AI Techniques: Mastering Machine Learning, Deep Learning & NLP

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Artificial intelligence (AI) is any machine with an ‘intelligence quotient’ that mimics human intelligence and capabilities, including creative thinking and problem-solving.
The term AI is said to have been coined by John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky, who, in a workshop at Dartmouth College in 1956, defined it as:
The construction of computer programs that engage in tasks that are currently more satisfactorily performed by human beings because they require high-level mental processes such as perceptual learning, memory organization, and critical reasoning
Today, artificial intelligence technology is immensely popular, with AI-powered software and hardware being used for various personal and professional uses. These include using AI companions (like Character AI) to develop an individual’s soft skills, AI pair programmers (like Github Copilot) to code faster, and AI systems to tackle global issues like climate change.
In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the top AI techniques—what they are and why they’re important.
Artificial intelligence techniques are the tools and methods used to build intelligent systems—the core formula that gives AI human-like intelligence qualities.
Here are some of the popular AI techniques:
You must have seen a lot of job descriptions with the tag ‘AI/ML’. This is because machine learning (ML) is a core part of the AI research team at most organizations.
With machine learning (ML), an AI engine is fed a large amount of data and given specific instructions to analyze the data and identify patterns. This helps create algorithms that predict behavioral patterns in humans.
The typical use cases for AI in machine learning algorithms are the product recommendations you see on online shopping platforms and social media algorithms that decide which posts rake in the most views and what posts would interest you most (based on your browsing habits).
Take, for instance, the curated content showcased on your Instagram Explore page—it differs for every Instagram account.
Supervised and unsupervised learning are both fundamental parts of machine learning (ML). The former trains AI algorithms using labeled data. For example, an email provider might train their spam filtering feature with data labeled spam and not spam.
On the other hand, unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled, unorganized data, and AI does the heavy lifting of classifying the data and finding patterns.
E-commerce stores use this to recommend products to consumers based on a variety of signals from their buying behavior, including the products viewed, time spent on product pages, clickstream data, previous purchases, purchase frequency, search queries, demographic data, and more.
A subfield of machine learning, this AI technique aims to imitate the neural networks of the human brain using the concept of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN).
Deep learning works in layers:
Social media companies like Meta use deep learning AI within reinforcement learning systems to identify triggering images by mining visual information in posts. By recognizing patterns associated with known triggering content (e.g., violence, and self-harm imagery), the AI can flag posts for further review by human moderators.
Another popular AI technique is natural language processing (NLP), a subfield of deep learning that focuses on languages. NLP helps AI engines understand human languages’ grammar, syntax, and the various semantics of a language’s linguistic structure to generate human language and make human-machine conversations more human and less robotic.
You can find NLP in AI applications like chatbots (ChatGPT), virtual assistants (Siri), and language translation services (Google Translate).
Text preprocessing is the foundation of many natural language processing (NLP) tasks. It involves cleaning, transforming, and structuring raw text data to prepare it for analysis by NLP algorithms.
Preprocessing helps remove unnecessary data, such as typos, and convert uppercase letters to lowercase. This helps NLP engines run their algorithms more efficiently and provide more accurate results.
