Product Manager Goals to Elevate Your Product Management Skills

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Product managers often have a lot on their plate. They must discover product opportunities, decide on the necessary features, negotiate with stakeholders for approvals, and monitor product metrics and customer satisfaction.
All of this is hectic if they don’t have a proper strategy. That’s why it’s important to set product manager goals.
Product manager goals should be relevant to cross-functional teams, stakeholder expectations, and managers themselves.
What are some examples of product manager goals? Which frameworks are the most effective for setting them? What should be your product’s success metrics? This guide explains it all in detail.
Product management is a universally adopted approach to handling your product’s life cycle.
The process involves planning, developing, managing, and deploying a quality product on time to achieve product-market fit. The ultimate goal is to deliver products that meet customers’ needs and business goals.
The product management process helps you:
Different companies follow different product management approaches based on their organizational goals, industry, and target market. However, project management typically involves the three functions below.
The product may evolve to have different requirements from ideation to launch. You might also have limited resources that you must utilize efficiently to achieve those demands.
That’s why planning ahead your product requirements and resource allocation is important.
For this, you have to create a clear roadmap detailing the features you want in the product, required resources, timelines for each stage of the product life cycle, pricing aspects, and customer requirements.
This is the execution step for cross-functional teams to collaborate and work on developing and delivering the right product on time.
Here, product managers work in strategic partnerships with:
They are the point of contact for all the teams in resolving any dependencies and issues.
Once your product is live, it’s time to monitor its performance in production.
This involves analyzing whether the product meets its business objectives and releasing enhancements, updates, or new features.
People often confuse a product manager with a product owner. There might be some overlap, but both have different goals to achieve.
A product owner guides the development team on what to do and when, while a product manager focuses on broader aspects such as setting strategies, prioritizing features, and creating product roadmaps for marketing, sales, development, and support teams.
The product owner is primarily seen in scrum teams. They ensure the timely delivery of product features in the development phase. Meanwhile, the product manager’s role is to engage with customers, marketing teams, and stakeholders and bring business to the company.
Before you build a house, you make a plan. You start with an outline and a blueprint of how it should look. Then, you start the actual construction.
Similarly, product management starts with planning, which includes goal setting.
Getting development teams, designers, and marketers moving towards the same goal is crucial to launch a successful product. Product manager goals help align multiple functions across the pod.
A good product manager oversees the entire product life cycle, from vision to launch, and defines goals that align with customers’ preferences and the company’s vision.
You’ll also need precise product goals to deliver quality products on time. It’s a way to understand what features your customers need, deadlines for each piece of work, UI requirements, scalability needs, and more.
Ultimately, with clear product manager goals, you can ensure that your whole product strategy is feasible, efficient, and scalable.
Product manager goals vary across verticals, product stages, and vision. Here are a couple of broad examples representing the primary types of goals in product management.
These are goals focused on revenue, team expansion, and cost-saving operations. For example, the image below highlights Walmart’s goals of 4% sales growth and 4%+ operating income to be achieved over the next three to five years.

Other examples:
| Increase the product’s pro plan ROI by 10% in a year. |
| Hire ten backend and two frontend developers to the engineering team in the next quarter. |
Targets set for product feature add-ons, improvements, and integrations come under development goals.
Examples:
| Add a ‘Pay Now’ button in V2.0 that directly takes customers to credit payment options. |
| Introduce a wallet feature in the next 30 days so users can manage digital funds easily. |
Goals focused on a shared product vision, cross-functional team collaboration, and dependencies constitute team goals.
Examples:
| Create and maintain a single, comprehensive product documentation for all the teams on ClickUp. |
| Scrum goals like daily stand-ups, weekly connect, and sprint plans keep teams aligned. |
Customer goals include KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) around customer attraction, experience, retention, and satisfaction. For example, the following image shows how HubSpot has aligned its mission with fulfilling customers’ needs.

Examples:
| Increase monthly website visitors to 100,000 by next quarter |
| Improve the customer retention rate by 25% by next year |
SaaS companies’ product management involves creating products that solve real-time problems and improving them to enhance user experience. They consider the following factors while setting goals.
