What Is a Production Schedule and How to Make One
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Your production line is set to deliver 10,000 units this month—but a supplier delay and a machine breakdown have disrupted your manufacturing schedule. These setbacks don’t just slow down operations; they increase costs, push deadlines, and create challenges for both your production lines and sales teams.
To stay on track, you need a well-structured production schedule. It’s the backbone of your manufacturing process. It ensures the right raw materials arrive on time, machines run efficiently, and workers are assigned effectively.
This guide will walk you through the production scheduling process, helping you build a plan that adapts to real-world disruptions—so you can maintain efficiency, meet deadlines, and keep production running smoothly.
A production schedule is a detailed plan that specifies what to produce, when to produce it, and in what quantity. It helps manufacturers allocate resources, coordinate workflows, and manage the production timeline to maintain an efficient and timely production process.
There are five main types of production schedules:
While the terms are often used interchangeably, production scheduling and production planning serve distinct but closely related roles:
In short, production planning sets the strategy, while production scheduling puts it into action. Together, they ensure efficient manufacturing operations and timely production.
📖 Also Read: How to Do Project Management for Manufacturing
Say you run a factory that produces 5,000 custom furniture pieces a month. Without a production schedule, raw materials arrive late, machines sit idle, and workers face unpredictable workloads—overloaded one day, waiting around the next.
The result? Missed deadlines, rising production costs, and unhappy customers. A well-structured production schedule prevents this by:
Production delays start long before manufacturing begins. If raw materials arrive late, everything slows down. A production plan establishes procurement timelines for on-time supplier deliveries. It also keeps tasks on track, helping teams stay in sync and deadlines on track.
Idle machines, overworked teams, and wasted materials drive up costs or halt production. On the other hand, a manufacturing production schedule optimizes labor, equipment, and inventory. It balances workloads and prevents stock shortages or excess.
Bottlenecks disrupt production, whether from machine failures, staffing delays, or unexpected demand spikes. A production schedule highlights these risks early, allowing managers to adjust resources, shift timelines, and prevent minor setbacks from turning into major delays.
Rush orders and last-minute changes inflate costs. A well-planned production schedule minimizes waste, controls labor expenses, and improves supplier coordination for efficient production processes.
Producing too soon leads to storage costs, and producing too late leads to backorders. A production schedule aligns output with customer demand, preventing costly overproduction and stock shortages.
🧠 Fun Fact: Every year, America celebrates the first Friday in October as National Manufacturing Day.
The effectiveness of your production schedule depends on the level of detail it includes. Here’s a breakdown of key elements to incorporate in your schedule template:
Write a clear and concise product description, including specifications, variations, and unique features. Then, define production targets by estimating the required units for each order and assign a firm deadline to maintain clarity and accountability.
Product Name: UltraFit Pro Resistance Bands
Product description:
The UltraFit Pro Resistance Bands are designed for full-body strength training, rehabilitation, and mobility exercises. Made from premium, snap-resistant latex, these bands provide progressive resistance to support all fitness levels. They are lightweight, portable, and come with a convenient carrying bag for easy storage and travel.
Specifications:
Production targets & timeline
Order quantity estimate:
Production deadline:
A well-structured production schedule does more than outline tasks—it ensures that the right personnel, tools, and materials are available for smooth production operations. For example:
💡 Pro Tip: Assign specific tasks to dedicated work centers to reduce equipment downtime, optimize labor efficiency, and maintain a consistent, predictable production process.
