It’s tougher to reach your project goals when you’re not sure about your current resources and what your team might need.
Without enough data, making informed decisions about project staffing, budget, and scope is hard. When work isn’t distributed properly, skills and experience go to waste, hindering project efficiency and employee satisfaction. And without a standardized measure, your workload arrangement and progress become muddled.
However, Full-time Equivalents or FTE in project management provide a common language for discussing progress, workload, and other resource management needs.
With FTE, you get transparency, collaboration, and a clearer view of workload capacity. This guides efficient personnel allocation, preventing overwork or underutilization.
Realistic project timelines built on accurate FTE calculations increase your project success rate and make your progress more predictable. Using Full-time Equivalents (FTE) correctly ensures that the right skills and experience are perfectly matched to your workload, boosting project efficiency and employee engagement.
This post covers all you need to know about leveraging Full-time Equivalents or FTE in project management.
Let’s get right into it!
- What is Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)?
- Importance and Benefits of FTE in Project Management
- Examples of FTE Application and Usage in Project Management
- FTE Vs. Headcount: A Comparative Analysis
- Steps to Calculating Full-Time Equivalent in Project Management
- Step 1: Determine the standard number of hours for a full-time employee
- Step 2: Calculate the total number of hours worked by all employees
- Step 3: Divide the total number of hours worked by the standard number of hours
- Step 4: Round the resulting FTE number to the nearest hundredth (if necessary
- Additional considerations for calculation of FTE in project management:
- How to Use FTE in Project Management
What is Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)?
Full-time equivalent (FTE) is a unit of measurement that represents the total number of full-time hours worked by a company’s employees. It is the workload of one full-time employee over a set period. It acts as a standard unit, and lets you compare output from part-time workers, contractors, and those on different schedules.
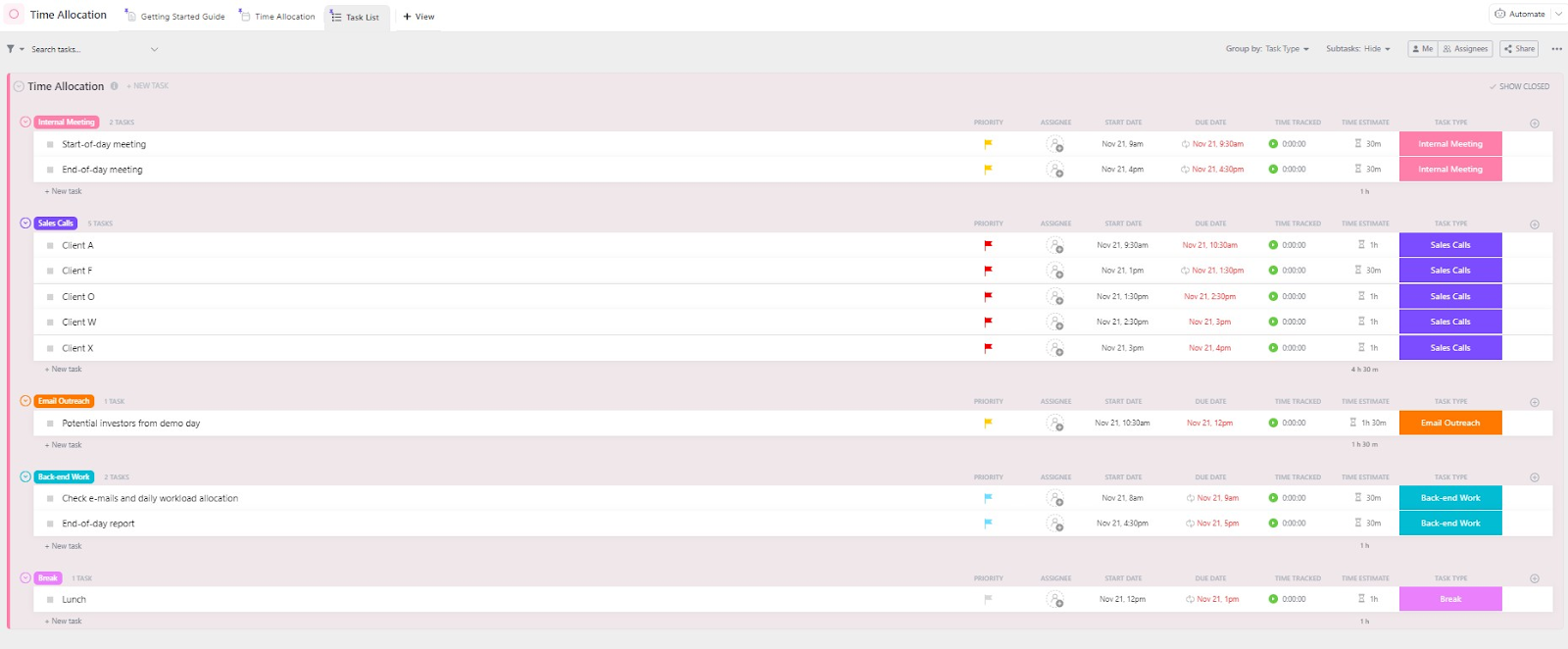
⭐ Featured Template
Whether you’re juggling full-time, part-time, and contract-based employees, this ClickUp’s Time Allocation Template standardises it all—so you can measure team capacity without the mental gymnastics. Try it now!
