How to Write a PRD (with Examples and Templates)

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Creating a successful product goes beyond just having an innovative idea; it requires extensive research, planning, and numerous iterations to find the most effective approach.
So, where should you begin?
Typically, product managers kick off the process by drafting a Product Requirements Document (PRD). This document delineates the intended product, detailing its purpose, key features, functionalities, and expected user response.
The next step involves circulating the PRD among key stakeholders, technical teams, and other relevant parties for feedback. Once the PRD is finalized, it becomes a foundational blueprint guiding all subsequent phases of your product development process.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to craft a comprehensive and effective PRD to ensure your product’s vision is clearly communicated and strategically executed.
1. What is a product requirements document (PRD)?
A PRD is a blueprint that defines what a product will do, how it will work, its features, technical expectations, and the metrics used to measure success.
2. Why is a PRD important for product development?
It aligns stakeholders, reduces ambiguity, prioritizes resources, prevents scope creep, and helps teams ship higher-quality products faster.
3. What should a PRD include?
A strong PRD covers objectives, scope, assumptions, constraints, user stories, feature definitions, dependencies, and success metrics.
4. How do you write an effective PRD step by step?
Document the product purpose, define goals, note constraints, explain strategic fit, list user requirements, detail features, and set measurable KPIs.
5. How does ClickUp help teams manage PRDs?
ClickUp enables collaborative Docs, templates, goals, dashboards, automations, and integrations—making it easier to draft, update, and execute PRDs in real time.
A PRD is a comprehensive blueprint that outlines a product’s necessary features and functionalities before its development begins.
This pivotal document specifies:
By integrating the product strategy, the PRD aligns the product’s development with broader business goals and ensures that every feature and functionality supports the company’s long-term vision and market positioning.
The PRD single-handedly bridges the gap between conceptual ideas and actionable development plans. But there’s more than that to it:
There are countless stories of projects that went astray due to poor communication. As a product manager, you would know what we’re talking about.
A well-executed PRD helps prevent these issues and ensures that your vision is perfectly translated into a tangible product that delivers on its promises.
Here are the top benefits of a PRD:
A good PRD includes the following components:
Before assembling your product requirement document, you must understand its components. While creating a PRD, think of:
Start by clearly defining the product and its aims. This includes a high-level overview of the product’s purpose, target audience, and differentiation from competitors. This foundational step sets the stage for all subsequent details in the PRD.
Clearly articulate the product’s goals and how they align with the broader business objectives. Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure the product’s success post-launch. These metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Pro Tip: Use ClickUp’s SMART Goals Template to set achievable goals and organize your tasks into smaller parts. This template keeps your team focused and motivated during a product launch.
Recognize any constraints that might impact the product development, such as technological limitations, budgetary restrictions, or regulatory requirements. Also, list down assumptions related to market conditions, technology trends, or user behavior that could influence the product’s design and minimum functionality.
Define the project’s scope by detailing what will be included in the product release criteria and what will not. This clarity helps prevent scope creep and ensures the development team focuses only on essential features.
Pro Tip: Use the ClickUp Scope of Work Template, which is ready-to-use and fully customizable. This template ensures that everyone is well-informed and in agreement, keeps the project moving forward, and guarantees that deadlines are reached.
Provide a detailed list of the product’s features. This should cover both core and secondary features, explaining how each addresses the needs of the target audience. Include specific details on how these features should function and their expected impact on the user experience.
Strong PRDs move from vision → constraints → execution → measurement, ensuring teams know exactly what to build and why.
Creating a PRD involves a structured approach that ensures every stakeholder clearly defines and understands all aspects of the product. These seven crucial steps can help you effectively guide your product development from conception to launch.
Conduct a thorough requirement analysis for your product. This includes the product’s purpose, target audience, and the core problem it solves.
Be specific about the intended use and the environment in which the product will operate. This foundational step ensures that everyone involved has a clear understanding of what is being built and why.
Detail both the business and technical goals and how they align with the overall company objectives.
Include measurable success metrics or KPIs to track progress. This step transforms broad ideas into specific, actionable objectives that drive the entire development process.
Identify and document any assumptions made during the planning and development phases.
Also, list constraints that could impact the project, such as technological limits, regulatory requirements, and budgetary limitations. Understanding these factors early helps plan realistic development timelines and prevents unforeseen challenges.
Elaborate on the background of the product concept by explaining the market research, customer insights, and competitive analysis that led to its inception.