Once you’ve understood why you need product manager goals, you can set them using product goals frameworks.
Objectives and key results (OKR) and SMART are popular frameworks for effectively setting product goals.
SMART is a structured and process-oriented framework for setting goals. SMART goals refer to the five traits of goals: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Set SMART goals across teams and departments using ClickUp’s SMART Goals Template.
You should define precise and narrow goals over broad, generic, and vague goals.
Example: Increase LinkedIn followers for ABC Company by posting daily and sending a weekly newsletter.
Defining measurable metrics makes it easier to track the progress and success rate of goals.
Example: Increase LinkedIn followers for ABC Company by 10,000 by posting daily and sending a weekly newsletter.
Set realistic goals so as not to exhaust your resources.
In the above example, if a weekly newsletter results in an unsustainable workload for a small team, you can scale it down to a bi-weekly newsletter.
Example: Increase LinkedIn followers for ABC Company by 10,000 by posting daily and sending a bi-weekly newsletter.
Goals should align with the business objectives and customer expectations.
If you own a social media marketing agency, having brand owners and promotion companies in your followers list helps. So include this in your goal.
Example: Increase LinkedIn followers for ABC Company by 10,000 by posting daily and sending a bi-weekly newsletter. Make sure the content we post targets social media influencers and brands.
Timelines for each milestone help in the timely delivery of the project.
Example: Increase ABC Company’s LinkedIn followers by 10,000 within Q2 of 2024. To achieve this, we post daily and send a bi-weekly newsletter. We also ensure the content reaches social media influencers and brands.
Companies use the OKR framework to set challenging and ambitious goals with measurable targets.
Different teams within your company may have different goals, resulting in varying definitions of success. However, using the OKR framework helps align these goals with the company-wide objectives and the organization’s mission.
What do we mean by OKR?
Objective: An objective is the aim or end result of a project or task. It defines exactly what you want to achieve. For example, improving customer satisfaction can be the objective of a customer success team.
Key Results: These are the metrics to measure the progress and success of the goal.
Key metrics to improve customer satisfaction in the above example would be NPS (Net promoter Score), customer retention percentage, and conversion percentage.
The tech giant Google pioneered the concept of OKRs. Today, it has been adopted by companies like Microsoft, Amazon, Adobe, Netflix, Spotify, Twitter, Unilever, and The Walt Disney Company, to name a few.
The framework promotes seamless collaboration, transparency, and agility within the organization. It ensures your business focuses on what matters the most.
Product management is vital in developing technology products.
As a product manager (PM) on a cloud project, you don’t need to be tech-savvy, but you should have a basic knowledge of cloud platforms, APIs and servers, and other core PM skills.
Your job is to simplify the complex tech architecture so stakeholders can understand its value.
Similarly, the product manager’s role in app development is crucial to ensure the app has responsive, easy-to-use, and fully functioning features.
Whether you’re working on an app or cloud computing, the product management process stays similar from planning to launch. It’s just about adjusting the requirements to fit the specific tech and user needs.
Performance indicators keep track of the product team’s progress and help product managers make decisions, especially when you’re developing tech products.
We’re sure many of you will consider buying if your friends or family recommend a product more than an advertisement by an unknown brand. Satisfied customers will likely promote your product in their circle.
That’s why customer satisfaction and customer loyalty are essential to many products’ success.
It’s important to know how happy your customers are with your product. The Net Promoter Score(NPS) is a metric for measuring this.
To measure NPS:
A high NPS score indicates that your customers are overall satisfied. You can analyze feedback at a more granular level to discover opportunities for improvement.
On the other hand, if your product gets a low score, you should know what it lacks—track user interactions or ask them directly to find where it falls short.
Overall, this NPS score illuminates both happy customer opinions and dissatisfaction points. Product managers shoulder this entire process of analyzing NPS and taking necessary actions.
Some goals have a short time span, while others take longer. Long-term goals focus on big ideas and longer visions, while short-term goals prioritize tasks to be completed in the near future.