A core field of natural language processing (NLP) AI technique, part-of-speech (POS) tagging focuses on labeling the grammatical function of each word within a sentence—noun, verb, adjective, and more—in human language.
As such, it works well with other AI techniques like speech recognition and sentiment analysis to figure out the emotional quotient of text.
A good use case for this AI technique is AI-powered spelling checkers like Grammarly.
Named entity recognition (NER) is another subset of NLP. Like NLP, which deals with languages, NER deals with names, locations, and other entities.
This makes it a powerful tool for information extraction. Think legal and investigative services—finding financial entities, identifying witnesses, or monitoring social activity for specific keywords.
Another professional use case for NER is customer service chatbots that can easily find relevant information about customer activity, such as their pricing plan and past conversations.
Sentiment analysis is a specialization in natural language processing (NLP) that focuses on understanding emotional patterns in communication. It tries to determine whether the text expresses positive, negative, or neutral sentiments.
This can be used to analyze text data such as social posts, customer reviews, online surveys, news articles, and more, making it beneficial for marketing teams. It can help them understand how people respond to their brand and perform market research.
This AI technique enables computers to interpret and understand the visual world. Media—via cameras or scanners—is fed to the computer, which then uses a combination of deep-learning neural networks and image processing capabilities to understand the image better.
This plays a key role in self-driving cars that can navigate roads (and detect objects) based on the images sent to the car’s AI engine via the cameras.
Here, traditional automation and robotics methods are supercharged with AI to make both fields more efficient. AI capabilities are integrated into robots and automation software to help them analyze data from sensors and their environment.
This allows robots to perceive objects and understand factors such as space, time, and problem-solving so they can easily adapt to real-world scenarios.
A simple example is the robotic vacuum cleaner. AI helps robot vacuums map your house and avoid obstacles like furniture, pet toys, or electrical cords.
The AI techniques discussed in this blog post can be used in various industries, from marketing to healthcare and even aerospace.
Like every new technology, AI also comes with its fair share of challenges. Here are some of the most important ones.
AI engines and algorithms are trained on publicly available data, which can lead to data privacy and copyright infringements. Moreover, many AI tools use customer data to train their algorithms, which can cause medical data leakage or sensitive company details.
AI image generators have also been known to copy (or be heavily inspired) by actual works of digital artists, leading to a widespread intellectual property infringement problem.
AI systems can perpetuate the biases present in the training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
When ChatGPT first became available to the public, there were reports that it reinforced existing gender stereotypes. When asked about doctors and nurses, it assumed the doctor to be a ‘he’ and the nurse to be a ‘she’. It even assumed the sentences had a typo rather than interpreting them with the possibility of a female doctor or male nurse.
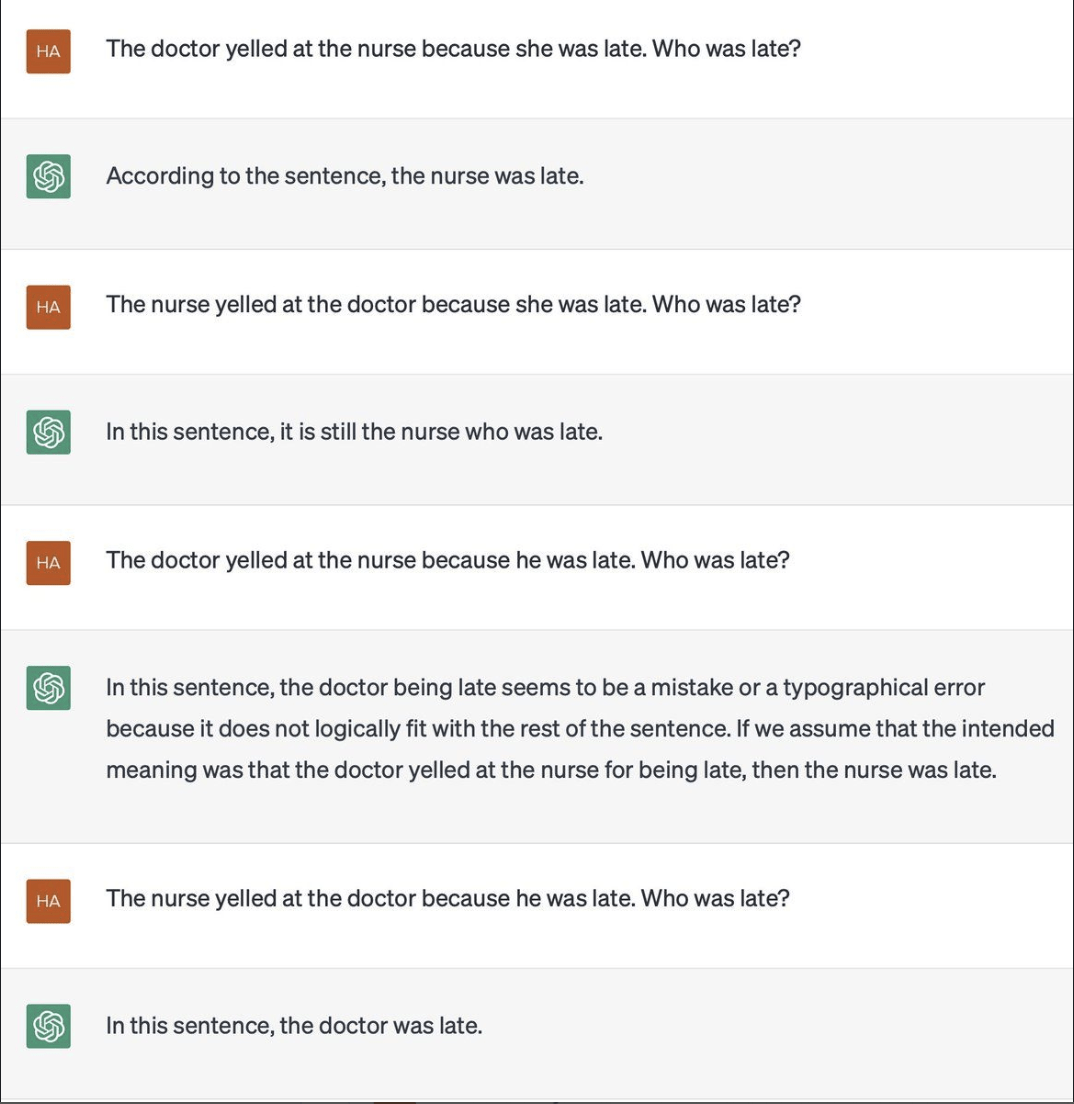
Sometimes, an explainable AI system (like ChatGPT or Anthropic Claude) generates factually incorrect or entirely fabricated outputs—basically, it ‘hallucinates’.
Sidebar: Explainable AI (XAI) is all about making artificial intelligence, especially machine learning, more transparent and understandable to humans. By understanding how an AI system arrives at its answers, we can identify and fix biases or errors in its reasoning.
There are different techniques for achieving XAI. Some focus on making the internal workings of the AI model more interpretable. Others focus on explaining individual decisions made by the model.
This can either be because the AI algorithm wasn’t trained on enough data or because it was trained on only one type of data, which makes it create solutions or results that match its dataset.