This step should also articulate how the product fits strategically within the broader company vision and product line. Highlighting this fit ensures that product development is not only a tactical move but also a strategic initiative aligned with long-term business goals.
Define the complete scope of the product by listing all the user stories and detailed requirements. This step should include what the product will do and what it won’t, helping to manage expectations and focus efforts on core functionalities.
User stories should be clear and concise, providing a narrative that describes how various features will be used from the end user’s perspective.
Break down the product into its individual features and describe each one in detail. Discuss the functionality of each feature, how it integrates with other parts of the product, and any dependencies it may have.
This step is crucial for the development team to understand what needs to be built and for the product team plan how to prioritize the development tasks effectively.
Establish clear, quantifiable metrics for evaluating the success of the product post-launch. These should align with the initial goals and objectives laid out in the PRD.
Some common metrics might include user engagement levels, performance benchmarks, sales targets, or customer satisfaction rates. Setting these metrics upfront is vital for continuously measuring the product’s performance and making informed decisions for future iterations.
The following two ClickUp templates are fully customizable and built for real-time collaboration:
Here are the two most prominent PRD examples/templates organizations use across industries to streamline their PRD writing approach. Both have slightly different components and formats and serve different needs.
The Clickup Product Requirement Document Template is designed to streamline your process of developing a product seamlessly. The template outlines the essential elements:
The most significant aspect of the template is that it is fully customizable. This means you can cater it specifically to your industry needs and get started in seconds.
The Clickup Product Requirement Template provides you with a ready-to-use workspace designed for stakeholders involved in product development. It helps document all development decisions, providing a useful reference for teams to review past choices and steadily improve their release plans.
