Effective Project Time Management Strategies [Proven to Work]

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Imagine consistently meeting your project goals, staying within budget, and delivering on time. Sounds like an ideal deal, right?
The reality is that 70% of projects fail to deliver as promised. Companies with structured time management complete 61% of projects on time versus just 41% without it.
Let’s explore how robust project time management can keep projects on track and ensure the planned ROI.
Project time management is the process of planning, scheduling, and controlling how long tasks and activities take to complete a project on time and within budget.
It’s one of the 10 critical knowledge areas defined by the Project Management Institute (PMI) and involves strategically breaking down work, estimating durations, sequencing tasks, and monitoring progress throughout the project lifecycle.
When done well, you gain control over timelines, allocate resources efficiently, and manage deadlines effectively, creating a win for you, your team, and your stakeholders.
Effective time management delivers seven concrete benefits:
The stakes are high. Companies with strong time management practices save 28 times more money than those without. But what does this look like in practice?
To achieve these benefits, you need a structured framework. That’s where PMBOK’s seven time management processes come in.
Before diving into the framework, let’s see how organizations applied these principles under extreme pressure.
The London Olympic Delivery Authority faced an immovable deadline: July 27, 2012. With 75,000+ workers and a £9 billion budget, failure wasn’t an option.
Their approach: Integrated master schedules with 3,000+ milestones, critical path analysis, and strategic buffer placement at integration points. Weekly schedule reviews with all contractors ensured alignment.
The outcome: All major venues completed on schedule, with the Olympic Stadium finished a year early.
Key lesson: Fixed deadlines require working backward from the end date and protecting critical path activities ruthlessly. Strategic buffers at integration points prevent cascading delays.
After the disastrous October 2013 launch, the team had just 60 days to fix Healthcare.gov before the enrollment deadline. The site was processing only 30% of transactions successfully.
Their approach: Daily 15-minute stand-ups, prioritized “punch lists” ranking fixes by impact, Kanban boards for real-time visibility, and a 24/7 war room that eliminated decision delays.
The outcome: By December 2013, the site processed over 80% of transactions successfully, ultimately enrolling 8 million people.
Key lesson: Crisis situations require ruthless prioritization and elimination of bureaucratic delay. Time-boxing decisions and maintaining laser focus enables aggressive schedule compression.
These examples prove that whether you’re managing a multi-year infrastructure project or a 60-day crisis recovery, the fundamentals remain constant: realistic planning, continuous monitoring, clear accountability, and strategic buffers.
Most project managers know they should manage time better, but few understand there’s a proven system for doing it.
The Project Management Institute’s PMBOK framework breaks time management into seven interconnected processes which can be immensely helpful.
These aren’t theoretical concepts. They’re practical steps that help organizations achieve a 92% success rate in meeting project objectives, compared to 33% for teams without structure.

Before touching any timeline, decide how your team will make scheduling decisions.
Your Schedule Management Plan answers three fundamental questions:
Which methodology fits this project?
Critical Path Method works great for construction with hard dependencies. Agile sprints make more sense for software with evolving requirements.
What tools will everyone use?
Define your project management platform, communication channels, and reporting dashboards upfront.
How often will you report progress?
Weekly for most projects, daily for critical initiatives, monthly for long-term programs.
This prevents the chaos that erupts when team members make conflicting assumptions.
One person thinks you’re using two-week sprints, while another assumes monthly milestones. By the time you discover the mismatch, you’ve lost a month of coordination.
Next, take your high-level Work Breakdown Structure and break it into tasks someone can actually do.
“Build website” isn’t an activity. It’s a wish. Real activities look like this:
The granularity sweet spot is activities that take between half a day and two weeks.
If they’re too detailed, you drown in administrative overhead tracking hundreds of micro tasks. Too vague and team members waste time figuring out what “build homepage” actually means.
Now map the logical order and ask which tasks must finish before others can start.
You can’t conduct user acceptance testing before you write code, just like you can’t finalize navigation structure until wireframes show where everything goes.
Dependency types you’ll encounter:
I like to use the Precedence Diagramming Method help visualize these connections because understanding dependencies matters because delays ripple forward.
If your designer misses their deadline by three days, every downstream task shifts three days too.
From there, figure out what you need before you estimate how long things take.
A task requiring a specialized DevOps engineer who’s available 20% of the time takes five times longer than if you had them full time.
You also need to account for equipment, software licenses, and materials.
That $500 plugin your developer needs? If procurement takes three weeks to approve the purchase, that’s three weeks of delay regardless of coding speed.
