How to Use Hugging Face for AI Deployment
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Most AI deployment projects fail not because teams picked the wrong model, but because nobody can remember three months later why they chose it or how to replicate the setup, with 46% of AI projects scrapped between proof-of-concept and broad adoption.
This guide walks you through using Hugging Face for AI deployment—from selecting and testing models to managing the deployment process—so your team can ship faster without losing critical decisions in Slack threads and scattered spreadsheets.
Hugging Face is an open-source platform and community hub that provides pre-trained AI models, datasets, and tools for building and deploying machine learning applications.
Think of it as a massive digital library where you can find ready-to-use AI models instead of spending months and significant resources building them from scratch.
It’s designed for machine learning engineers and data scientists, but its tools are increasingly used by cross-functional product, design, and engineering teams to integrate AI into their workflows.
Did You Know: 63% of organizations lack proper data-management practices for AI. This often leads to stalled projects and wasted resources.
The core challenge for many teams is the sheer complexity of deploying AI. The process involves selecting the right model from thousands of options, managing the underlying infrastructure, versioning experiments, and ensuring technical and non-technical stakeholders are aligned.
Hugging Face simplifies this by providing its Model Hub, a central repository with over 2 million models. The platform’s transformers library is the key that unlocks these models, allowing you to load and use them with just a few lines of Python code.
However, even with these powerful tools, AI deployment remains a project management challenge, requiring careful tracking of model selection, testing, and rollout to ensure success.
📮ClickUp Insight: 92% of knowledge workers risk losing important decisions scattered across chat, email, and spreadsheets. Without a unified system for capturing and tracking decisions, critical business insights get lost in the digital noise.
With ClickUp’s Task Management capabilities, you never have to worry about this. Create tasks from chat, task comments, docs, and emails with a single click!
Navigating the Hugging Face Hub can feel overwhelming when you’re first starting. With hundreds of thousands of models, the key is to understand the main categories to find the right fit for your project. The models range from small, efficient options designed for a single purpose to massive, general-purpose models that can handle complex reasoning.
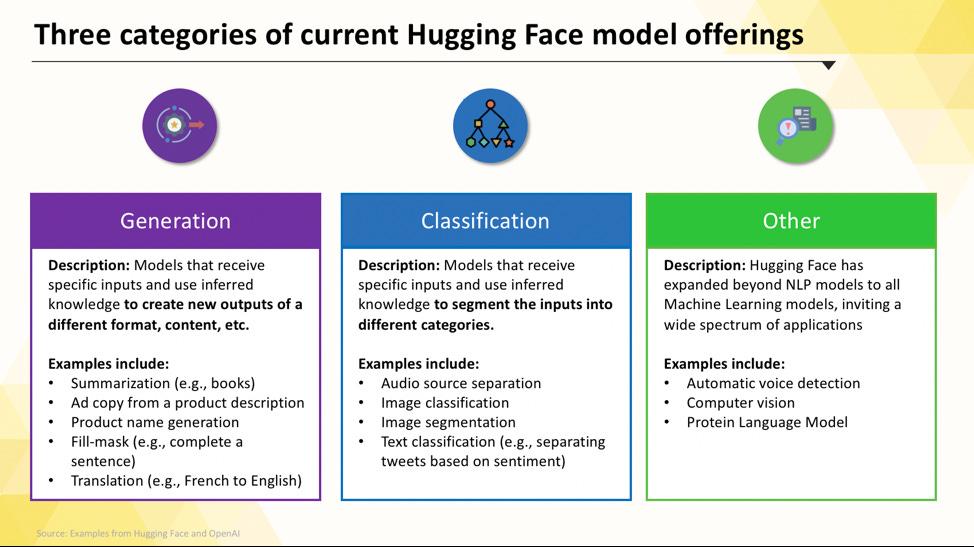
When your team needs to solve a single, well-defined problem, you often don’t need a massive, general-purpose model. The time and cost to run such a model can be prohibitive, especially when a smaller, more focused AI tool would work better. This is where task-specific models come in.
These are models that’ve been trained and optimized for one particular function. Because they’re specialized, they’re typically smaller, faster, and more resource-efficient than their larger counterparts.
This makes them ideal for production environments where speed and cost are important factors. Many can even run on standard CPU hardware, making them accessible without expensive GPUs.
Common types of task-specific models include:
📚 Also Read: How to Use Hugging Face for Text Summarization
Sometimes, your project requires more than just simple classification or summarization. You might need an AI that can generate creative marketing copy, write code, or answer complex user questions in a conversational way. For these scenarios, you’ll likely turn to a Large Language Model (LLM).
LLMs are models with billions of parameters trained on vast amounts of text and data from the internet. This extensive training allows them to understand nuance, context, and complex reasoning. Popular open-source LLMs available on Hugging Face include models from the Llama, Mistral, and Falcon families.