Its structure supports both beginners and advanced users. The template offers a fully customizable environment that allows teams to adapt the workspace to fit their specific needs.
Moreover, ClickUp’s Project Management Tool lets you access 15+ views and custom statuses to ensure comprehensive requirement management planning for each stage of the product development process. With this template, you can begin within seconds with efficiency and clarity from the outset.
Agile environments demand flexible, continuously updated requirements. Teams must accommodate shifting priorities, evolving stakeholder input, and rapid iteration while keeping visibility across developmen
In the agile product development world, product managers face distinct challenges when gathering requirements for a Product Requirements Document (PRD). Here are some of the most common issues:
To overcome these challenges, you need a flexible approach and tools that allow for iterative updates. This is where Clickup’s Agile Project Management Tool comes into the picture. It helps you easily modify requirements, track changes, and keep the entire team informed in real time.
Besides this, the ClickUp Product Feature helps simplify the process of shipping products faster and more efficiently. You can leverage tools like ClickUp Docs, ClickUp Goals, and roadmaps to facilitate comprehensive planning and tracking.
You can use ClickUp Docs to create and revise the document collaboratively and ensure that all team members contribute and stay updated.
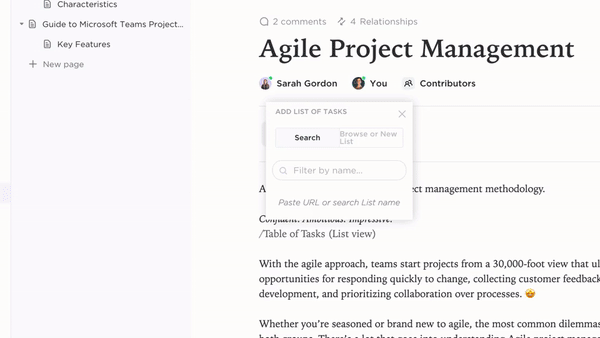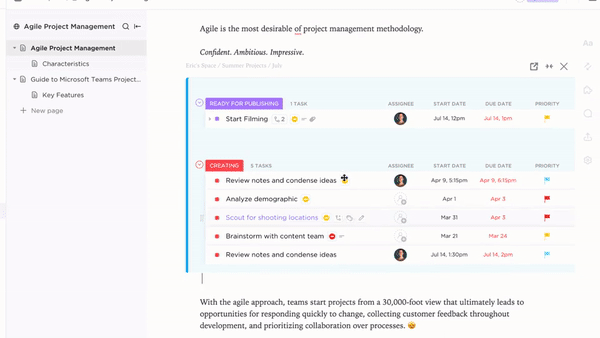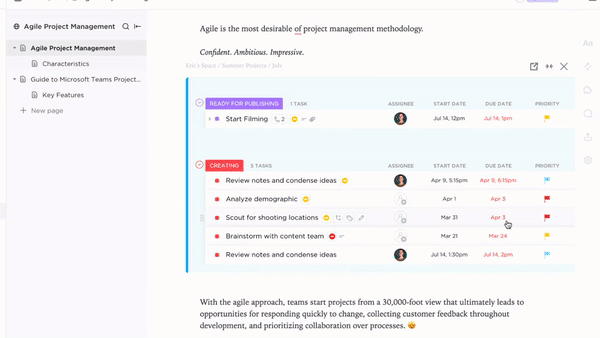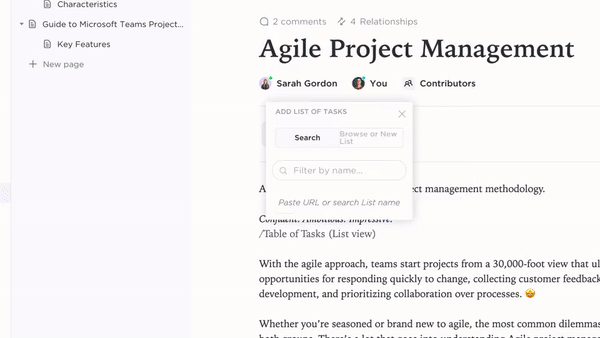
ClickUp Goals help set and track key objectives related to the PRD, ensuring product development stays aligned with strategic milestones.

ClickUp Brain, ClickUp’s AI assistant, can help you accelerate the development process by generating product roadmaps, test plans, and technical specifications. This helps you save valuable time on planning and documentation.

The ClickUp Dashboard feature provides a visual overview of project statuses and enables teams to monitor real-time progress.

