and pinpointing the most important drivers of your outcome. To identify the root causes of output variations, you can use tools like fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, or failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA).
ClickUp’s Process FMEA Lean Six Sigma Template is designed to help you identify potential risks and control processes.
This comprehensive template makes it easy to:
With a clear understanding of your ‘Y’ and key ‘x’ variables, you’re ready to move into the Improve stage.
In this stage, you will:
The Control stage is where DMAIC really shines. It’s about ensuring your improvements stick and lead to long-term success. To do this:
By following these steps, you’re not just implementing Y=f(x); you’re creating a system for ongoing optimization and success in your projects.
To make the most of Y=f(x) in project execution, you must follow some key practices. These will help you leverage this powerful tool effectively and achieve your project management KPIs.
When implementing Y=f(x), it’s crucial to choose the relevant data and the right metrics. Start by clearly defining your project goals. Ask yourself what specific insights or outcomes you’re aiming for. This will guide your selection of data and visualization techniques.
Remember, Y=f(x) is all about understanding the relationship between inputs (x) and outcomes (Y). To do this effectively:
By setting up the formula correctly, you’ll be better equipped to select the right tools to verify X-Y relationships. This approach helps you understand cause and effect, measure performance, and identify areas for improvement in your projects.
Data visualization is a powerful ally when working with Y=f(x). It’s a blend of art and science that can significantly enhance your project management efforts. Here’s how to make the most of it:
Effective visualizations simplify complex data sets. They allow you to quickly spot patterns, trends, and outliers in the collected data, leading to more informed decisions.
Also Read: Types of charts for visualizing project data