Long-term goals clarify what you want to achieve in the next five or ten years. They provide you with purpose and a path. You can reach them by breaking them into smaller milestones with closer deadlines.
If long-term goals are the destination, short-term goals form the journey toward it.
Here are the key differences between them.
| Feature | Short-term goals | Long-term goals |
| Focus | Immediate results & milestones | Future direction & vision |
| Timeframe | Weeks, months (up to a year) | Years (2-5 or more) |
| Examples | * Increase user engagement by 15% in Q3* Launch a new feature by the end of the month * Improve app performance by 20% | * Become the market leader in the fitness tracker category by 2027 * Develop a new product line targeting a broader customer base * Achieve a user base of 1 million by 2025 |
| Metrics | * User growth, retention, engagement * Conversion rates, sales figures * Bug fixes, performance improvements | * Market share, brand awareness * Customer satisfaction, loyalty * Product innovation, technology advancements |
| Impact | Drives immediate growth & iteration | Shapes overall product direction & success |
| Development | More concrete, measurable, actionable | Broader, aspirational, strategic |
| Flexibility | Can be adjusted based on short-term results | Less flexible, requires long-term commitment |
Product managers set short-term goals to achieve their long-term vision. They also set daily, weekly, and quarterly targets to accomplish short-term goals.
Daily targets are highly practical. With clear to-dos by the end of the day, your brain always strives to reach that finish line.
Weekly goals are long enough to make considerable progress toward your short-term goals. They motivate you to stick to the plan.
Quarterly goals are the checkpoints for your annual goals. If something is missed in a quarter, it signals the need to adjust the plan. This way, you won’t miss out on anything on the final day.
Adding new features, integrating additional tools, designing a product theme, and collecting customer opinions come under short-term goals.
Long-term goals reflect the overarching vision of a company. They cover broad aspirations such as improving ROI and scaling business operations.
For example, including a UI component by next month is a short-term business goal, while improving the overall customer satisfaction by 30% in the next two years can be a long-term goal.
If you have clear long-term goals, you would estimate the resources and budget required and manage them efficiently.
Brand-building strategies can also be included in long-term goals. Investing in these strategies will yield a rewarding long-term return on investment.
You can include all important business metrics into a KPI dashboard and track them to continuously monitor progress towards achieving the long-term goal.
Ultimately, long-term goals impact broader aspects of a company, such as expansion, customer satisfaction, employee retention, brand reputation, and more.
You can consider the below tips to set the right product manager goals.
Before finalizing your goals, check if they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Following the SMART system helps you prioritize tasks and work with clear intentions, leading to well-defined goals.
Once you have set the perfect goals, you will likely be 376% more successful.
Set up different types of goals: personal, team, and project goals.
Categorizing goals like this gives your team a clear product roadmap for outlining their tasks and priorities.
KPI stands for key performance indicators.
KPIs ensure that you are on the right path towards achieving the goal.
You can set up KPIs for customer satisfaction, product quality, user engagement, and others to measure how well that particular division performs.
For example, if your KPI is customer satisfaction, collect customer feedback and analyze metrics such as NPS score, customer satisfaction score (CSAT), and others. Then, compare the scores with the goal you’ve set at the beginning.
This way, you can measure your goal’s success rate.
Tip: Check out these product management KPIs to know more about success-measuring metrics.
Many product managers leverage agile methodologies to achieve their goals. Agile is a flexible project management approach that breaks down large projects into smaller, more manageable pieces. These pieces are then tackled in short development cycles, often lasting two weeks.

Scrum is a popular Agile framework that uses these cycles, called sprints, to deliver working product features collaboratively and iteratively.
By adopting Agile principles, product managers can ensure their goals are achievable within set timeframes and adaptable to changing priorities.
Any agile method follows these five key steps:
Planning | Teams collaborate and set product goals, with the purpose of creating a plan that satisfies stakeholders and customers |
| Development | This is the execution step where teams design and develop promised features of the product |
Testing | In this step, testers collaborate with developers to create test cases and run them to evaluate how the product performs in production |
| Deployment | The product gets deployed for real-time users to start using it |
| Maintenance | The team continuously monitors the product to identify improvement opportunities or reduce product downtime |
Agile practices are highly flexible and adaptable to change, even at the last minute. Check out these agile principles to know more.
