What Are LLM Agents in AI and How Do They Work?
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Have you ever wondered how technology keeps getting smarter, faster, and more personalized?
Meet the driving force behind this evolution: LLM Agents. These advanced systems, powered by large language models (LLMs), are changing the way industries work and expanding what AI can do.
LLM agents are built to meet the growing need for smarter, more flexible solutions in today’s tech-driven world.
🌎 Fact Check: Studies show that the LLM Market is set to grow to $260M by 2030, thanks to their ability to not only understand commands but also learn, adapt, and handle complex tasks with little input.
Let’s take a closer look at how LLM agents work, their real-world uses, and some popular tools that use LLMs.
LLM agents are advanced AI systems that leverage large language models to understand and generate human language.
Unlike traditional AI systems, LLM agents are designed to perform complex tasks that require sequential reasoning, planning, and memory. They can think ahead, remember past conversations, and use different tools to adjust their responses based on the situation and style needed.
This makes them particularly useful for solving complex problems that demand a high level of cognitive processing and adaptability.
By integrating these capabilities, LLM agents can handle intricate workflows, provide personalized assistance, and continuously improve their performance through learning and adaptation.
ClickUp Brain is a good example. You can ask the tool (using conversational language) to create content, summarize content, answer questions, and perform tasks within your workflow. Because it resides within your ClickUp Workspace and can perform actions within it, it serves as the perfect AI assistant for work.
AI agents are designed for specific tasks and objectives. Here are the main types:
LLM agents function by combining advanced natural language processing, real-time data analysis, and memory mechanisms. The agent’s internal logs are crucial in recording previous thoughts, actions, and user interactions, enhancing the agent’s capabilities in long-range reasoning and contextual awareness.
When a user interacts with the agent, it processes input using its core model, retrieves relevant information from its memory, and executes tasks via integrated tools or APIs. This interconnected process allows the agent to adapt its responses and actions to specific user needs, making it versatile and efficient.
Additionally, the use of external tools enhances the functionality of LLM agents, particularly in automation workflows and dialog management.
For instance, ClickUp Brain leverages LLM technology to analyze workflows, propose optimized strategies, and deliver personalized suggestions. By understanding context and learning from user behavior, it acts like a proactive project manager, improving productivity and streamlining processes.
📽️ Bonus Watch: Curious about how LLMs can help you manage projects? Watch the video below:
LLM agents are adept at handling a wide range of tasks, including:

By tackling such diverse tasks, LLM agents frees up users and organizations to get creative, innovate. and adapt in a rapidly changing environment
So what exactly happens under the hood?
A lot! LLM agents are built with carefully designed components that work together to process information, make decisions, and execute tasks effectively.
An LLM agent is composed of:
Each component contributes to the agent’s ability to handle complex tasks dynamically by working together seamlessly and interdependently.
For instance, the agent core’s decision-making depends on the working memory for retaining critical information, while planning modules use this input to strategize effectively. This interconnectedness ensures smooth operation and adaptability in diverse scenarios.
The core acts as the brain of the LLM agent, powered by models like GPT-4 or BERT. It interprets input, understands context, and directs other components to perform tasks.
For example, in a project management tool, the core processes user commands to assign tasks or prioritize workflows seamlessly.
Working memory temporarily holds and processes information during interactions, allowing for a smooth user experience.
This memory structure ensures the agent adapts and improves with use.
LLM agents excel at analyzing tasks, breaking them into steps, and finding solutions. They:
For instance, they can prioritize deadlines or flag issues in project management workflows.
Modules enhance the agent’s abilities and connectivity.
For example, API integrations allow an agent to pull data, analyze patterns, and offer actionable insights.
The advancements in LLM agents have spurred the development of innovative tools and platforms. These solutions integrate cutting-edge AI capabilities to enhance productivity, streamline workflows, and enable smarter decision-making. Here are some of the top tools leveraging LLM agents:
OpenAI’s GPT models, including the powerful GPT-4 Turbo, are widely recognized for their advanced natural language capabilities.
From drafting compelling content and powering chatbots to solving complex problems, these models offer versatility and precision. Businesses can fine-tune them for domain-specific tasks, making them indispensable for tailored applications like legal document analysis or e-commerce recommendations.
Google Bard brings robust AI assistance directly into Google’s ecosystem. It stands out for its ability to generate accurate content, simplify query responses, and optimize workflows. Whether you’re drafting an email, refining a presentation, or planning schedules, Bard seamlessly integrates with tools like Gmail and Google Workspace to ensure smooth operations and time savings.