Y=f(x) isn’t just a one-time tool; it’s a framework for ongoing optimization. Here are some strategies to ensure continuous improvement:
💡Pro Tip: The AI Project Manager in ClickUp helps you analyze data from multiple sources and identify any variance or outliers. Set up an automation to notify your team when a process requires attention.
By implementing these best practices, you’ll be able to harness the full power of Y=f(x) as a tool for continuous improvement, data-driven decision-making, organizational strategy, and project success.
Managing projects effectively requires a versatile tool that can adapt to the dynamic nature of project management. ClickUp is an all-in-one project management tool offering an integrated approach to managing Y=f(x)-based projects, making it an indispensable asset for project managers.
By leveraging its extensive features, project managers can ensure that every variable is accounted for, optimized, and aligned with the desired outcome.
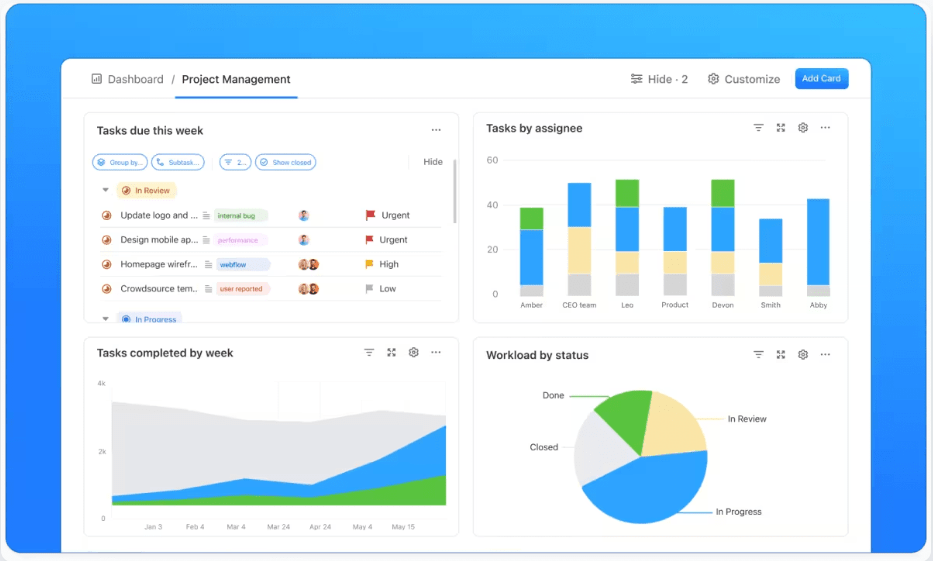
While there are many advantages of using ClickUp for managing Y=f(x)-based projects, here are some of the primary benefits:
Here are some ways you can use ClickUp’s capabilities to execute your Y=f(x) project management strategy:
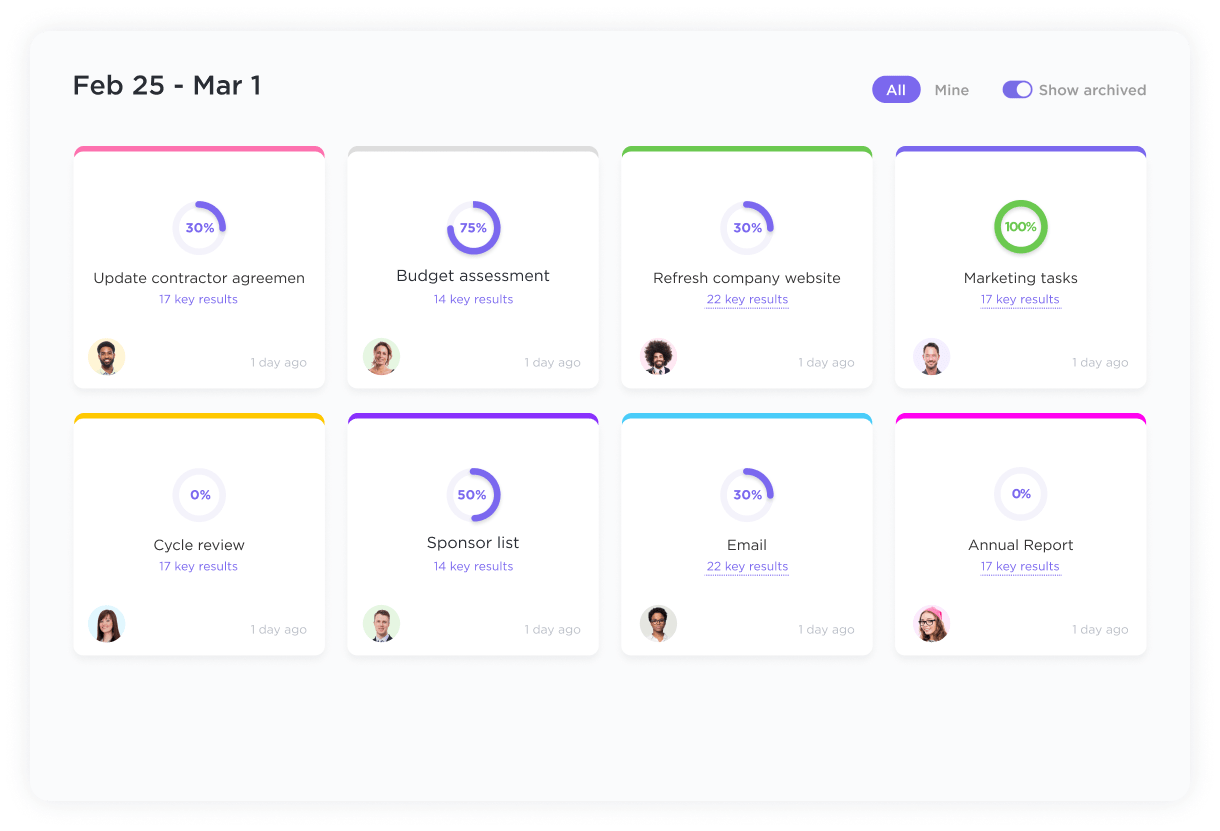
ClickUp’s DMAIC Template helps you manage and track a DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) project. This Whiteboard template will ensure you adopt a systematic approach to improving processes and increasing efficiency. Use it to:
With ClickUp, you can meticulously manage your project process and optimize the ‘x’s—the various inputs and factors that influence your project’s success. Here’s how:
Also Read: Project estimating techniques
ClickUp goes beyond traditional project management software by offering a suite of features that facilitate not just management but also collaboration and communication:
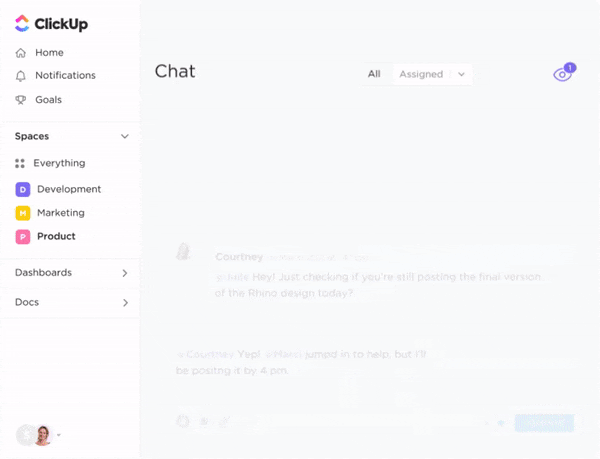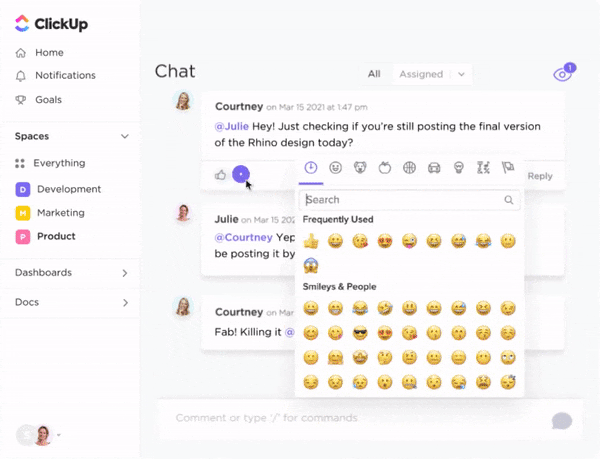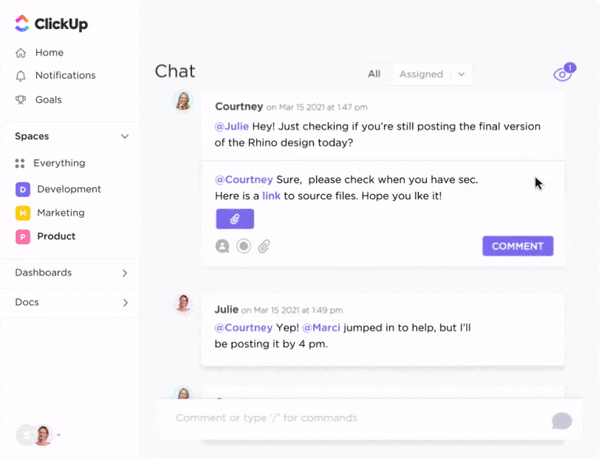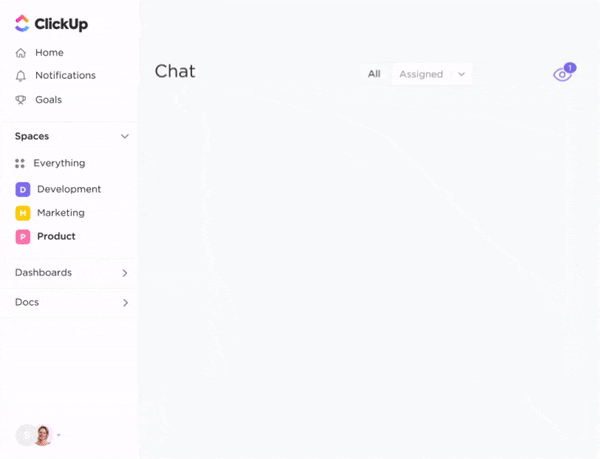