To optimize production scheduling, prepare these essential processes and docs:
1. Bill of Materials (BOM): Maintain a detailed list of raw materials, components, and subassemblies to streamline material procurement and ensure efficient resource allocation
📌 Example Bill of Materials (BOM) for a Smart Wireless Earbuds production:
| Item No. | Component | Material | Quantity per Unit | Supplier |
| 001 | Earbud shell | ABS plastic | 2 pcs | XYZ Plastics |
| 002 | Speaker driver | Neodymium magnet | 2 pcs | Acme Audio |
| 003 | Battery | Lithium-ion | 1 pc | PowerTech |
| 004 | PCB board | Fiberglass | 1 pc | CircuitWorks |
| 005 | Bluetooth module | Integrated circuit | 1 pc | SmartTech |
| 006 | Charging case | Polycarbonate | 1 pc | XYZ Plastics |
| 007 | USB-C port | Stainless steel | 1 pc | ConnectX |
| 008 | Packaging box | Cardboard | 1 pc | GreenPack |
2. Routing process
Establish a step-by-step sequence of operations, specifying the work centers involved in each stage of manufacturing for a smooth workflow
📌 Example: Smart Wireless Earbuds production routing
| Step No. | Operation | Work Center | Time per Unit |
| 1 | Injection molding | Plastics dept. | 3 min |
| 2 | Speaker Driver assembly | Audio assembly line | 5 min |
| 3 | Battery installation | Electronics line | 4 min |
| 4 | PCB soldering | PCB assembly | 6 min |
| 5 | Bluetooth module setup | Electronics line | 4 min |
| 6 | Final earbud assembly | Final assembly | 5 min |
| 7 | Quality inspection | QA department | 3 min |
| 8 | Packaging & labeling | Packaging line | 2 min |
By implementing a detailed BOM and Routing Process, production efficiency is maximized, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring timely delivery. 🚀
Monitoring key supply chain KPIs—such as on-time delivery, inventory turnover, and production efficiency—helps optimize production schedules by identifying potential issues early and enabling quick corrective actions.
Production managers can also track inefficiencies in real time and adjust the production plan accordingly to keep operations running smoothly.
A flexible production schedule adapts to unforeseen challenges, like supply chain disruptions, equipment maintenance, or labor shortages.
A master production schedule goes beyond simply listing production tasks—it integrates effective scheduling and time management techniques to enhance manufacturing efficiency.
Here are three key production planning and scheduling techniques:
Forward scheduling begins as soon as an order is received or when resources become available. Its core aim is to complete production as early as possible. This approach helps the manufacturing team estimate the earliest possible completion date by factoring in lead times, resource availability, and task durations.
Works backward from the final deadline, determining the latest possible start time for each step to meet delivery requirements. This method prioritizes just-in-time production, reducing inventory costs while ensuring timely order fulfillment.
Takes a realistic approach by factoring in capacity constraints, such as available machine hours and workforce limits. If resources aren’t available, tasks are automatically rescheduled for the next open time slot, preventing overloading and production bottlenecks.
💡 Pro Tip: To keep production on track, use forward scheduling for flexible projects, backward scheduling for fixed deadlines, and finite capacity planning when dealing with resource constraints.