ClickUp’s Integrations streamline the workflow between code repositories and project management tasks. This allows development teams to link commits, pull requests, and branches directly to Tasks in ClickUp, enhancing traceability and reducing context switching.
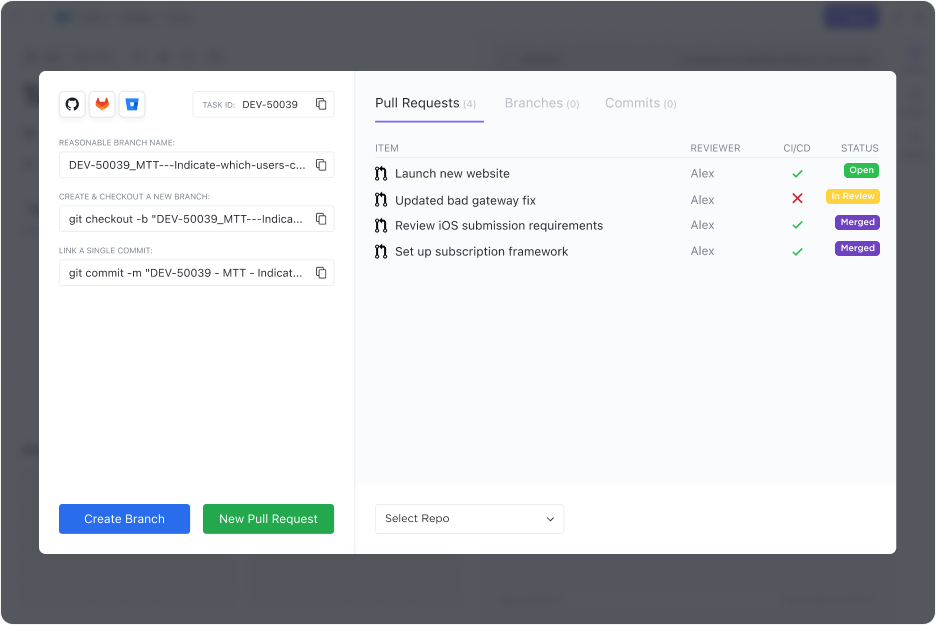
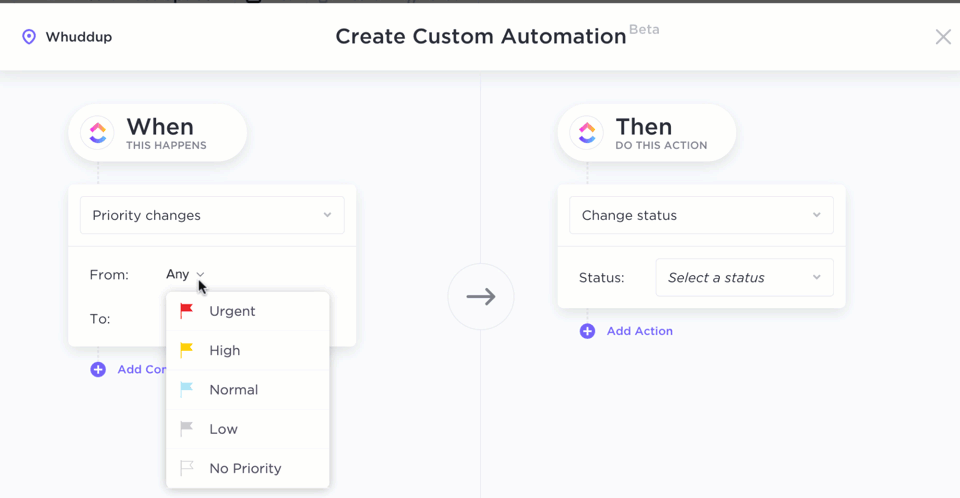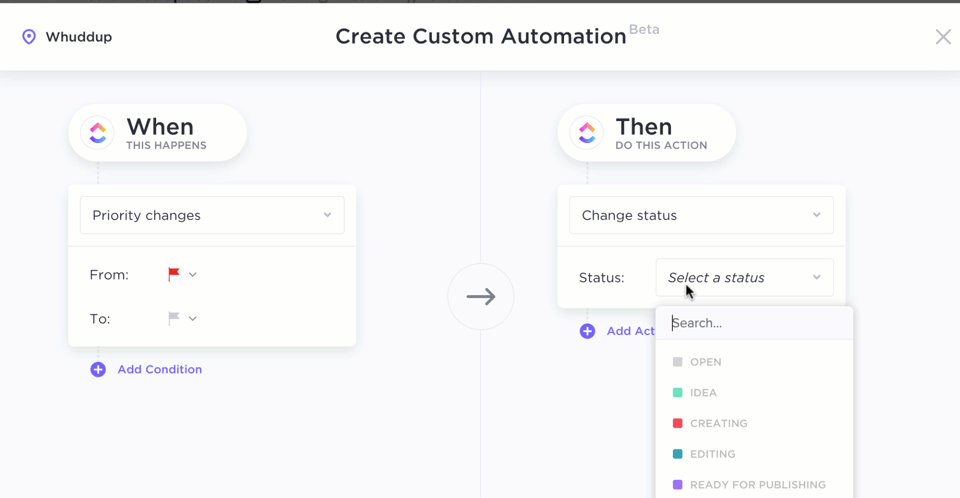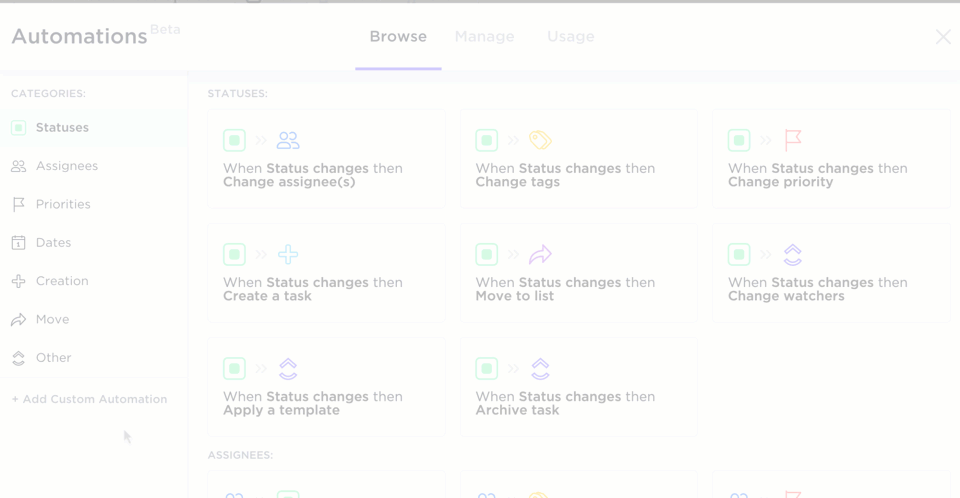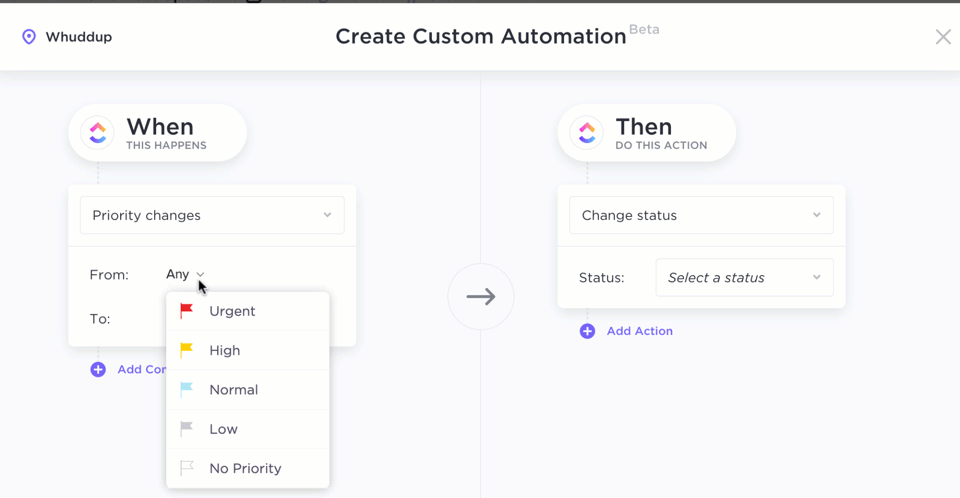
Through ClickUp Automations, you can also automate repetitive tasks, such as updating statuses or assigning tasks based on specific triggers. This feature reduces manual workload, allowing teams to focus more on strategic tasks and speeding up the development cycle.
Organizations like STANLEY Security have leveraged ClickUp to master solutions to their challenges effectively. Connor Nash, their Global Experience Analytics Manager, explains their approach:
As a technology innovation team, we need to stay organized and flexible to adapt to changing project requirements. We use a variety of project management techniques to reach our goals, and ClickUp has been central to that. We’re able to customize and automate ClickUp to suit each specific initiative, and it has allowed us to streamline and simplify our workflows, which has increased our team’s capacity exponentially
PRDs define how the product will be built, BRDs explain why the business needs it, and MRDs capture what the market demands. Together they connect strategy, opportunity, and execution.
The primary distinction between a Product Requirements Document (PRD), a Business Requirements Document (BRD), and a Market Requirements Document (MRD) lies in their focus:
Let’s take a brief look at the comparison:
| Aspect | PRD | BRD | MRD |
| Focus | Focuses on the technical and user requirements of the product, describing features, functionalities, and system behaviors. | Focuses on the business needs, outlining the impact on various business departments and the overall business objectives. | Focuses on market demands and customer needs, describing what the market requires from the product. |