To calculate FTE, divide each employee’s working hours by the company’s full-time workweek hours.
For example, if a company considers 40 hours per week full-time, and an employee works 40 hours per week, their FTE is 1.0. Similarly, if employees work 20 hours per week at the same company, their FTE would be 0.5.
FTE is important for annual human resource planning and managing labor costs. It can also help your company understand their part-time workers’ efficiency.
Importance and Benefits of FTE in Project Management
FTE is valuable because it streamlines your resource allocation, enhances project execution, and improves your project’s success rate. Here’s a breakdown of the benefits and importance of FTE in project management:
- Standardized measurement and greater transparency: FTE allows you to measure and compare efforts across full-time, part-time, or contracted resources with a single unit. This helps simplify resource allocation, budget planning, and workload distribution. Using FTE in project management as a common language facilitates communication and transparency regarding your project goals, resource allocation, and workload among stakeholders
- Improved budget forecasting and ROI: Knowing the total FTEs dedicated to a project facilitates accurate estimates of salaries, benefits, and other expenses. This ensures budget transparency and helps avoid financial overruns. Optimized resource allocation minimizes wasted time and maximizes output, leading to a better return on investment for your project
- Efficient project scheduling and higher success rates: Your FTE calculations enable realistic project timelines by factoring in available project resources and their capacity. This prevents unrealistic deadlines and fosters efficient project execution. Ensuring you plan resources accurately is key to increased project success rates. It helps your team meet deadlines while staying within budget
- Better workload balancing and talent management: Monitoring FTEs per team member ensures equitable workload distribution, preventing overwork and maximizing individual productivity. This leads to happier and more efficient project team members. FTE metrics also help you identify critical roles, skill gaps, and training needs within your team, enabling strategic talent management and development
- Accurate resource planning and improved decision-making: Effectively estimate the workforce required for successful completion by quantifying project needs regarding FTEs. It helps in hiring decisions, outsourcing needs, and managing internal team workload. Data-driven insights from FTE calculations empower better staffing, budgeting, and project scope decision-making
Examples of FTE Application and Usage in Project Management
FTE (Full-Time Equivalent) brings clarity and structure to resource allocation and workload distribution in organizations. Here are specific examples of how the FTE model is used:
1. Staffing a new project
Imagine you’re launching a new marketing campaign requiring content creation, social media management, and data analysis.
By estimating the workload for each task and converting it to FTEs (e.g., content creation – 0.75 FTE, social media – 0.5 FTE, data analysis – 0.25 FTE), you get a clear picture of the human resources needed.
Based on the total FTE (1.5 FTE), you can decide whether to hire full-time employees, part-time specialists or outsource specific tasks.
2. Budgeting and cost estimation
Knowing the project’s total FTE allows you to estimate personnel costs more accurately.
For instance, if the average annual salary for your required skillset is $50,000, and the project needs 1.5 FTEs for a year, the personnel cost estimate would be (1.5 FTEs * $50,000/FTE) = $75,000.
Using FTE in project management helps secure appropriate funding and set realistic project budgets.
3. Monitoring workload and preventing burnout
Tracking individual FTEs within your team ensures fair workload distribution and prevents overworking.
If a team member’s FTE consistently exceeds a healthy limit (e.g., 1.2 FTE), it indicates potential overload and necessitates adjustments like delegating tasks, hiring additional support, or revising project deadlines.
4. Measuring team efficiency and productivity
Analyzing FTE data over time reveals insights into your team’s performance and identifies areas for improvement.