Resource availability directly controls duration. I once watched a mobile app project stall for six weeks because the team needed a specific Android device for testing and nobody thought to order it until development finished.
That’s why I suggest getting familiar with resource allocation from the start, which makes things much easier in the long run.
With resources identified, you can finally answer the question everyone’s been asking: how long will this actually take?
I will typically use PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) to account for uncertainty with three estimates:
Why weight it? Because most likely scenarios happen most often, and this formula reflects that probability mathematically.
Poor estimation drives 39% of project failures. Taking time to estimate accurately here saves you from explaining delays later.
Now you have everything you need: activities, sequences, resources, and durations. Time to build the actual schedule.
Everything comes together here when you build your actual project schedule model.
The Critical Path Method identifies your longest chain of dependent activities, which determines your minimum project duration.
Think of it as finding the backbone of your project timeline. This is where planning gets real because you’ll see exactly when things need to happen and what delays you can absorb versus what kills your timeline.
Three key outputs emerge from this process.
First, your critical path reveals the sequence of tasks that controls your project end date. Any delay here pushes everything back, so these activities demand your closest attention.
Second, float or slack time shows how much wiggle room non-critical activities have before they impact the finish date. This flexibility lets you shift resources strategically when problems arise.
Third, milestones create key checkpoints that signal progress and allow for course correction. These aren’t just arbitrary dates but meaningful markers that keep everyone aligned.
The most important process is ongoing, not a one-time event.
Monitoring actual progress against your baseline helps spot variances and take corrective action. This continuous loop separates projects that finish on time from those that drift into chaos.
Your control activities fall into four categories:
Track performance data by monitoring daily or weekly depending on project pace. Use burndown charts, Gantt updates, and completion percentages to maintain visibility.
Calculate variances using Schedule Variance (SV = Earned Value minus Planned Value) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI = Earned Value ÷ Planned Value) to measure progress quantitatively.
Numbers don’t lie, and these metrics cut through optimistic status reports.
Investigate causes when problems appear by digging into root causes immediately.
Understanding why keeps you from repeating mistakes.
Implement fixes by taking corrective action before small delays become catastrophic. Reallocate resources, adjust sequences, or negotiate deadline extensions early while you still have options.
Only 34% of organizations consistently complete projects on time. The difference comes down to effective schedule control that catches and corrects issues early.
Tip: These seven processes work together as a system. Skip one and you’re guessing. Follow them all and you gain the structure that separates successful projects from the ones that spiral out of control.
Understanding what changes when you adopt structured time management helps justify the investment.
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | PMBOK Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Rough estimates, informal discussion | Documented methodology, defined tools, clear roles |
| Task Definition | High-level milestones only | Detailed activity breakdown at actionable level |
| Dependencies | Assumed or discovered late | Mapped systematically with precedence diagrams |
| Duration Estimates | Single-point guesses | Three-point PERT calculations with probability |
| Schedule Development | Simple task list or spreadsheet | Critical path analysis with float calculations |
| Monitoring | Periodic status meetings | Continuous variance analysis with SV/SPI metrics |
| Success Rate | 33-41% on-time completion | 61-92% on-time completion |
| Resource Efficiency | 12% waste from inefficiency | 28x better cost management |
The numbers speak for themselves. Structured approaches don’t just feel better, they deliver measurably superior results.
Getting your project management right means getting your time management right. These five steps transform theory into practice.
Know what you’re aiming for before you start planning.
Define specific objectives that answer three questions: What does success look like? What will change when you’re done? Who benefits and how?
Then break the journey into measurable milestones.
Clear milestones break projects into manageable chunks, create accountability, and make stakeholder communication straightforward.
Once you’ve mapped your destination, you need a roadmap to get there.
Your schedule translates milestones into daily reality.
Start by listing every task, then sequence them based on dependencies and visualize the flow with a Gantt chart. This foundation prevents chaos.
I learned this on a website project that missed its deadline by six weeks because nobody mapped task relationships upfront.
