Interprofessional Collaboration Examples and How to Implement Them
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Back in the day, getting medical treatment involved multiple to-and-fros with doctors, nurses, and pharmacists!
Each worked in isolated silos, handling their duties. If the doctor’s prescription wasn’t clear, the pharmacist had no way of helping you.
Thankfully, interprofessional collaboration has created a solid system where healthcare professionals work closely, share insights and documentation, and communicate effectively.
With an integrated system, a doctor’s prescription simply appears on the pharmacist’s screen, saving you the hassle of running back and forth.
In this blog, we’ll explore real examples of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare and ways to apply these practices. 🩺
Interprofessional collaboration (IPC) is the mutual and active participation of medical professionals from different fields when tackling complex cases or achieving shared goals.
This collaborative approach is especially critical in healthcare, where patients often require input from multiple health workers—such as doctors, nurses, and pharmacists—working together to deliver well-rounded, patient-centered care.
A 2024 survey with 150+ registered nurses revealed that 87% had engaged in a good interprofessional collaboration environment in their organization. This led to:
🔍 Did You Know? The American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN) includes ‘true collaboration’ as one of its six essential standards for creating a healthy work environment and successful patient outcomes.
Coordinate across roles and reduce miscommunication with ClickUp’s Communication Plan Template. It helps map who needs what, when, and how—perfect for smoother interprofessional collaboration. Try it for free today!
Interprofessional collaboration is not limited to healthcare—it’s valued in fields like education, business administration, social work, and IT, where cross-functional collaboration is essential to achieving shared goals.
Let’s look at some interprofessional collaboration examples in each sector. 👇
In healthcare, interdepartmental communication and relationships are necessary for delivering holistic and patient-focused care.
Here’s how professionals work collaboratively to meet different needs:
The Froedtert & MCW hip fracture program, launched in early 2017, allowed patients to get immediate treatment in a more coordinated fashion and with a collaborative team.
Once the hip fracture is diagnosed, the ED staff activates the hip fracture protocol. A report goes out to the orthopaedist, who looks at the X-rays and plans the surgery; the perioperative medicine specialist performs the intake on the patient; the anesthesiologist evaluates the availability of the operation room; and a regional pain specialist, who keeps the patient composed until surgery while minimizing opioids.
In addition, nutritionists help with patients’ nourishment and hydration before surgery (especially in elderly patients).
📌 Outcome: Before the launch of this program, the average wait time for diagnosis to surgery was 38 hours. With this new protocol, patients go into surgery within 24 hours.
Everyone becomes highly skilled and specialized in their respective areas, and they know how to work well with each other. It’s all about the depth and breadth of care – and all of medicine is increasingly becoming team-based like this.
Chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease need long-lasting care and management. Hence, implementing an IPC framework for managing chronic conditions makes sense.
The framework would include a team of all important medical professionals specializing in chronic diseases.
Physicians, who develop personalized treatment plans; nurses, who support day-to-day care and follow-ups; dietitians, who provide nutritional guidance to maintain balanced health; and pharmacists who monitor the safety and effective dosage of medications throughout the treatment.
A nurse-led Community Health and Wellness Center at Texas developed an interprofessional collaborative practice (IPCP) program over 10 years, focusing on chronic disease management.
Key components included a patient navigation program and regular IPC meetings to discuss patient cases.
📌 Outcome: From 2014 to 2020, the rate of depression screening and follow-up improved from 16% to 91%, and the hypertension control rate improved from 50% to 62%. Lessons learned include recognizing partner contributions and the worth of each team member.
Managing patients with chronic pain is a lot easier when you’ve got an interprofessional team of:
📌 Outcome: A well-rounded approach provides patients with relief options that address both physical and emotional challenges associated with chronic pain.
🧠 Fun Fact: The World Health Organization (WHO) actively promotes interprofessional collaboration through its Framework for Action on Interprofessional Education & Collaborative Practice. This initiative encourages healthcare workers from diverse disciplines to learn together and work as a team, aiming to improve global health systems.
When patients face serious, life-limiting illnesses like cancer, palliative care IPC teams work together with social workers and chaplains to improve their quality of life.
For example, oncologists lead the medical plan, while nurses handle day-to-day comfort measures. Social workers reach out to families to provide emotional support and necessary resources. Chaplains offer spiritual care, helping patients and their families find peace.
📌 Outcome: Families receive consistent guidance and compassion from primary care providers, helping them navigate difficult healthcare decisions.
Managing complex medication regimens requires input from various health professionals. Physicians prescribe, setting the groundwork for safe use. Pharmacists monitor interactions, dosages, and refills, keeping therapy effective. Nurses educate patients on taking medications correctly and identifying side effects. Social workers ensure patients can access and afford their medications, assisting with financial support if needed.
📌 Outcome: Reduced risks of adverse drug interactions and improved patient confidence in medication adherence.
In education, interprofessional collaboration occurs when professionals from different backgrounds collaborate to create a supportive, inclusive learning environment.
Here are a few examples:
Students with special needs require one-to-one support to navigate learning challenges and reach their full potential.