For example, if your team consistently delivers projects with fewer FTEs than initially planned, it indicates increased efficiency and team productivity. Conversely, consistently exceeding planned FTEs might suggest inefficiencies or unrealistic project timelines for you.
5. Communicating project progress and resource utilization to stakeholders
Using FTE as a common metric in project management simplifies communication with stakeholders like clients or investors.
You can present progress reports in terms of utilized FTEs or available FTEs for specific tasks and future projects, providing project managers with a clear understanding of resource utilization and project advancement.
Bonus Example
A software development team needs to build a new e-commerce platform. They estimate the project requires 8,000 hours of work.
If a full-time developer works 40 hours per week, this translates to 200 FTE weeks (8,000 hours/40 hours/week).
The team can hire four full-time developers for 20 weeks each (4 developers * 20 weeks/developer = 80 FTE weeks) or a combination of full-time and part-time developers to reach the required 80 FTE weeks.
FTE Vs. Headcount: A Comparative Analysis
FTE (Full-Time Equivalent) and headcount are project management terms used to measure the size of a workforce, but they differ in scope and purpose. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Focus | Headcount | Counts the total number of employees, regardless of working hours or positions. It’s a simple headcount of individuals employed by the organization |
| FTE | Measures the total workload capacity of the workforce by converting all hours worked into a standardized unit of one full-time employee (typically 40 hours/week). It considers part-time, temporary, and contracted workers alongside full-time employees | |
| Applications | Headcount | Useful for simple workforce size assessment, organizational structure planning, office space allocation, and basic HR reporting |
| FTE | Valuable for resource planning, budget forecasting, project workload management, benchmarking efficiency, and analyzing team productivity | |
| Advantages | Headcount | Easier to calculate and understand, provides a clear picture of overall company size |
| FTE | More accurate reflection of workforce capacity, enables better resource allocation, facilitates accurate budget planning, and allows for cross-company comparisons | |
| Disadvantages | Headcount | Doesn’t consider individual workloads or part-time employees, which can lead to inaccurate resource planning and budget estimations |
| FTE | More complex to calculate, requires detailed tracking of hours worked, and may not be relevant for all organizational functions | |
| Choosing the right metric | Headcount | Suitable for basic workforce size tracking and internal reports |
| FTE | Preferred for resource planning and project work management, budgeting, efficiency analysis, and benchmarking |
Decision tips
Consider the purpose of your analysis. If you need a simple count of employees, headcount is sufficient. If you need to understand workload capacity, resource allocation, or project needs, use an FTE calculation. You can use both metrics in conjunction for comprehensive insights.
Steps to Calculating Full-Time Equivalent in Project Management
Step 1: Determine the standard number of hours for a full-time employee
Your organization or industry standards typically decide this. The most common standard is 40 hours per week, which can vary depending on location and sector.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of hours worked by all employees
Include both full-time and part-time employees. Consider overtime or any additional hours worked. You can gather this information from timesheets, payroll records, or HR systems.
Step 3: Divide the total number of hours worked by the standard number of hours
Use the formula: FTE = Total Hours Worked / Standard Hours for Full-Time Employee.
Step 4: Round the resulting FTE number to the nearest hundredth (if necessary
Most organizations use FTEs up to two decimal places for precision. Let’s say a company has five full-time employees working 40 hours per week and three part-time employees working 20 hours per week.
The total hours worked per week would be: (5*40) + (3*20) = 260 hours
Assuming a 40-hour workweek, the FTE would be: 260/40 = 6.5 FTEs
Additional considerations for calculation of FTE in project management:
- Annual FTE: To calculate annual FTE, multiply the standard weekly hours by the number of weeks in a year (52) and use that as the denominator in the formula
- Part-time employees: Calculate their FTE by dividing their actual hours worked by the standard full-time hours. For example, a 20-hour per week employee would be 0.5 FTE
- Different work schedules: If employees have varying hours or shifts, calculate their FTE individually based on their actual hours worked
- Vacation, sick leave, and holidays: These absences can be factored in by adjusting the total hours worked accordingly
How to Use FTE in Project Management
Here are some practical ways to apply FTE in project management:
Estimating resources for project planning
Quantify workload by calculating the FTEs required for each task or phase of the project. It provides a clear understanding of the overall effort needed for completion.
Using FTE in project management also helps to identify your staffing needs. Determine the number of full-time, part-time, or temporary employees required to meet the project’s FTE demands. Optimize resource allocation and allocate FTEs strategically across different tasks based on skills, availability, and workload capacity.