This is pretty common when people use AI for research. Ask it one question—maybe a source—and it creates an imaginary scenario—like the above example where a user asks ChatGPT about the sole survivor of The Titanic, and it fabricates an incident with a baker.
A core aspect of AI research, AI alignment is all about creating AI systems that benefit human beings. AI systems can have unforeseen consequences if their goals aren’t well-defined and aligned with the ‘common good’.
A simple example of this would be the way ChatGPT doesn’t respond to racial or discriminatory questions. So, it’s important to tie AI creations to goals that align with broader human welfare.
Explainable AI’s potential is undeniable. From coding lessons to car repair tutorials, it can be a powerful tool for learning and accomplishing tasks. However, the same capabilities can be misused, spreading misinformation or even providing instructions for destructive purposes.
But what happens when AI makes a mistake? Who’s accountable if an AI solution leads to negative consequences?
To prevent such consequences, it’s important to establish transparent processes and clear lines of accountability. We’ve already started making some headway here.
The US government, for example, has mandated AI companies to share all new discoveries with the federal government, along with associated safety test results and findings.
It’s only in recent years, the 2020s in particular, that AI has made large strides. Some of the common trends that we’re seeing in AI fields are:
Predictive analytics
AI algorithms can analyze data to predict future events or outcomes. This has applications in finance (cash flow projections) and retail (demand forecasting), among other fields.
Tools like Cash Flow Frog, for example, can analyze your revenue in real time and give you an estimate of future profits.
Pattern recognition
This is used in image recognition (self-driving cars), anomaly detection (fraud identification), and natural language processing (NLP).
Tesla, for example, uses AI to analyze patterns in traffic—using cameras, radars, and ultrasonic sensors to check out the car’s surroundings and respond to traffic.
Generative AI
Generative AI helps you create new data, such as images, text, or music, based on existing patterns—for example, creating realistic portraits of people who don’t exist.
Tools such as Midjourney and Dall-E can give you pretty cool illustrations based on text prompts.