The trade-off for this power is the significant compute resources they require. Deploying these models almost always necessitates powerful GPUs with a lot of memory (VRAM).
To make them more accessible, you can use techniques like quantization, which reduces the model’s size at a small cost in performance, allowing it to run on less powerful hardware.
📚 Also Read: What Are LLM Agents in AI and How Do They Work?
Your data isn’t always just text. Your team might need to generate images for a marketing campaign, transcribe audio from a meeting, or understand the content of a video. This is where multimodal models, which are designed to work across different types of data, become essential.
The most popular type of multimodal model is the text-to-image model, which generates images from a text description. Models like Stable Diffusion use a technique called diffusion to create stunning visuals from simple prompts. But the possibilities extend far beyond image generation.
Other common multimodal models you can deploy from Hugging Face include:
Like LLMs, these models are computationally intensive and typically require a GPU to run efficiently.
📚 Also Read: 50+ AI Image Prompts to Create Stunning Visuals
To see how these different types of AI models translate into practical business applications, watch this overview of real-world AI use cases across various industries and functions.
What’s your organization’s AI Maturity?
Our survey of 316 professionals reveals that true AI Transformation requires more than just adopting AI features. Take the AI maturity assessment to see where your organization stands, and what you can do to improve your score.
Before you can deploy your first model, you need to get your local environment and Hugging Face account set up correctly. It’s a common frustration for teams when different members have inconsistent setups, leading to the classic “it works on my machine” problem. Taking a few minutes to standardize this process saves hours of troubleshooting later.
transformers and huggingface_hub. You can install them using pip: pip install transformers huggingface_hubhuggingface-cli login and pasting your token when prompted, or you can set it as an environment variable in your system. The command-line login is often the easiest way to get startedpipeline function from the transformers library. If it runs without errors, you’re ready to goKeep in mind that some models on the Hub are “gated,” meaning you must agree to their license terms on the model’s page before you can access them with your token.
Also, remember that tracking who has which credentials and what environment configurations are being used is a project management task in itself, and it becomes more critical as your team grows.
🌟 If you’re integrating Hugging Face models into broader software systems, ClickUp’s Software Integration Template helps visualize workflows and track multi-step technical integrations.
The template provides you with an easy-to-follow system where you can:
Once you’ve tested a model locally, the next question is: where will it live? Deploying a model into a production environment where it can be used by others is a critical step, but the options can be confusing. Choosing the wrong path can lead to slow performance, high costs, or an inability to handle user traffic.
Your choice will depend on your specific needs, such as expected traffic, budget, and whether you’re building a quick prototype or a scalable, production-ready application.
If you need to quickly create a demo or an internal tool, Hugging Face Spaces is often the best choice. Spaces is a free platform for hosting machine learning applications, and it’s perfect for building prototypes that you can share with your team or stakeholders.
You can build your app’s user interface using popular frameworks like Gradio or Streamlit, which makes it easy to create interactive demos with just a few lines of Python.
Creating a Space is as simple as selecting your preferred SDK, connecting a Git repository with your code, and choosing your hardware. While Spaces offers a free CPU tier for basic apps, you can upgrade to paid GPU hardware for more demanding models.
Keep in mind the limitations:
When you need to integrate a model into an existing application, you’ll likely want to use an API. The Hugging Face Inference API allows you to run models without having to manage any of the underlying infrastructure yourself. You simply send an HTTP request with your data and get a prediction back.
This approach is ideal when you don’t want to deal with servers, scaling, or maintenance. Hugging Face offers two main tiers for this service:
Using the API involves sending a JSON payload to the model’s endpoint URL with your authentication token in the request header.
For teams that already have a significant presence on a major cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure, deploying there can be the most logical choice. This approach gives you the most control and allows you to integrate the model with your existing cloud services and security protocols.
The general workflow involves “containerizing” your model and its dependencies using Docker, and then deploying that container to a cloud compute service. Each cloud provider has services and integrations that simplify this process:
While this method requires more setup and DevOps expertise, it’s often the best option for large-scale, enterprise-grade deployments where you need full control over the environment.
When using Hugging Face for AI deployment, “running inference” is the process of using your trained model to make predictions on new, unseen data. It’s the moment your model does the work you deployed it for. Getting this step right is crucial for building a responsive and efficient application.
The biggest frustration for teams is writing inference code that is slow or inefficient, which can lead to a poor user experience and high operational costs. Fortunately, the transformers library offers several ways to run inference, each with its own trade-offs between simplicity and control.
pipeline() function abstracts away most of the complexity, handling the data preprocessing, model forwarding, and post-processing for you. For many standard tasks like sentiment analysis, you can get a prediction with just one line of codeAutoModel and AutoTokenizer classes directly. This allows you to manually handle how your text is tokenized and how the model’s raw output is converted into a human-readable prediction. This approach is useful when you’re working with a custom task or need to implement specific pre- or post-processing logicMonitoring the performance of your inference code is a key part of the deployment lifecycle. Tracking metrics like latency (how long a prediction takes) and throughput (how many predictions you can make per second) requires coordination and clear documentation, especially as different team members experiment with new model versions.