Communicating project progress to stakeholders
Use FTEs to transparently communicate project progress, resource management, and workload distribution to stakeholders. Track progress and report utilized FTEs and available FTEs for specific tasks to indicate project status and identify potential delays or resource constraints.
Monitoring workload and preventing burnout
Track individual FTEs by assigning FTEs to each team member to ensure fair workload distribution and prevent overwork. Identify potential overloads or assess individual FTEs regularly to detect signs of potential burnout or overwhelming workloads.
If FTEs exceed healthy limits, implement adjustments such as delegating tasks, hiring additional support, or extending project timelines.
Creating realistic project budgets
Multiply the FTEs required by the average salary for the relevant roles to estimate personnel expenses accurately.
Factor in benefits and overhead and include additional costs like benefits, taxes, and overhead associated with each FTE to create a comprehensive budget.
Track your spending by monitoring actual FTE costs against the budget throughout the project to identify potential deviations and take corrective actions.
Measuring team efficiency and productivity
Analyze FTE data by comparing planned FTEs with actual FTEs used to measure team efficiency and identify areas for improvement. Track your performance trends by monitoring FTE data to identify patterns in team productivity, informing future project planning and resource allocation decisions.
Also compare your team’s FTE utilization with industry benchmarks to assess performance and identify potential areas for optimization.
You can also use FTE-based data to facilitate stakeholder decisions regarding project scope, budget adjustments, or resource reallocation.
Simplify Your FTE Management with ClickUp
Now that you’re ready to leverage Full-Time Equivalent, get yourself a project management tool to help you plan and manage resources effectively.
ClickUp is that ideal project management tool—it will do the heavy lifting to help you estimate, track, and improve resource allocation.
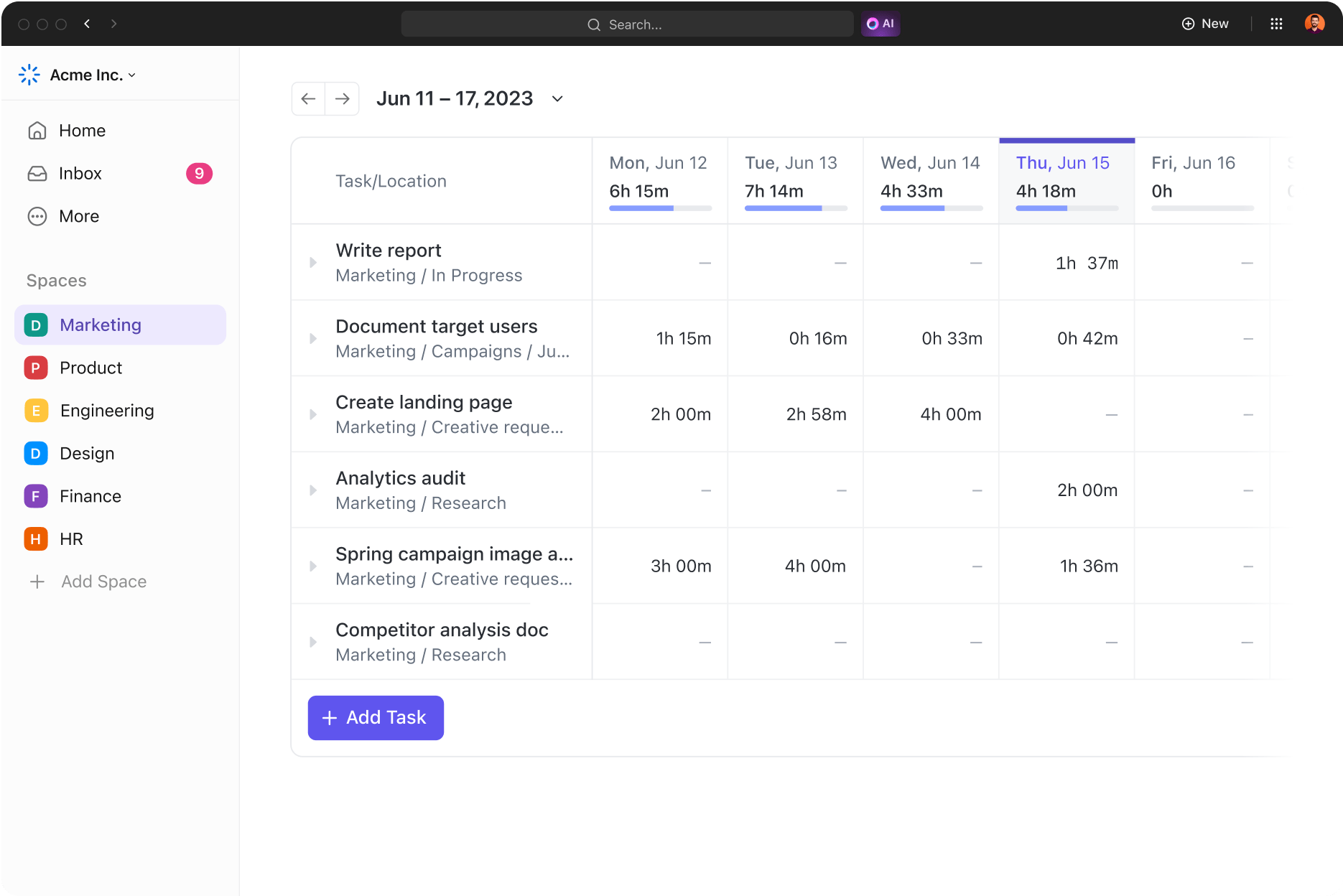
Accurately record all hours your team worked on tasks and projects using the ClickUp Time Tracker.