The production line determines the sequence of operations and material flow in manufacturing. However, the production schedule keeps this line moving.
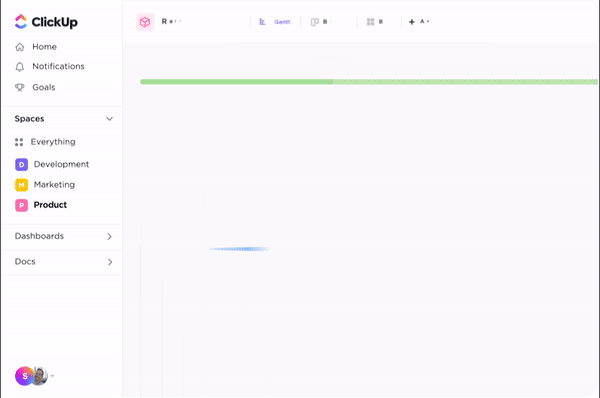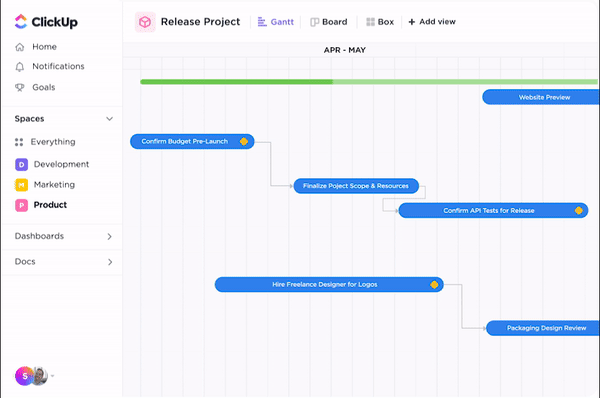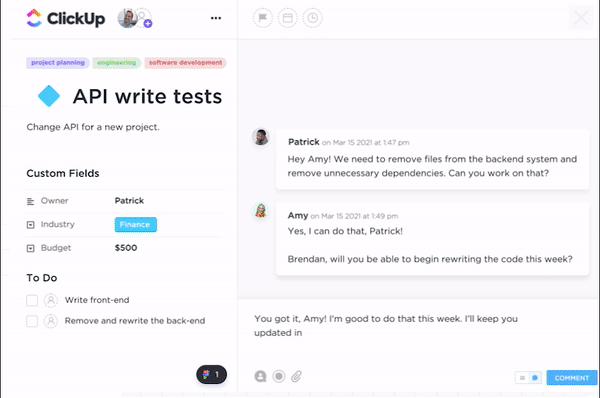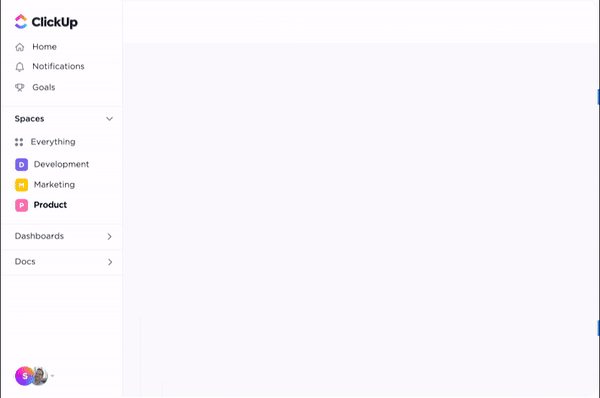
An inaccurate schedule can lead to bottlenecks, delays, and reduced efficiency and output, disrupting the entire process. However, adopting a project management calendar tool or creating a Gantt Chart to visualize these processes can make it less complex.
ClickUp, the everything app for work, is a solid tool for organizing production schedules and optimizing resource allocation without switching between multiple platforms.
📮ClickUp Insight: Low-performing teams are 4 times more likely to juggle 15+ tools, while high-performing teams maintain efficiency by limiting their toolkit to 9 or fewer platforms. But how about using one platform?
As the everything app for work, ClickUp brings your tasks, projects, docs, wikis, chat, and calls under a single platform, complete with AI-powered workflows. Ready to work smarter? ClickUp works for every team, makes work visible, and allows you to focus on what matters while AI handles the rest.
Here’s how you can break the process down into four key steps:
Before diving into production activities and setting project timelines, clarify your goals to ensure your schedule aligns with business operations and avoids unnecessary delays. A well-defined scope keeps production efficient and on track.
Here’s what you can do:
A production schedule is a shared roadmap, keeping teams aligned and production running smoothly.
Once your goals are set, the next step is to define each production operation. Establish a clear routing process that maps out the sequence of tasks and the movement of materials throughout the facility.
In other words, lay the groundwork for inventory management and material planning.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
| Efficient production process | Role of a production manager | Examples |
| Identify and sequence operations | Break down the production process into a series of different tasks | For instance, in a manufacturing plant producing metal parts: Raw material inspection Cutting (e.g., laser cutting, water jet cutting) Forming (e.g., bending, stamping) |
| Determine resource requirements | For each operation, identify the specific resources required | For example: Machinery: List the specific machines and equipment needed (e.g., CNC machines, welding robots, assembly lines) Labor: Determine the skill sets required for each operation (e.g., skilled machinists, welders, quality control inspectors) |
| Assign resources | Assign specific machines, equipment, and personnel to each operation based on their availability and capabilities | For example: Assign ‘CNC Router 1’ and ‘CNC Router 2’ to the ‘Cutting’ operation Assign ‘Welder A’ and ‘Welder B’ to the ‘Welding’ operation |
💡 Pro Tip: Use production scheduling software like ClickUp to visualize and organize your production flow for continuous improvement.
ClickUp Tasks help break down your production process into manageable units of work and provide valuable insights into the interdependencies between different to-dos. You can also customize them to reflect different manufacturing operations.