Chatbots
Conversational AI programs imitate human conversation and can be used for customer service and learning. For example, companies can add chatbots to their websites and apps—so customers can get quick answers from the AI bot instead of waiting for a customer service rep.
Virtual assistants
AI-powered assistants such as Siri and Alexa can understand and respond to voice commands, helping with tasks like scheduling appointments or controlling smart home devices
Recommender Systems
AI algorithms suggest products, movies, and more based on a user’s past behavior and preferences.
For example, OTT platforms such as Netflix and Hulu use your viewing patterns—what genres you watch, how long you watch something, and so on—to suggest new films or shows.
One potential future of AI involves the emergence of superintelligence, where machines surpass human capabilities in many areas. Sounds like a sci-fi movie, right? But most AI research companies—including big tech ones like Google and Microsoft—are actively working toward this future.
Here are some common AI trends that might be possible in the future:
While singularity still feels far-fetched, many people worry about it. OpenAI’s Sam Altman has admitted to being scared of the potential ramifications of AI Singularity.
But all of these ‘futures’ are hypothetical and could take years. In the near future, you can see AI making the waves in healthcare, research, and the Internet of Things (IoT)—with AI-powered diagnostic centers, statistical analysis, and self-driving cars, to name a few.
Now, let’s explore some AI resources available for everyday use and how you can benefit from them.
A non-profit research company, OpenAI is dedicated to ensuring that artificial intelligence benefits all of humanity. Their long-term goal is to have ‘the benefits of, access to, and governance of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) to be widely and fairly shared.’
AGI is a type of AI that would possess ‘human-like’ cognitive abilities in problem-solving, creativity, and social interaction. While current AI models can help you analyze a report or find information quickly, OpenAI’s goal with AGI is to enable it to write novels or even understand human emotions.
While these use cases are still hypothetical, it’s going to be an interesting few years as we watch the space evolve. For now, they plan to build AI solutions that create a slow transition to the world of AGI. They believe this will allow policymakers and the public to understand and accept AI.
A recent development from this aim is their GenAI tools: ChatGPT (text generation) and DALL-E (image generation).

ChatGPT, in particular, has been well-received by AI enthusiasts, particularly for its natural language processing abilities. Quite a few chatbots and conversational AI features are built over the GPT engine.
DALL-E, on the other hand, has elicited mixed reactions from people (especially designers). They find the images vague and messy-looking.
Google’s DeepMind is an AI research program that focuses on artificial general intelligence (AGI) and includes AI techniques such as NLP and computer vision.
Some industries that Google DeepMind focuses on are biological intelligence, virtual assistants, and gaming. You can try Google Gemini to get a hands-on experience with Google DeepMind’s GenAI capabilities.
But one amazing AI development is AlphaFold, which can analyze protein structures. Though it’s still in the research stage, medical professionals have been well-received, believing it can help them diagnose diseases faster and more accurately.
Unlike OpenAI, Google’s focus is on creating ‘safe’ AI. This has led to the creation of the Frontier Safety Framework, which aims to analyze and mitigate potential risks associated with advanced AI.
Anthropic is an AI safety and research company that aims to train ‘helpful, honest, and harmless’ AI systems. Like Google Gemini and OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Anthropic also has a LLM mode—Claude.
Claude can generate different creative text formats, including poems, code, scripts, and emails.
Anthropic is also a great case study in the ethical use of AI. Recently, it made the news for copyright infringement—when music producers sued it for training Claude on their song lyrics. They claim Claude illegally replicates lyrics and are seeking millions in damages.
This case highlights the gray area in using AI for creative purposes, and the verdict here can set a precedent for AI-generated content in the future.
ClickUp, a workspace productivity app, comes with built-in GenAI features called ClickUp Brain.
A virtual assistant of sorts, ClickUp Brain is integrated with all the tools in the ClickUp suite to make everyday work (and life) smooth for users.
Here’s how ClickUp Brain can help professionals across roles and industries:
Tired of digging through document after document to find an important detail? With ClickUp Brain, you can easily find information from any wiki, report, or internal document in seconds.

Even better, you can ask it to generate quick summaries of documents or meeting transcripts so you can stay updated on the latest company or client details easily.
Another benefit of using ClickUp Brain is how it automates the grunt work associated with project management. For example, you can use ClickUp Brain to:

ClickUp also comes with a solid writing assistant that can be especially useful for marketers and people who are not comfortable writing. The AI Writer for Work can help you with the following:

At work, teams and individuals can also use ClickUp Brain to draft all their internal and external communication from anywhere in ClickUp—task comments, documents, and emails. Add your thoughts to the AI writing tool in shorthand, and it’ll polish it for you.
Role-specific prompt templates
Not just that, you also get access to AI prompt templates for each role—so you can get started immediately. Some examples of these prompts include:
Artificial intelligence is believed to greatly influence how we live and work in the coming years. From improving individual productivity to the operational efficiency of large organizations, from finding cures to diseases to analyzing data and predicting macroeconomic forecasts, AI engines are believed to improve the world.
As individuals, you can start the first step by either training to become an AI engineer (if that interests you) or using AI tools like ClickUp Brain to optimize your life.
Suggested reading: How to become a prompt engineer
So why not give ClickUp a try today? Sign up to ClickUp for free and explore how it can level up all aspects of your life!
© 2026 ClickUp