ClickUp leverages LLM-powered capabilities to elevate productivity. With features such as AI-assisted task creation, workflow automation, and predictive deadline management, teams can handle projects more efficiently. It also enables contextual learning from user inputs, ensuring personalized suggestions and adaptive improvements over time. ClickUp empowers teams to stay organized and achieve their goals with ease.
Read More: Discover How to Use AI to Automate Tasks. Or, if you’d like to see it action, check out this video:
💡 Pro Tip: ClickUp offers features like Goals for tracking progress, Dashboards for visualizing data, and Docs for collaborative document creation, all powered by a core of AI. Together, this is what makes us the everything app for work! Sign up for free and give ClickUp a spin!
Hugging Face provides an open-source treasure trove of pre-trained models and APIs for developers. Whether you need sentiment analysis, language translation, or summarization, their library has you covered. The platform also offers user-friendly tools for training and deploying custom models, making it a go-to resource for AI enthusiasts and professionals aiming to build tailored solutions.
Anthropic’s Claude is designed with safety and ethical AI interactions at its core. It produces human-like responses while minimizing the risks of generating harmful content. Claude is particularly suited for industries like finance, healthcare, and education, where trust and accuracy are paramount. Its commitment to ethical considerations makes it a preferred choice for businesses prioritizing AI responsibility.
From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to customer service chatbots and content generation tools, LLM agents are everywhere. Companies in retail, healthcare, education, and finance use them to enhance user experiences, automate processes, and deliver personalized services.
🎯 For example, a retail company might use an LLM agent to analyze customer purchase history and recommend products, while a healthcare provider could streamline appointment scheduling and follow-up reminders with the help of such technology.
Whether it’s analyzing vast datasets or offering tailored suggestions, LLM agents provide the intelligence needed to help companies stay competitive.
One of the standout features of LLM agents is their ability to understand and generate human-like text. They can draft emails, create content, translate languages, and summarize large volumes of information.

Businesses in customer support, education, and marketing leverage these capabilities to save time and improve communication. For example, an LLM agent can automate email responses or generate content ideas tailored to specific audiences.

LLM agents analyze customer feedback, social media posts, or reviews to gauge sentiment and emotion. This helps businesses understand public opinion, monitor brand health, and adjust strategies accordingly.
🎯 For example, Amazon uses LLM technology to analyze customer reviews and identify trending sentiments about new product launches, enabling them to refine marketing strategies.
Additionally, they power recommender systems by suggesting products, services, or content based on user preferences—whether it’s a streaming platform curating your next movie or an online store recommending a product.
These agents act as intelligent assistants that deliver precise answers and detailed insights in real time. In healthcare, they can support medical professionals by analyzing symptoms and suggesting treatment options.
In project management, tools like ClickUp Brain can provide real time insights and updates on ongoing projects. Their ability to serve as expert systems makes them indispensable in industries requiring accurate and instant information.
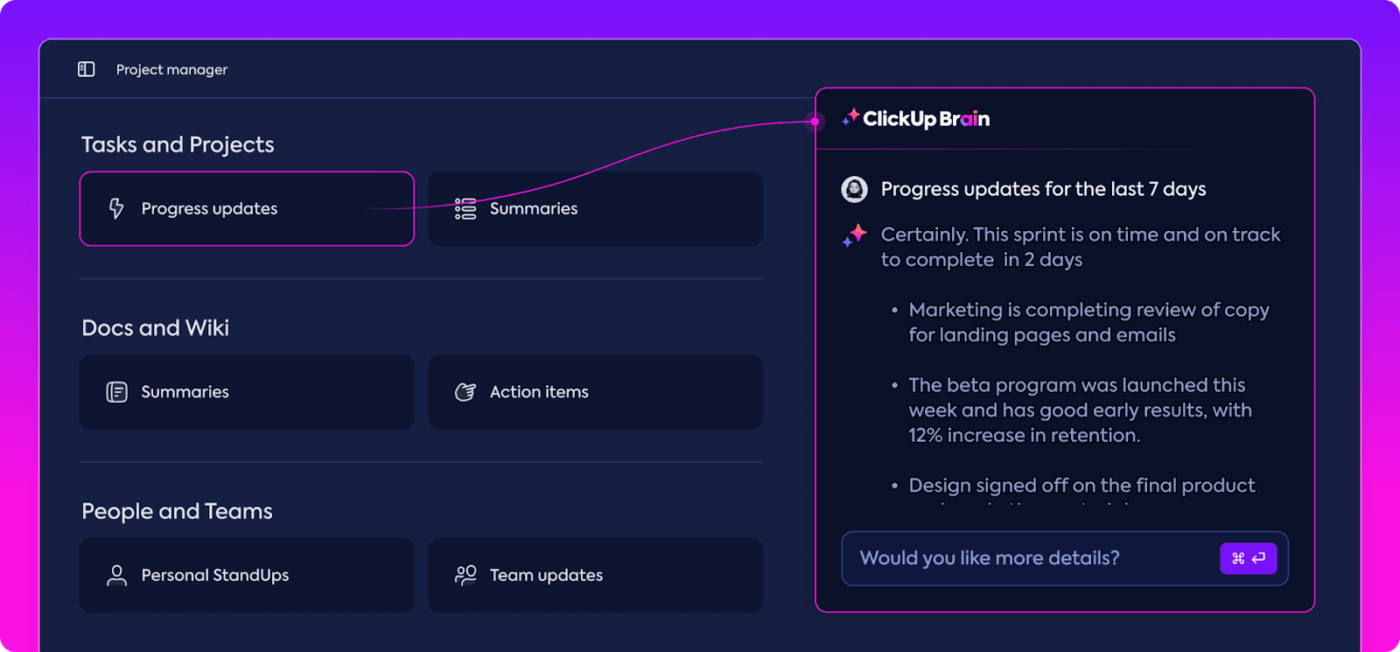
By integrating with tools like ClickUp, LLM agents streamline operations and improve productivity. ClickUp’s Connected Search, powered by natural language processing, allows you to locate tasks, projects, or documents using simple conversational queries, eliminating manual searches and ensuring smoother workflows.

