How to Use T-Shirt Sizing as an Agile Estimation Technique
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Imagine stepping into a clothing store, eyeing a t-shirt, and knowing instantly if it’s the right fit without trying it on. That’s the essence of T-shirt sizing in agile project management. A new project or practice with your team brings complex questions, like how much time it will take or how much effort it will require.
It’s similar to picking a t-shirt size—small, medium, large, extra large (XL), or double XL(XXL)—to represent the effort and complexity of user stories or tasks.
This method has become a backbone of agile estimation, especially for agile teams that aim for quick, efficient, and collaborative decision-making. This intuitive estimation technique simplifies the complex process of measuring the scale of tasks in project development.
T-shirt sizing gives a more digestible picture and is less intimidating than exact numerical figures. From the product owner to each team member, everyone gets a clear picture of how much effort capacity planning, time, and resources might go into a sprint planning or a development cycle.
T-Shirt Sizing in Agile is a simple technique for estimating the size, complexity, or effort required for tasks or projects.
In this method, different sizes of T-shirts—such as Extra Small (XS), Small (S), Medium (M), Large (L), Extra Large (XL), and sometimes Double Extra Large (XXL)—are used as a symbolic representation for the scale of work.
The idea is to categorize tasks into these T-shirt sizes instead of using precise numbers or detailed metrics. Each T-Shirt size represents a relative estimation of how big or complex a task is.
For example, a ‘Small’ might indicate a quick and easy task, while an ‘Extra Large’ might represent a very complex and time-consuming task.

This approach helps teams quickly assess and discuss the scope of work more intuitively and less technically. The T-shirt approach makes it easier for everyone, especially those new to the project or Agile methodology, to understand and participate in the estimation process, especially in the early stages of the project.
T-shirt sizing in Agile streamlines team discussions, fostering a consensus on the scope of work with greater ease to ensure team members’ roles and enhance project management.
In Agile, story points represent a unit of measure for expressing an estimate of the overall effort required to fully implement a product backlog item or any other piece of work.
While both T-shirt sizing and story points are agile estimation techniques, their approach and application differ. T-shirt sizing, characterized by its qualitative and less detailed, is ideal for initial, high-level estimations.
In contrast, with their quantitative and detailed approach, story points are more suited for careful sprint planning, providing precise estimations crucial for tracking progress.
| Aspect | T-Shirt Sizing | Story Points |
| Definition | Uses size labels (XS, S, M, L, XL) for task estimation. | Assign numerical values to tasks for estimation. |
| Focus | Emphasizes relative size and complexity. | Highlights the effort and time required. |
| Approach | Qualitative and less granular. | Quantitative and more detailed. |
| Use Case | Ideal for initial, high-level estimations. | Suitable for detailed sprint planning. |
| Advantage | Simplifies discussions, less intimidating than numerical scores. | Provides precise estimations for planning. |
| Methodology | More subjective, based on team consensus. | Often calculated using past performance data. |
| Clarity | Easier for newcomers to grasp. | Requires understanding of Agile and past sprints. |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to changes in project scope. | Requires re-estimation for significant changes. |
T-shirt sizing in Agile is more than a tool for estimating project tasks; it represents a fundamental shift in how teams approach project planning and execution. It is crucial for several reasons beyond its role in simplification and communication.
T-shirt sizing reduces the pressure often associated with exact estimates by using non-numerical but relative estimates of sizes. It also encourages active and honest participation in planning sessions by reducing the stress related to precise estimates.
This leads to a more open and less stressful environment during planning sessions, encouraging team members to participate more actively and honestly in the estimation process.
T-shirt sizing enables early identification of larger, more complex tasks, facilitating proactive planning. By categorizing tasks into sizes, teams will quickly identify larger, more complex tasks with higher risks. This early identification allows for proactive planning to mitigate potential challenges rather than reacting to issues as they arise during development.
Capacity planning tools support the T-shirt sizing methodology in Agile project management. When used alongside T-shirt sizing, they bring a more structured and quantifiable aspect to the otherwise qualitative nature of this estimation technique.
T-shirt sizing provides a strategic overview of project demands, aiding resource allocation and long-term planning. It embodies the Agile mindset of flexibility and adaptability. It allows teams to make quick adjustments as project requirements evolve without requiring extensive re-estimation that numerical methods might require.
It provides a bird’s-eye view of project demands, helping managers allocate resources effectively and plan future projects with a clearer understanding of the team’s velocity, capacity, and complexity. This strategic advantage allows organizations to plan long-term and ensures that resources are utilized most efficiently.
When utilizing T-shirt sizing in Agile project management, following best practices to ensure efficient estimation is crucial. This t-shirt sizing technique, popular among agile teams, balances simplicity with accuracy in project estimation. Here are some essential dos and don’ts:
Widely used by many agile development teams, Agile T-shirt sizing simplifies the estimation process, yet, like any other estimation technique, it has its advantages and limitations.