For instance, compare estimated FTE with actual hours logged to identify workload discrepancies and refine future estimates.
Customize and allocate time effectively with ClickUp’s Time Allocation Template to match your specific business’ FTE tracking requirements. Compare workflows across teams and find ways to optimize your processes with ClickUp’s Time Studies Template.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 50% of people structure their time by dedicating certain days to admin vs. focused work, but only 22% say they automate or delegate tasks.
Manual time management helps, but it doesn’t eliminate the repetitive tasks that still eat into deep work. ✔️
ClickUp’s Calendar, Time Blocking, and AI Agents work together to protect your time. Automatically schedule repetitive work, move tasks based on priority, and trigger reminders—so your week runs itself.
💫 Real Results: Lulu Press saves 1 hour per day, per employee using ClickUp Automations—leading to a 12% increase in work efficiency.
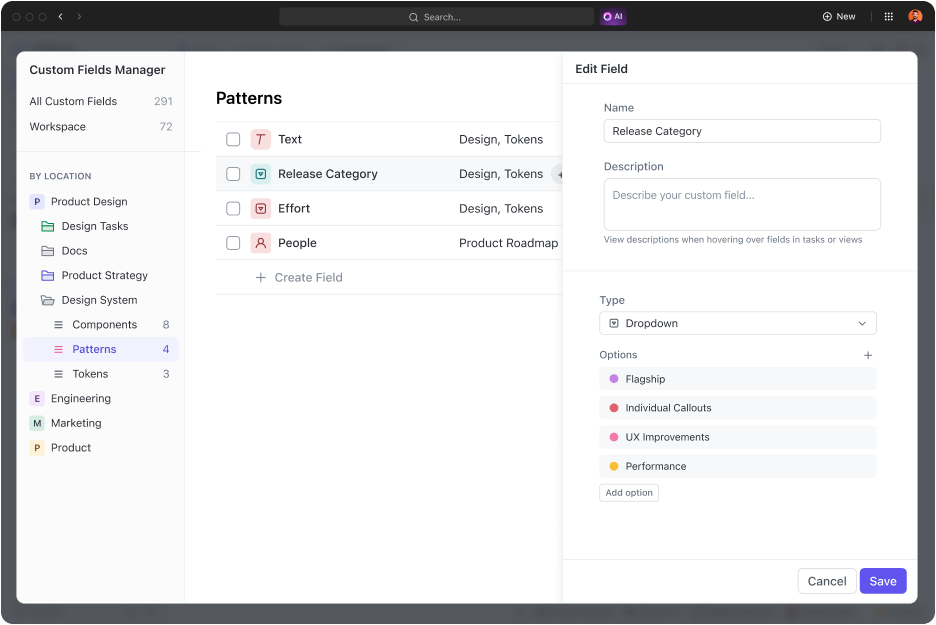
Create Custom Fields to store and track FTE data directly within tasks and projects, so that it is organized and accessible.