Additionally, ClickUp’s AI tools automate repetitive tasks, freeing up time for strategic decision-making.
While ClickUp Brain is built into the ClickUp platform to enhance project management and collaboration, Brain MAX takes things further as a standalone desktop app. It extends AI-powered search, automation, and productivity tools beyond ClickUp—letting you instantly search across ClickUp, Google Drive, Figma, GitHub, and the web, all from one unified workspace.
Whether you’re summarizing meetings, finding files, or automating repetitive work, Brain MAX keeps everything at your fingertips.
While LLM agents offer incredible potential, their implementation comes with challenges that you need to address to ensure optimal performance and usability.
Adopting LLM agents isn’t always smooth. Users might find these systems too complex to interact with or have unrealistic expectations about their capabilities.
This can lead to frustration or a lack of trust. Proper training, intuitive interfaces, and managing expectations are crucial to overcoming these hurdles and making the technology approachable for everyone.
LLM agents, while powerful, often struggle with memory limitations. They may lose context during long conversations or forget previously shared information.
This can lead to incomplete answers or the need for users to repeat information. Developers are addressing these limitations with enhanced memory algorithms and better storage techniques, but the challenge remains a work in progress.
Although LLM agents excel at generating responses, they may struggle with complex planning or solving intricate problems. Their decision-making capabilities can be limited, especially when tasks require deep reasoning or creativity.
💡 Pro Tip: Combining LLM agents with specialized tools, frameworks, or even human oversight can help bridge these gaps and improve their effectiveness.
Despite these challenges, ongoing advancements in AI research are steadily improving the usability, memory, and problem-solving capabilities of LLM agents, bringing them closer to their full potential.
🎯 For instance, OpenAI’s recent release of fine-tuning capabilities for GPT-4 Turbo has enabled more efficient and tailored responses, addressing specific user needs and enhancing memory retention over extended interactions.
By following these steps, you can build and deploy LLM agents that are tailored to your specific needs, enhancing productivity and efficiency in your organization.
The future of LLM agents is incredibly promising, driven by advancements in AI technology and an ever-growing demand for intelligent automation. Here’s a glimpse into what lies ahead.
LLM agents are evolving rapidly, with new trends reshaping their potential. One key trend is the development of multi-modal agents—tools that can process and generate not just text but also images, audio, and video, offering richer and more dynamic interactions.
🎯 For example, OpenAI’s DALL-E is a multi-modal tool that generates images from text descriptions, showcasing the potential of such technology.
Another significant shift is the focus on personalized AI agents that adapt to individual user preferences and needs, making them more effective and relatable in various industries, from customer support to healthcare.
🎯 For instance, IBM watsonx Assistant is a tool for building customised AI assistants and chatbots.
Generative AI, the foundation of LLM agents, continues to advance at an impressive pace. Future models are likely to feature:
LLM agents are changing how we use technology, making it easier to communicate, solve problems, and get work done. As AI keeps growing, it’s exciting to think about what’s next. One things for certain, these tools will keep transforming how we work and live, raising the bar with each new iteration and advancement.
By staying curious and trying new things, we can make the most of what AI has to offer. With tools like ClickUp Brain, teams can work smarter, streamline workflows, and boost productivity, all within the te same platform where they chat, work, and store information. Intrigued about how AI can change your work? Sign up for ClickUp today!
© 2026 ClickUp