📚 Also Read: Best AI Team Collaboration Tools to Use
Let’s walk through a complete example of deploying a simple sentiment analysis model. Following these steps will take you from choosing a model to having a live, testable endpoint.
distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english. Read its model card to understand its performance and how to use ittransformers and torch. Run pip install transformers torchpipeline and test it with a sample sentence. For example: classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis", model="distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english") followed by classifier("ClickUp is the best productivity platform!")app.py file that loads your model and defines a simple Gradio interface to interact with itAfter these steps, you have a live model. The next phase of the project would involve monitoring its usage, planning for updates, and potentially scaling the infrastructure if it becomes popular.
For teams managing complex AI deployment projects with multiple phases—from data preparation to production deployment—the Software Project Management Advanced Template by ClickUp provides a comprehensive structure.
This template helps teams:
Even with a clear plan, you’re likely to hit a few roadblocks during deployment. Staring at a cryptic error message can be incredibly frustrating and can halt your team’s progress. Here are some of the most common challenges and how to fix them. 🛠️
🚨Problem: “Model requires authentication”
🚨Problem: “CUDA out of memory”
🚨Problem: “trust_remote_code error”
trust_remote_code=True when you load the model. However, you should always review the source code first to ensure it’s safe🚨Problem: “Tokenizer mismatch”
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("model-name")🚨Problem: “Rate limit exceeded”
Tracking which solutions work for which problems is crucial. Without a central place to document these findings, teams often end up solving the same issue over and over again.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 1 in 4 employees uses four or more tools just to build context at work. A key detail might be buried in an email, expanded in a Slack thread, and documented in a separate tool, forcing teams to waste time hunting for information instead of getting work done.
ClickUp converges your entire workflow into one unified platform. With features like ClickUp Email Project Management, ClickUp Chat, ClickUp Docs, and ClickUp Brain, everything stays connected, synced, and instantly accessible. Say goodbye to “work about work” and reclaim your productive time.
💫 Real Results: Teams are able to reclaim 5+ hours every week using ClickUp—that’s over 250 hours annually per person—by eliminating outdated knowledge management processes. Imagine what your team could create with an extra week of productivity every quarter!
Using Hugging Face for AI deployment makes it easier to package, host, and serve models—but it doesn’t eliminate the coordination overhead of real-world deployment. Teams still need to track which models are being tested, align on configurations, document decisions, and keep everyone—from ML engineers to product and ops—on the same page.
When your engineering team is testing different models, your product team is defining requirements, and stakeholders are asking for updates, information gets scattered across Slack, email, spreadsheets, and various documents.
This work sprawl—the fragmentation of work activities across multiple, disconnected tools that don’t talk to each other—creates confusion and slows everyone down.
This is where ClickUp, the world’s first Converged AI Workspace, plays a key role by bringing project management, documentation, and team communication into a single workspace.
That convergence is especially valuable for AI deployment projects, where technical and non-technical stakeholders need shared visibility without living in five different tools.
Instead of scattering updates across tickets, docs, and chat threads, teams can manage the entire deployment lifecycle in one place.
Here’s how ClickUp can support your AI deployment project:
Successful Hugging Face deployment depends on a solid technical foundation and clear, organized project management. While the technical challenges are solvable, it’s often the coordination and communication breakdowns that cause projects to fail.
By establishing a clear workflow in a single platform, your team can ship faster and avoid the frustration of context sprawl—when teams waste hours searching for information, switching between apps, and repeating updates across multiple platforms.
ClickUp, the everything app for work, brings your project management, documentation, and team communication into one place to give you a single source of truth for your entire AI deployment lifecycle.
Bring your AI deployment projects together and eliminate tool chaos. Get started for free with ClickUp today.
Yes, Hugging Face provides a generous free tier that includes access to the Model Hub, CPU-powered Spaces for demos, and a rate-limited Inference API for testing. For production needs requiring dedicated hardware or higher limits, paid plans are available.
Spaces is designed for hosting interactive applications with a visual front-end, making it ideal for demos and internal tools. The Inference API provides programmatic access to models, allowing you to integrate them into your applications via simple HTTP requests.
Absolutely. Through interactive demos hosted on Hugging Face Spaces, non-technical team members can experiment with and provide feedback on models without writing a single line of code.
The primary limitations of the free tier are rate limits on the Inference API, the use of shared CPU hardware for Spaces, which can be slow, and “cold starts” where inactive apps take a moment to wake up./
© 2026 ClickUp