ClickUp is where tasks, documents, goals, and communication converge to create a seamless workflow. It equips you to navigate the complexities of project management with confidence and precision.
The Y=f(x) formula isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a practical tool that can be applied to the day-to-day operations of project management. By integrating this formula into various aspects of project work, managers can enhance decision-making, streamline strategic management, and leverage data for predictive modeling.
Incorporating Y=f(x) into decision-making processes means that every choice is backed by an understanding of how different factors will impact a project’s progress and outcomes. Here’s how you can apply it:
By embedding Y=f(x) into the strategic management process, project managers can ensure that their decisions are data-driven and aligned with project goals.
Data analysis and predictive modeling are critical components of modern project management. Y=f(x) provides a framework for these activities:
Leveraging Y=f(x) in data analysis and predictive modeling turns raw data into actionable insights, enabling project managers to anticipate and shape the future of their projects.
Y=f(x) is a powerful tool that has a significant impact on project management success. The concept helps project managers better understand the relationship between inputs and outcomes. This enables them to better plan future project proposals, set relevant goals, and improve performance measurement.
The DMAIC framework provides a structured approach to implement Y=f(x), guiding projects from defining goals to controlling processes for long-term success.
To make the most of Y=f(x), it’s crucial to choose the right project metrics, effectively use data visualization, and focus on ongoing improvement. Integrated project management software such as ClickUp offers a range of features that help you do all this and more. Rely on it to reach peak efficiency, drive innovation, and achieve better results in your projects.

© 2026 ClickUp

There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.