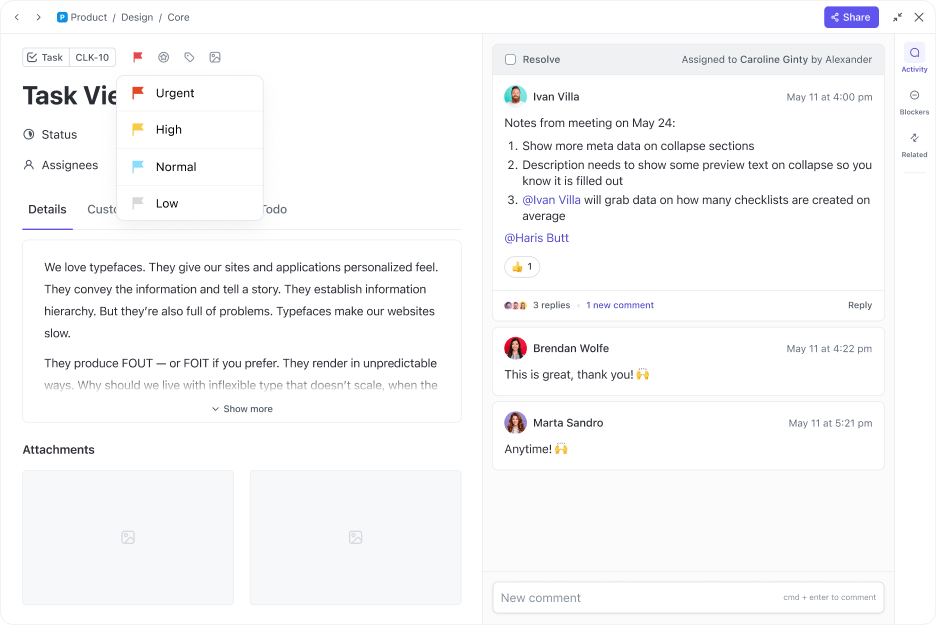
Here’s how to use ClickUp Tasks to gain control over your production operations:

💡 Pro Tip: Standardize workflows by creating task templates for common production steps like equipment maintenance, quality control checks, or inventory restocking.
👀 Did You Know: On average, American employees in the production and manufacturing industry work 40 hours a week and earn $34.64 by the hour.
Realistic, data-driven deadlines are essential for keeping production on track. To achieve this, break the production schedule into milestones and establish regular review periods to assess progress.