T-shirt sizing in Agile is gaining popularity as an estimation method, with the ‘State of Agile report’ stating that 23% of teams use T-shirt sizing.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing T-shirt sizing for agile estimation. Let’s walk use an example of developing a new feature for a mobile app:
Define what each T-shirt size means in your project context. For instance, ‘Small’ could indicate tasks that take a few hours, while ‘Large’ might involve tasks spanning several days.
For our mobile app feature, a ‘Small’ task could be drafting a basic user interface sketch, while a ‘Large’ task might be coding the main functionality of the feature.
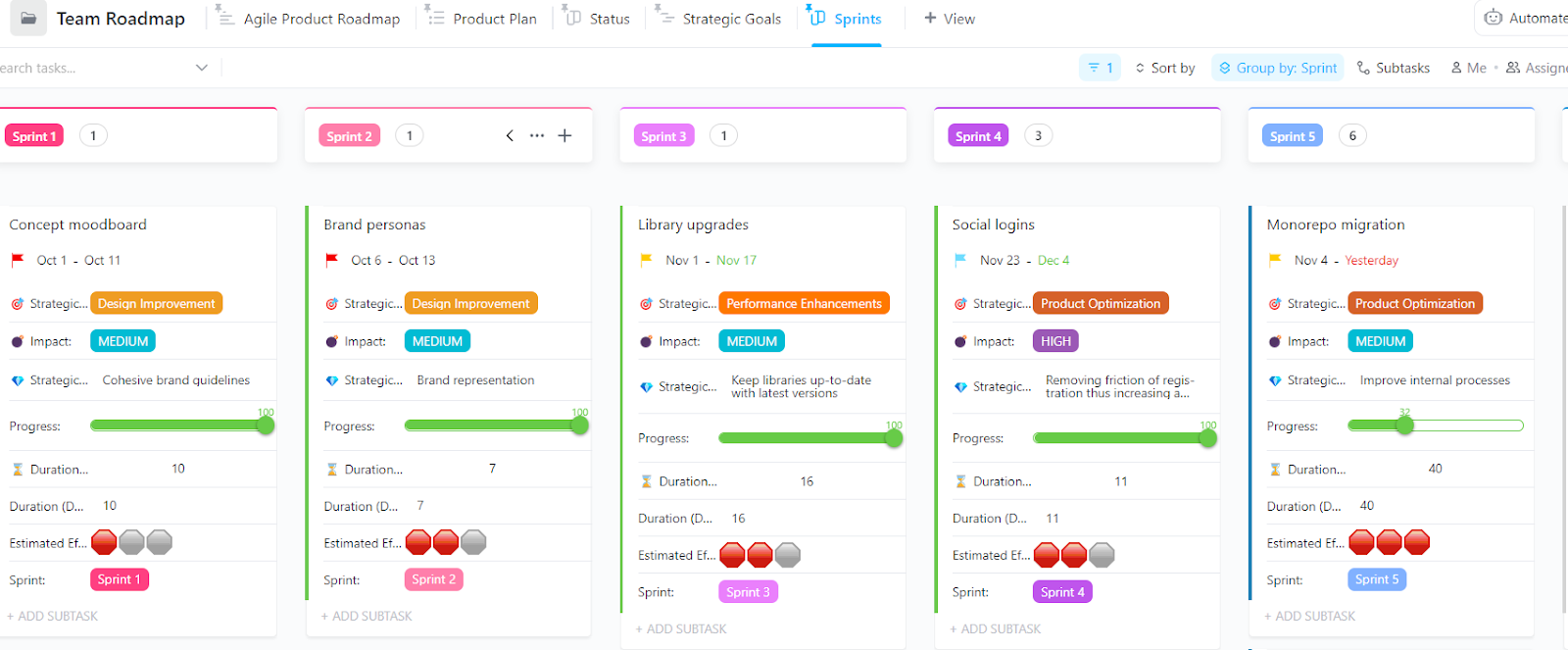
Use ClickUp’s Agile Team Roadmap Template to represent these sizes visually in your project plan. Refer to these capacity planning templates that offer structured guidance and can be tailored to your Agile project’s needs.
Gather your team for a sizing session. Each member should have a good understanding of the tasks or user stories to be estimated.
Everyone must be involved in our app, from the UI designer to the back-end developer.
Use ClickUp’s collaboration tools to facilitate this discussion, ensuring all team members can contribute regardless of location.

Go through each task or user story and assign a T-shirt size. Get team consensus or input from the product owner to do this.
For instance, designing the icon for the app feature might be ‘Small,’ while integrating the feature with existing app systems could be ‘Large.’
ClickUp’s flexible Task Management system allows for easy assignment and adjustment of sizes as more information becomes available.
📮ClickUp Insight: 92% of knowledge workers risk losing important decisions scattered across chat, email, and spreadsheets. Without a unified system for capturing and tracking decisions, critical business insights get lost in the digital noise. With ClickUp’s Task Management capabilities, you never have to worry about this. Create tasks from chat, task comments, docs, and emails with a single click!
Remember that T-shirt sizing is an initial estimation. Be prepared to refine sizes as the project progresses, and more details emerge.
For example, if the feature integration is more complex than initially thought, you might upgrade it from ‘Large’ to ‘Extra Large.’
ClickUp’s Agile tool features enable easy updating and tracking of these changes.