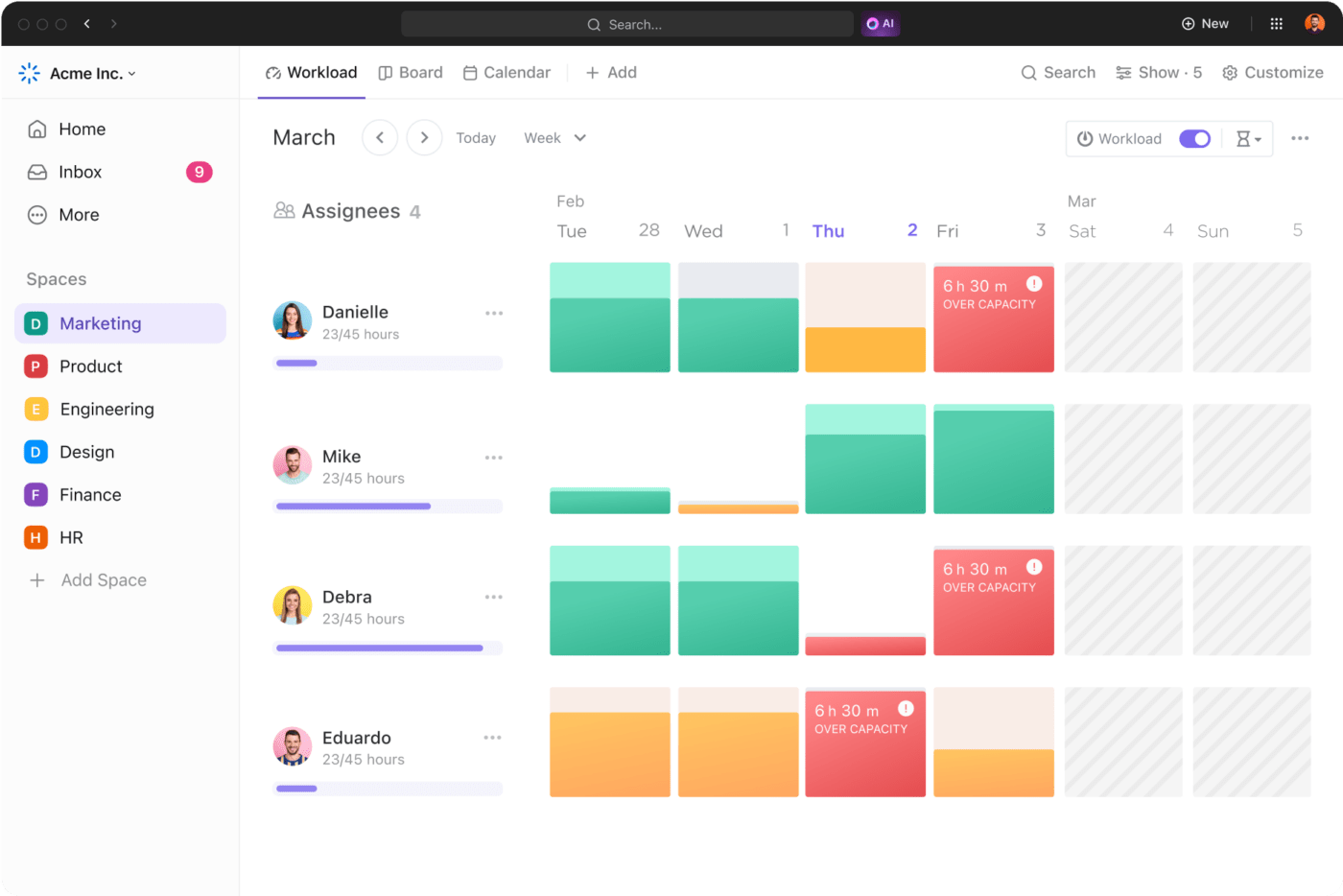
Visualize team capacity and individual workloads through ClickUp Dashboard to ensure fair distribution and prevent burnout. Assign tasks based on available FTEs, thus optimizing resource allocation and preventing overwork.
Moreover, if someone overworks, you can use ClickUp to prevent over-allocation by setting capacity limits for each team member based on their FTE availability.
Also, include FTE custom fields in the ClickUp Reporting Dashboards feature to analyze workload trends, identify bottlenecks, and track progress.
You can also create customizable dashboards to visualize FTE data alongside metrics like task completion rates and project timelines. Visualize the data the way you want, and share it with all relevant stakeholders.
To run a successful project, project managers must understand and optimize their FTE. Choosing the right project management software can help you do this efficiently and at scale.
Get started for free with ClickUp today.