Start by defining lead times based on past data to determine accurate timelines for each task. Incorporate buffer time to account for unexpected delays and prevent last-minute pressure. Finally, schedule regular progress reviews—whether weekly or bi-weekly—to identify potential issues early and implement timely solutions.
A caveat: avoid scheduling tasks too tightly. A planned production schedule prevents chaos in case of a machine breakdown or delayed material shipment.
ClickUp’s Calendar View can help you combat this.
Visually representing tasks and their due dates within a calendar format allows for a clear understanding of your production plan.
Here’s how it can help further:

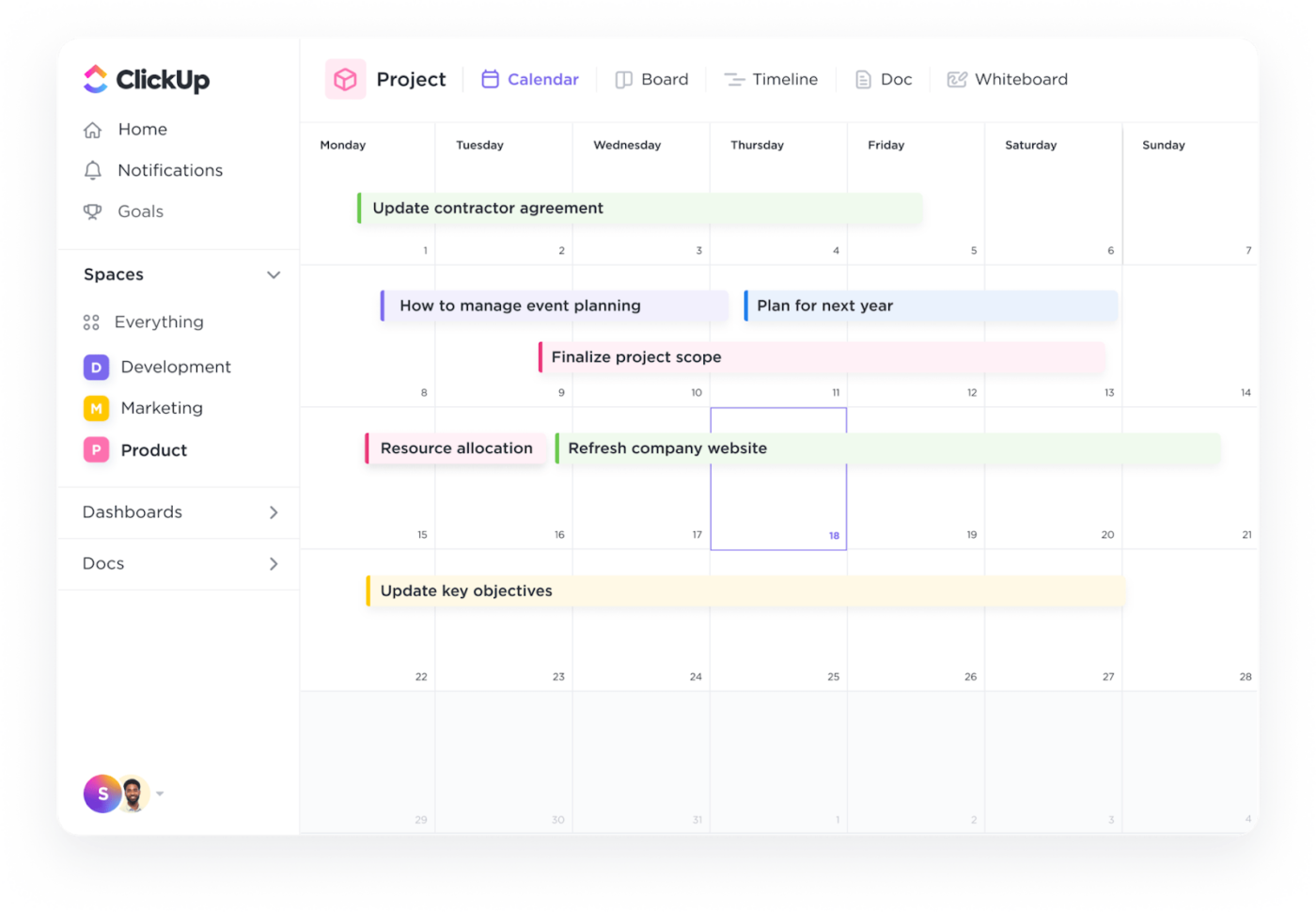
Get our best tips on creating a project/production calendar through this video 👇🏽
A production schedule isn’t a “set it and forget it” plan—it requires active monitoring to stay effective. Equipment failures, worker shortages, and supply chain disruptions can all impact timelines, making regular tracking essential.
Real-time tracking software updates production progress, ensuring managers stay informed. Identifying bottlenecks early is crucial; investigating the issue and redistributing resources can help prevent significant delays if a step takes longer than planned.