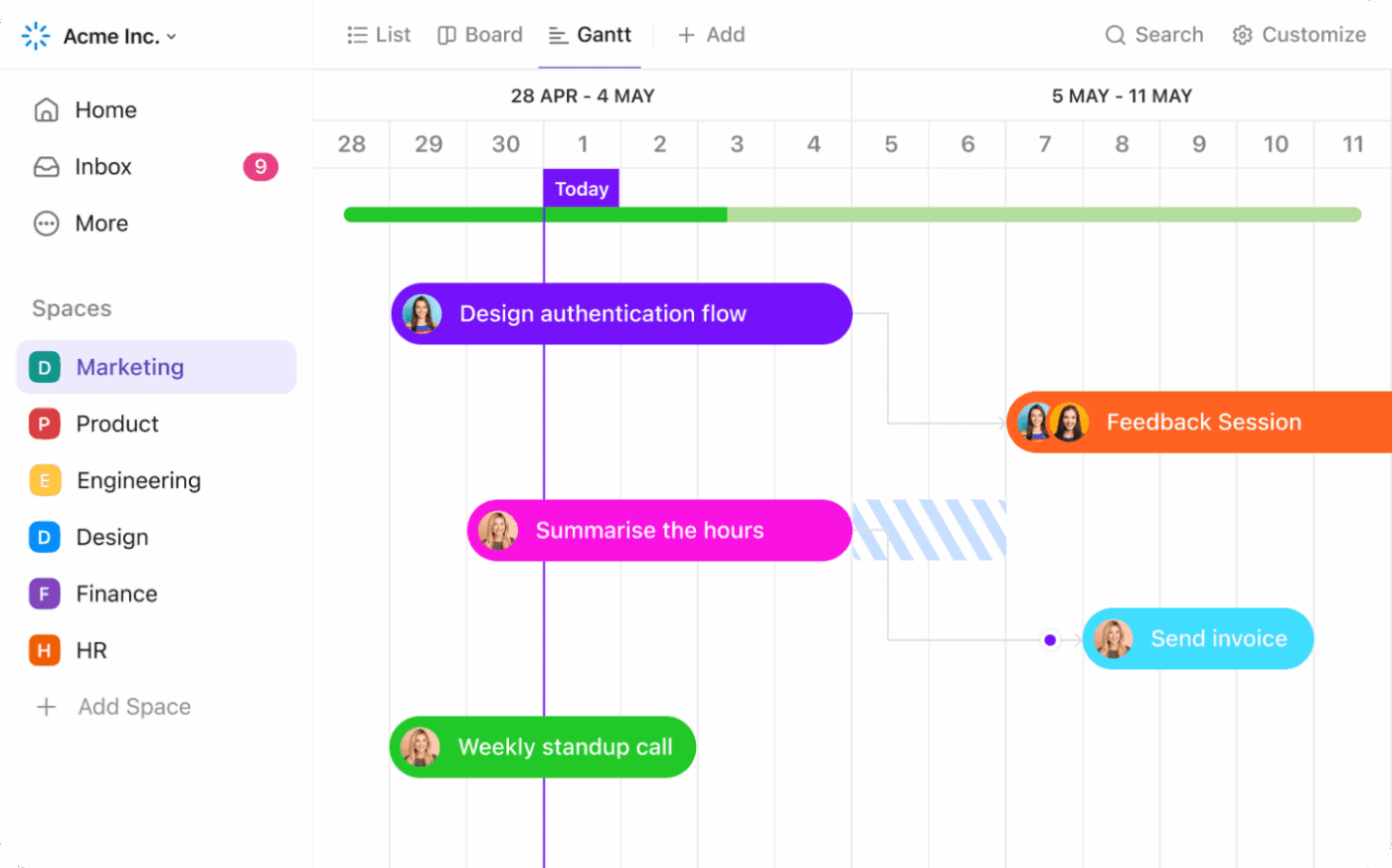
Once you’ve mapped the sequence, assign realistic timeframes using PERT estimates rather than wishful thinking.
Build in buffer time at integration points where multiple work streams converge, because these junctions are where delays compound. Keep your schedule adaptable so you can adjust when circumstances shift.
But even a perfect schedule becomes useless if you’re working on the wrong things first, which is why prioritization comes next.
Start by asking which tasks deliver the most value for the least effort, then focus there.
Critical path activities demand your attention first because any delay pushes your entire deadline back. Tasks with float give you breathing room to absorb problems without derailing everything.
Check in with your team regularly and reassess after major milestones, because priorities shift as projects evolve and what felt urgent last week might matter less today.
I typically use prioritization tools to make this process easier. A small investment now goes a long way later.
Smart prioritization tells you what to work on. Now you need smart techniques for how to work on it.
There are many time management techniques in my aresnal, but these three methods work especially well across industries and team sizes:
Techniques optimize how you work, but you still need visibility into whether it’s actually working.
Time tracking tools provide actionable insights into where time actually goes.
You’ll boost accountability, cut inefficiencies, make smarter resource decisions, and gather historical data that sharpens future planning.