| Purpose | To guide the development team by providing detailed descriptions of product features and technical requirements. | To communicate the business needs and requirements to stakeholders to ensure alignment with business goals. | To ensure the product meets market demands and captures customer needs effectively. |
| Primary Audience | Developers, designers, and technical teams who will build and implement the product. | Business stakeholders, project managers, and department heads are involved in the strategic planning of the project. | Marketing teams, product managers, and strategic planners focusing on market trends and customer demographics. |
| Outcome | Serves as a blueprint for the development process, ensuring that the product meets specified technical standards and user expectations. | Serves as a foundational document that aligns the project with business strategies and objectives, ensuring that it meets the intended business goals. | Provides a strategic overview of the market landscape to guide product positioning and marketing strategies. |
| Detail Level | Highly technical, detailing the product’s functionalities, user interaction, and technical specifications. | More general, focusing on high-level business needs and objectives without delving deeply into technical specifics. | Market-focused, detailing customer segments, market trends, and competitive analysis without specific technical details. |
👉🏽Read More: BRD vs. PRD: What New Product Managers Need to Know
When creating a PRD for your product, consider these essential do’s and don’ts to ensure its effectiveness:
Crafting a comprehensive PRD is an essential step in the product development process, ensuring clarity, alignment, and strategic execution. When creating a PRD, you can take inspiration from various requirement-gathering templates available in the market.
But you don’t have to do it all on your own. Integrating dedicated requirements management tools can revolutionize how PRDs are managed. These tools streamline efforts, improve communication, and provide agile solutions that adapt to changing requirements. As you move forward, leveraging such robust project management tools within ClickUp will help transform your product vision into reality more efficiently.
It’s time to enhance your PRD process and see tangible results by harnessing the power of efficient project management.
© 2026 ClickUp