Additionally, adapting to changes by shifting priorities, rescheduling tasks, or allocating extra workers to critical stages ensures production stays on track despite unforeseen disruptions.
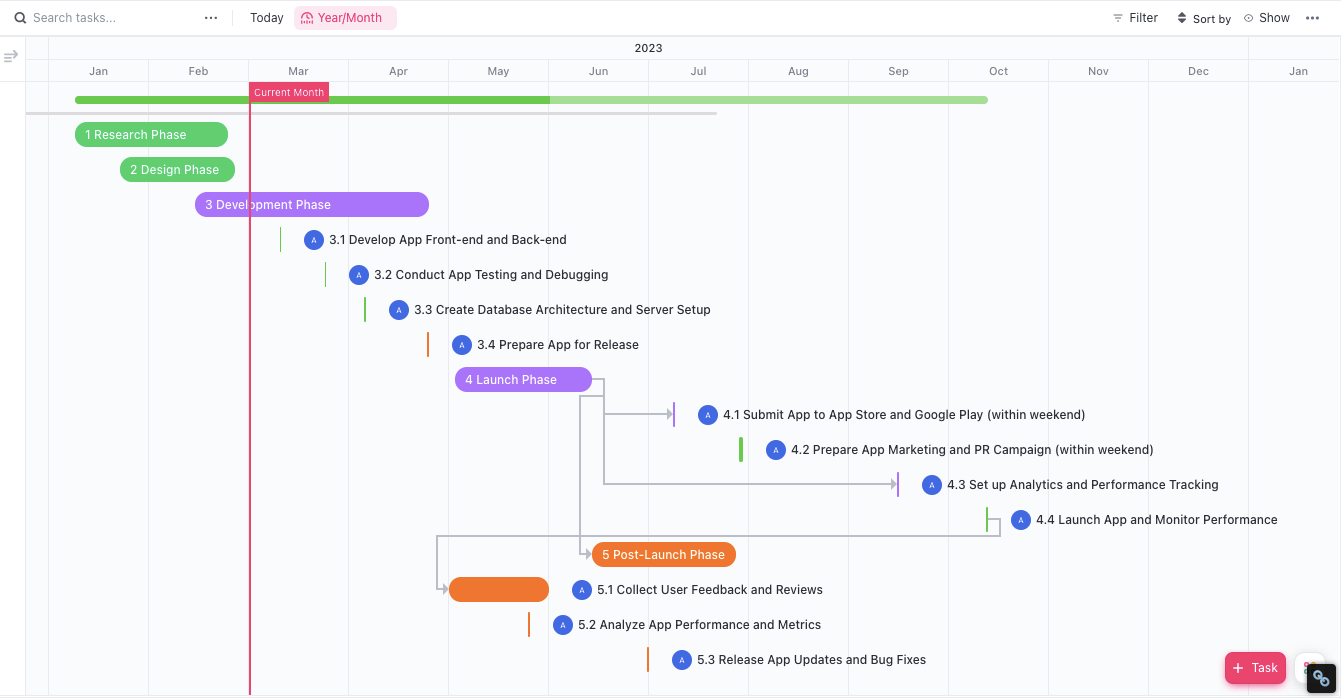
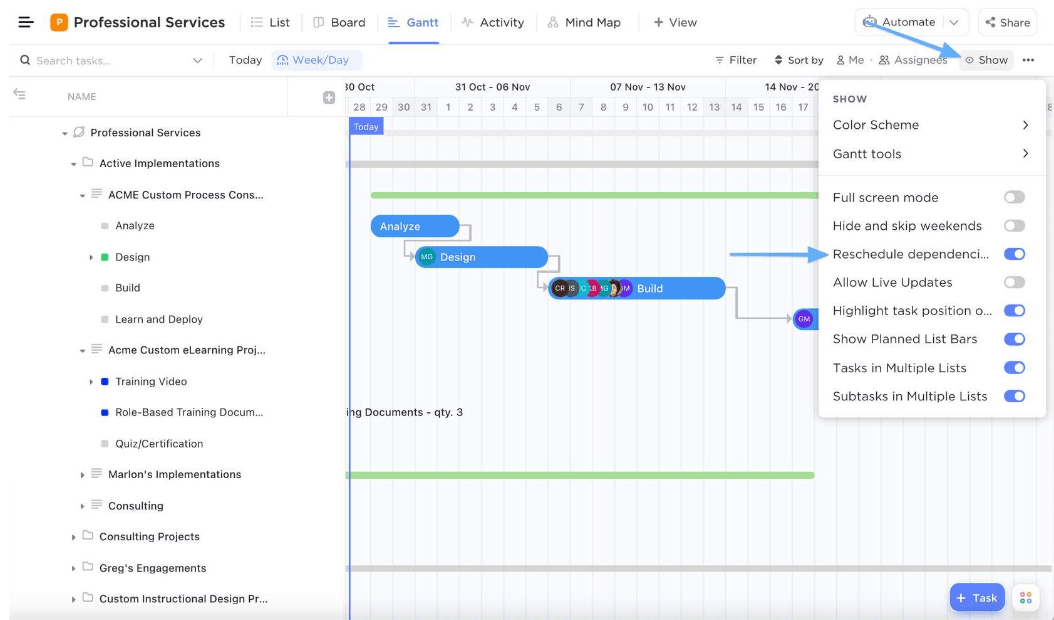
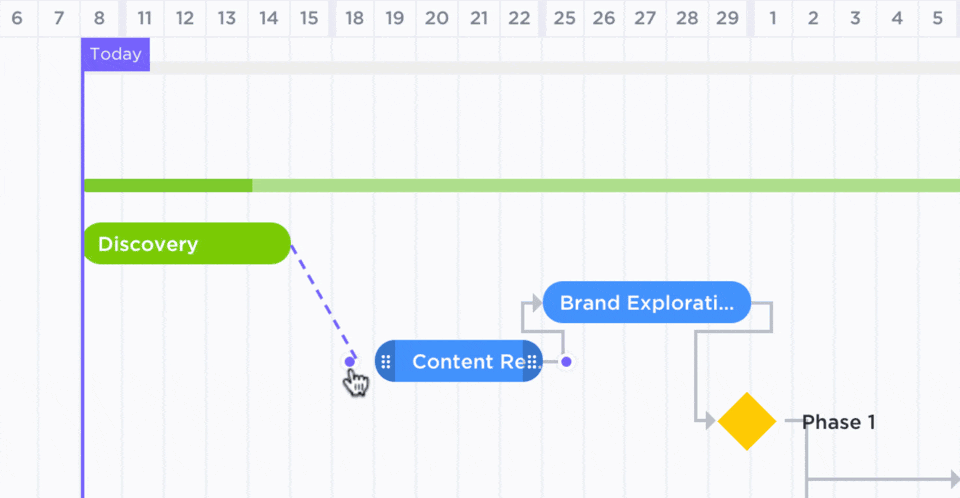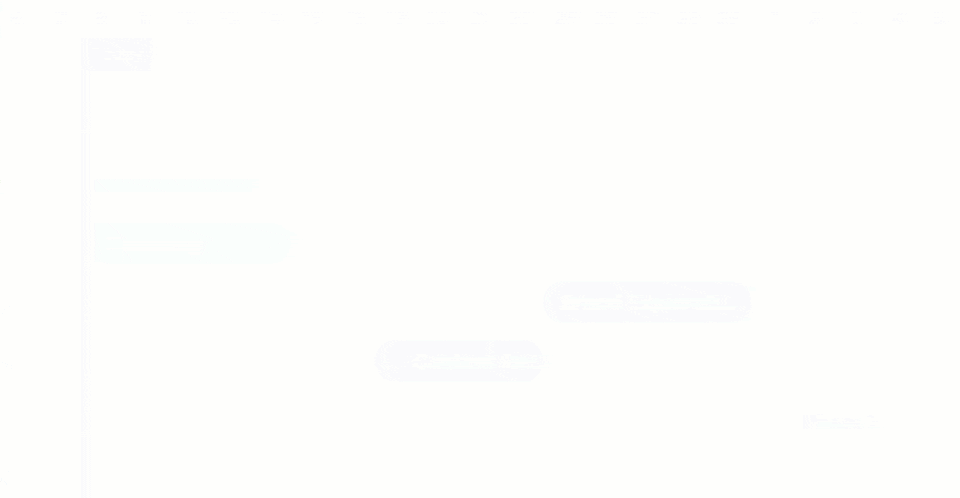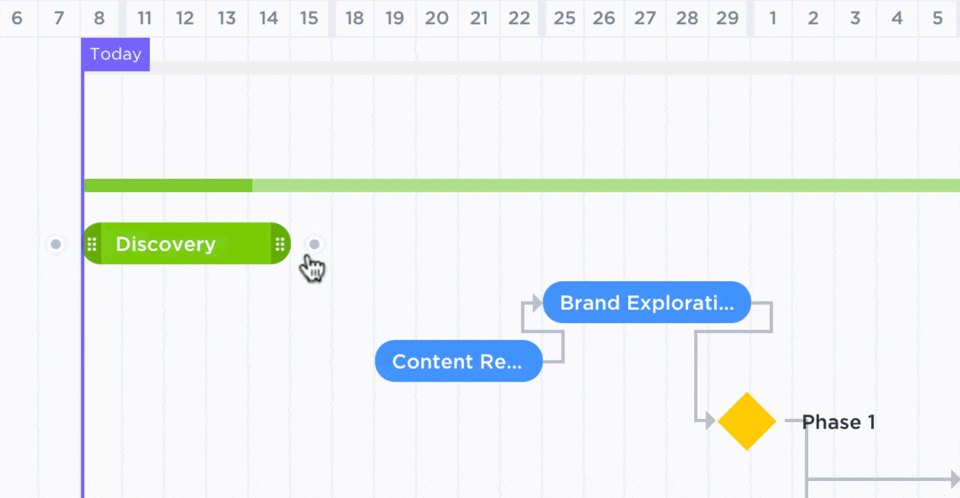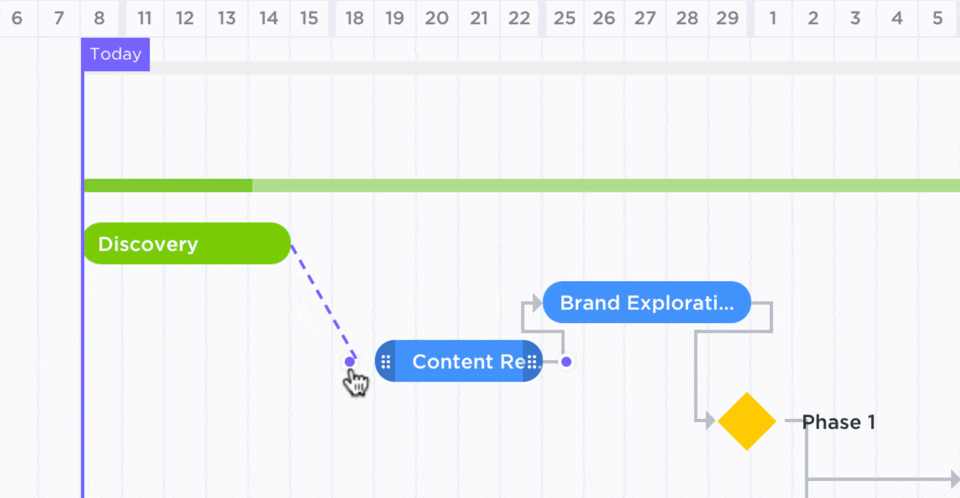
You can use ClickUp Gantt Charts to adjust a schedule in real time and keep the production process intact. These interactive charts visually represent project timelines, allow multiple users to track progress, and highlight potential roadblocks.