While T-shirt sizing is great for high-level estimates, it should complement other techniques like story point estimates for detailed planning.
Detailed planning might be necessary for our app feature for complex tasks like data encryption.
ClickUp’s integration capabilities allow for seamless combination with other tools and methods used by your Agile team.

Translate T-shirt sizes into actionable plans for your sprints. Determine how many and which sizes of tasks can be realistically tackled in each sprint.
For instance, you might plan to complete all ‘Small’ and ‘Medium’ tasks in the initial sprints.
Utilize ClickUp’s Resource Planning Template to allocate tasks based on their sizes effectively.
Continuously monitor and measure the progress of tasks and adjust your T-shirt sizes and sprint plans accordingly.
For example, if a ‘Medium’ task like finalizing the user interface design takes longer than expected, adjust your plans accordingly.
ClickUp’s analytics and reporting dashboard provide valuable insights into the performance and progress of your tasks, aiding in effective tracking and adjustment.
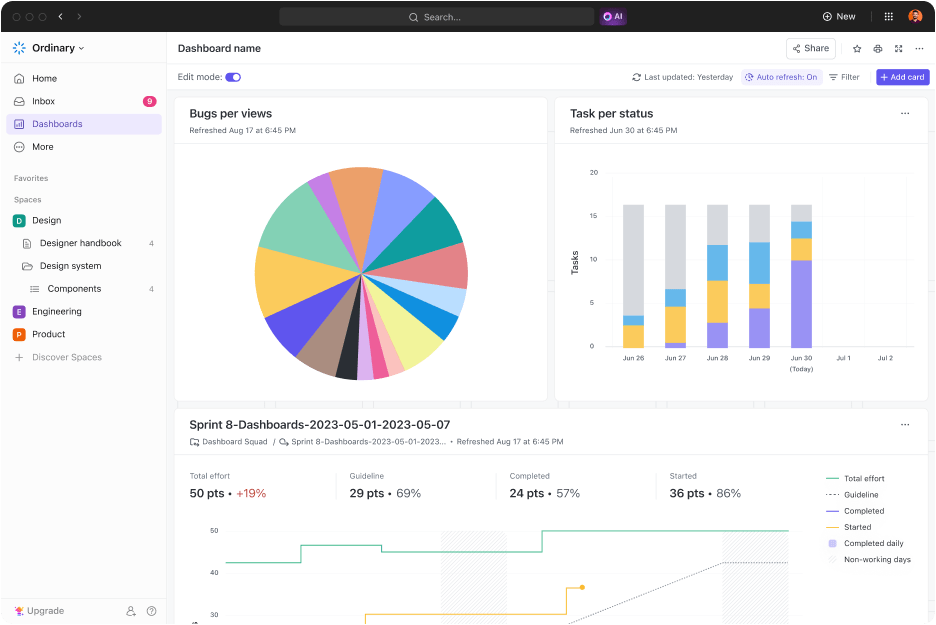
After each sprint or at regular intervals, review the accuracy of your T-shirt size estimations.
You can gather team feedback, learn from experiences, and refine your estimation process.

T-shirt sizing in Agile is particularly effective in various scenarios, such as web development, software application development, and marketing campaigns. It enables teams to visualize the scope of tasks and allocate resources accordingly, from simple features labeled as ‘Small’ to complex undertakings designated as ‘Extra Large.’
Consider a team working on updating and maintaining a company website. Here, tasks are categorized based on their complexity and effort. A small task like a text update requires significantly less time and resources than a large task such as developing a unit testing a new authentication system.
This example talks about developing a mobile application with various user functionalities. It reflects a range of tasks in a software development project. Each size represents the numerical value of the task’s relative effort and time required, aiding in agile estimation techniques and planning.
In marketing projects, T-shirt sizing helps visualize the scope of various campaigns and activities, aiding project managers and teams in allocating resources and setting priorities. For example, check out this task of planning and executing marketing strategies for product promotion.
T-shirt sizing in Agile project management is a catalyst for fostering a collaborative, efficient, and adaptable approach to project planning and execution. Agile software development teams, especially those new to Agile methodologies or working on projects with variable scopes, can benefit significantly from the simplicity and flexibility that T-shirt sizing offers.
Looking towards the future, the key to maximizing the effectiveness of T-shirt sizing lies in its integration with other Agile practices and tools. As teams become more seasoned in Agile practices, T-shirt sizing can serve as a springboard for more advanced agile estimation techniques, providing a solid foundation for accurate planning and resource management.
ClickUp emerges as an invaluable ally. With its comprehensive suite of Agile features, including robust task management systems, collaborative tools, and analytic capabilities, ClickUp will seamlessly integrate T-shirt sizing into your Agile workflow.
Whether planning a sprint, tracking progress, or conducting retrospectives, ClickUp’s versatile platform supports and enhances the T-shirt sizing estimation process. It’ll help you ensure that your projects are well-planned and agile in adapting to changing demands and priorities.
© 2026 ClickUp