Tools like ClickUp integrate time management into a broader project framework, giving you one place to plan, execute, and analyze.
The difference between projects that succeed and those that spiral? Consistent application of these five steps, supported by the PMBOK framework you learned earlier.
ClickUp offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to meet the diverse needs of teams across various sectors, such as software development, marketing, and more.
ClickUp Time Management combines essential project management functionalities with advanced time management strategies to help teams streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and efficiently achieve project objectives.

ClickUp’s Time Management suite transforms how teams track, manage, and allocate time across projects. It integrates seamlessly into your workflow, offering tools that adapt to your project’s needs, whether for individual tasks or team collaborations. Here’s what you can do with the time management features:
Here’s how ClickUp stands out in enhancing project time management:
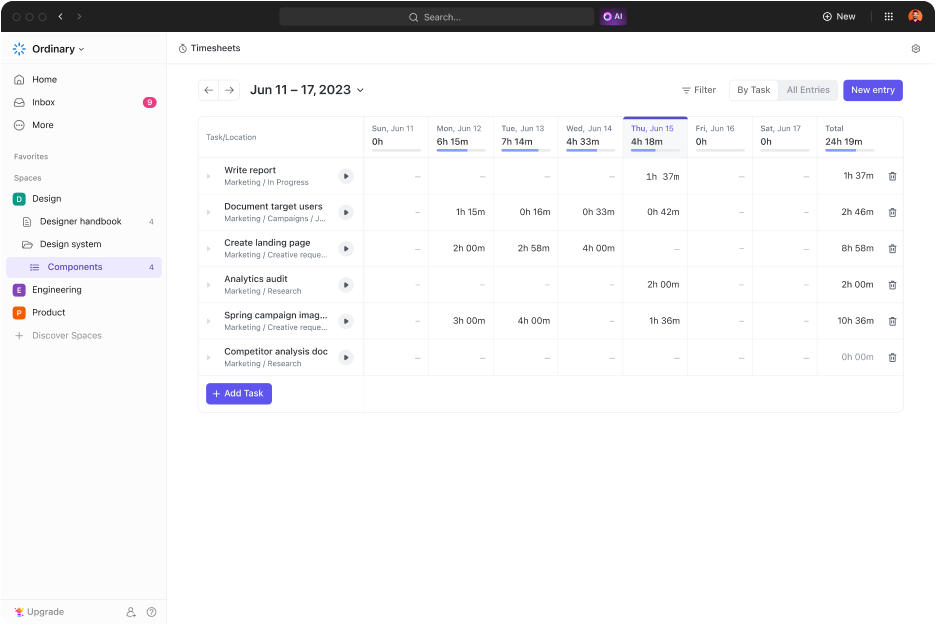
ClickUp Project Time Tracking is crucial for teams looking to understand and optimize how time is spent on their projects. This feature allows for precise recording and monitoring of the time dedicated to each task, providing transparency and aiding in effective resource management. With the project time tracking features, you can:

ClickUp Time Estimates allow teams to set realistic expectations for task durations, which is fundamental for effective project planning and deadline management. This feature helps align team efforts and manage client expectations. This feature helps you:
ClickUp also provides various templates, such as time management templates and project schedule templates, to streamline how you track, manage, and optimize time across any project.
These ready-to-use templates provide a robust framework for setting deadlines, assigning tasks, and monitoring progress, ensuring your project stays on schedule and within budget. Let’s look at the two major templates from ClickUp that assist in time management:
The ClickUp Time Management Schedule Template is crafted to transform how you and your team execute daily tasks. It helps ensure efficient use of time and meeting project deadlines effectively. Here’s what you can do with this template:
ClickUp Time Box Template offers a structured approach to managing tasks efficiently—making it ideal for beginners and seasoned professionals. This template helps prioritize tasks or events that standardize your calendar through strategic time blocking. With this template, you can:
Slack time is the delay a task can experience without pushing back your project deadline. Also called float, it’s calculated by subtracting earliest start time from latest start time. Critical path tasks have zero slack, while non-critical tasks offer flexibility when problems arise.
Lead time is when you start a successor task before its predecessor finishes. For example, you might begin documentation while coding is 80% complete. This overlap accelerates your schedule by running dependent activities in parallel, though it introduces risk if predecessor tasks change.
Lag time is the mandatory waiting period between dependent tasks. Unlike problem-caused delays, lag is intentional and built into your schedule. Concrete must cure 48 hours before construction continues. You can’t eliminate lag by adding resources because external factors control it.
© 2026 ClickUp