Here’s how to adjust your project schedule and maintain the production flow:
💡 Pro Tip: Use a free production schedule template to build a plan that works for you—without starting from scratch. Try the ClickUp Production Schedule Template!
Being a smaller team and having thousands of orders from around the world, we need to be ultra efficient and ClickUp Gantt charts allow us to track all of our production and logistics in one place, which made our production team two thirds more efficient.
📖 Also Read: Free Gantt Chart Maker Software
Imagine a textile factory producing 10,000 garments per week. To meet customer demand while minimizing waste and delays, the factory needs a well-structured production schedule.
Every stage—from demand forecasting to shipment planning—must be carefully timed to keep operations running smoothly.
Before production even begins, the factory gathers order data from retailers and fashion brands. They analyze seasonal demand, past sales trends, and production capacity to determine the scope of the order:
🧠 Fun Fact: Manufacturing is expected to produce around 1,812 petabytes of data annually, surpassing other sectors like communications and finance. To handle the growing complexity of decision-making from this digital information, manufacturers are using smart technology to analyze data patterns and solve previously unanticipated issues.
A structured weekly plan and a continuous workflow keep you in line with your production process. For example, for manufacturing 10,000 garments per week, your plan can look like this:
This continuous workflow ensures deadlines are met without bottlenecks.
To avoid production delays, the factory must ensure all materials arrive on time and in the right quantities. This involves:
Making full use of human and machine resources is key to efficiency. The factory optimizes production by:
Even with a solid plan, unexpected disruptions can throw things off course. A proactive approach helps keep production on track:
With a real-time tracking system, managers quickly assess situations and make data-driven scheduling decisions to minimize downtime.
Before garments leave the factory, they undergo multiple quality checks for fabric defects, stitching accuracy, and overall durability.
Any rejected items are either reworked or discarded to maintain brand reputation. Once approved, packaging teams organize shipments based on retailer delivery schedules for timely delivery.
🚀 The result?
An optimized production schedule helps the textile factory minimize waste, meet customer demands, and maximize efficiency. This means high-quality garments reach stores on time, keeping both retailers and consumers happy.
👀 Did You Know: The food manufacturing industry is the largest employer in U.S. manufacturing, leading the sector in 19 states. It even outpaces the transportation equipment manufacturing industry, which holds the second spot nationwide.
Effective production scheduling sounds like the perfect way to improve processes—until reality steps in. Here are some common obstacles that can throw your schedule off track:
These challenges can lead to production delays, increased costs, and unhappy customers.
The universe won’t always grant you flexible deadlines and unlimited raw materials, but smart planning can help eliminate surprises and keep your production schedule on track. Follow these seven best practices to stay ahead:
By following these best practices, you’ll keep operations running smoothly—no matter what the universe throws your way.
Creating a production schedule isn’t just about setting deadlines—it’s about optimizing every step to maximize efficiency and profits. By clearly defining objectives, breaking complex tasks down into manageable steps, and tracking progress, you can prevent costly delays and keep operations running smoothly.
But juggling multiple tools to manage these processes can slow you down. ClickUp brings everything together in one place, combining workspace knowledge with robust tracking and visualization tools, so you can focus on production—not app-hopping.
Sign up for ClickUp for free today and take control of your production schedule with a clear, streamlined workflow.
© 2026 ClickUp