Considering user feedback while setting goals helps prevent deviations from customer expectations in the end product. User feedback generally represents the target audience’s voice, so if you can address their pain points, your product’s success is likely.
Moreover, user reviews help identify opportunities for product improvements. And this continuous improvement keeps you competitive in the industry.
Additionally, considering customer opinions makes them feel valued, building long-term trust and loyalty toward your brand.
Crafting clear and achievable goals is essential for product managers. However, navigating different goal-setting frameworks and translating them into actionable plans can be time-consuming. This is where ClickUp comes in.
ClickUp’s product management platform offers a suite of pre-built goal-setting templates and features, designed to streamline the process and ensure your team and product goals are aligned.
These structured templates come pre-formatted in popular frameworks, such as SMART goals, OKR (Objectives and Key Results), and Balanced Scorecard (BSC).
Simply using a template and filling in its fields ensures you follow a specific goal-setting framework. Further, customizing the template metrics and fields tailors it to your business needs.
Take the ClickUp OKR Framework Template, for instance. It lets you:
The ClickUp Goals feature allows you to set and track various goals in one place. Calendars with clear timelines, reminders based on progress, and performance dashboards help you achieve product success faster.
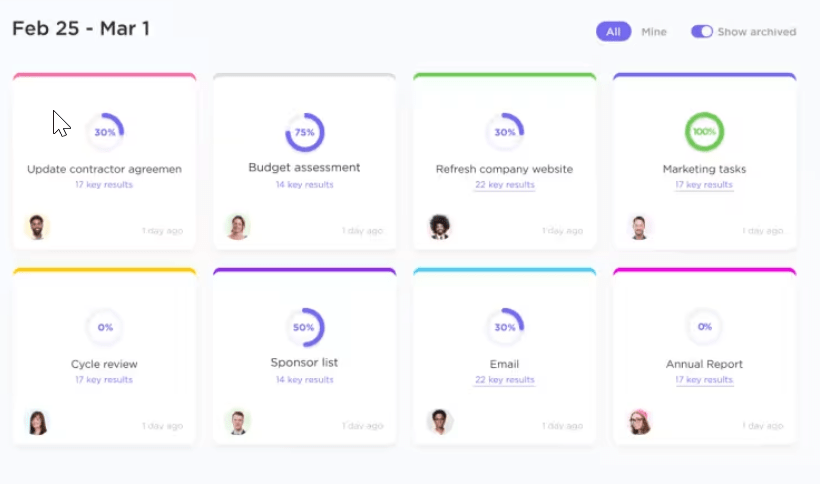
Let’s say your goal is to get 10,000 customers by the end of next quarter. Here is how you can use ClickUp for this.
Goal setting, task assignment, progress tracking, proper access controls, and setting reminders are all streamlined with the ClickUp product management platform.
Setting the right goals is vital for your teams to be on the same page and work for the same vision. They help your business deliver quality products and features within the given timeframe.
A product manager understands the product opportunities, customer demands, and stakeholders’ requirements and sets clear and relevant goals to meet them. They use goal-tracking apps like ClickUp to do this.
Product management templates, like ClickUp’s built-in product strategy templates, make your job easier and motivate your team members by providing timely reminders of their progress.
With goal-setting, tracking, and performance analysis tools, ClickUp will help you develop and ship a perfect product while paving the way for personal and professional growth. Try ClickUp today!
An example of a SMART product goal is to invest 20% of the product profits into monthly ad campaigns to increase customer reach by 50% within the next quarter.
An example of an effective SMART goal is discovering potential cost-saving opportunities in shipping to reduce supply chain expenses by 5%.
The goal of a product management team is to identify opportunities, define strategy, create a roadmap, and track the team’s progress to ensure the timely delivery of a quality product.
© 2026 ClickUp