Special educators design individualized education plans (IEPs), while occupational therapists assist with developing fine and gross motor skills. Psychologists offer support for emotional and behavioral challenges and provide strategies to cope with social and academic pressure.
📌 Outcome: Laser-focused guidance promotes inclusivity and helps students meet personalized learning goals. Collaborative efforts create a safer, more conducive environment for learning and growth.
Guiding students toward future careers involves a collaborative relationship between teachers, career counselors, and industry mentors.
Teachers identify students’ strengths and interests, guiding them toward suitable career paths. Career counselors provide detailed information about education and skill requirements for different professions. Industry mentors share real-world experiences and insights, helping students envision future roles and set goals accordingly.
📌 Outcome: Students gain clarity on career goals, motivating them to work toward skills that align with future opportunities.
The increase in mental health issues is alarming. That is why, to address mental health issues at early stages, schools and educational institutions use the IPC framework.
Teachers are the first to notice distress signs in students and can refer them to counselors for one-on-one support. Counselors provide coping strategies and resources to help students manage stress and anxiety. Psychologists handle more severe cases, ensuring things don’t go off-track and students receive timely mental health care.
📌 Outcome: Teams create a supportive framework that equips students to handle academic and personal stress.
🔍 Did You Know? 4 in 10 (40%) students in the United States experience moderate to severe distress.
In social work, interprofessional teamwork is crucial for delivering well-rounded support to individuals, families, and communities.
Social workers, educators, and healthcare providers team up to protect children’s welfare.
Social workers intervene in cases of abuse or neglect and connect families to essential resources. Educators monitor academic and behavioral changes, which can signal issues at home. Healthcare providers address physical and mental health.
📌 Outcome: Social workers implementing interprofessional collaboration offer holistic interventions that protect vulnerable children while promoting stability and well-being.
Supporting individuals in substance abuse recovery requires a structured approach, including therapy, peer support, and a tailored treatment plan.
To address underlying causes and sustain long-term sobriety, the following must work together:
📌 Outcome: Collaborative efforts strengthen neighborhoods and benefit patients from a structured, supportive system throughout the addiction recovery.
Survivors of domestic violence need help from social workers, mental health counselors, and law enforcement.
Social workers provide access to emergency shelters, legal aid, and support networks. Mental health counselors help survivors process trauma and develop coping strategies. Law enforcement ensures safety by enforcing protective measures and supporting survivors through legal proceedings.
📌 Outcome: Survivors gain access to essential resources, empowering them to rebuild their lives with security.
In the corporate world, cross-department collaboration fuels innovation. In fact, it’s among the best practices for effective project collaboration and aligns operations with company goals.
Product development teams, for instance, bring together product managers, engineers, and marketing experts. While managers set the vision, engineers design solutions, and marketers ensure the product reaches the right audience—resulting in launches that are both functional and appealing to the market.
Customer support and sales teams also work closely, with support resolving issues and sales ensuring customers’ needs are met. This dynamic duo strengthens customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Meanwhile, HR and finance align hiring needs with budget constraints, balancing company growth with financial health.
Data analysis and marketing teams create a powerful pairing. Analyst insights are used to measure campaigns that truly resonate.
Together, these high-functioning teams ensure that every aspect of the business is optimized, from product launches to customer engagement and staffing.
Building a collaborative culture, whether through casual social events, team-building activities, or the right technology, helps bring employees together, sparks innovation, and boosts productivity.
With the right strategies and tools, you can break down silos, encourage knowledge sharing, and build a team that works together seamlessly toward shared goals.
Here are some key strategies to promote interprofessional collaboration in your organization:
Studies consistently show that when healthcare professionals from different disciplines work together, patient care improves in several key areas. Let’s break it down:
A review of 51 studies found that IPC in primary care led to better clinical outcomes 50% of the time. Patients reported positive experiences and improvements in health conditions.
Economic results didn’t show much change, but humanistic outcomes (think patient satisfaction) were significantly better in most cases.
Research from the University of Saskatchewan strongly compares successful sports and healthcare teams. It highlighted that clear roles, trust, and collective leadership are crucial.
When healthcare teams function well together, they can overcome adversity and provide better care.
A systematic study of 23 trials found that IPC interventions led to improvements in clinical measures like blood pressure and cholesterol levels, especially for chronic disease management.
This means that IPC isn’t just a feel-good approach—it directly improves health outcomes.
A systematic literature review of 65 studies showed that IPC was particularly effective in managing patients at risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Teams involving general practitioners, nurses, and pharmacists had the most success, especially for conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Here’s an overview of essential tools that support cohesive teamwork in healthcare:
Healthcare teams rely on health techs and digital platforms to streamline communication, task management, and information sharing. Some of the core tools driving this collaboration are:
Other than that, management tools like ClickUp are becoming a popular choice for interprofessional collaboration among healthcare leaders. Here’s how!
Using ClickUp Tasks, you can create detailed task lists, assign duties, and set clear deadlines so nurses and doctors know their responsibilities.
ClickUp Task Priorities allows you to label tasks using different priority levels—from low to urgent—each color-coded. Your team instantly sees which tasks require immediate attention.
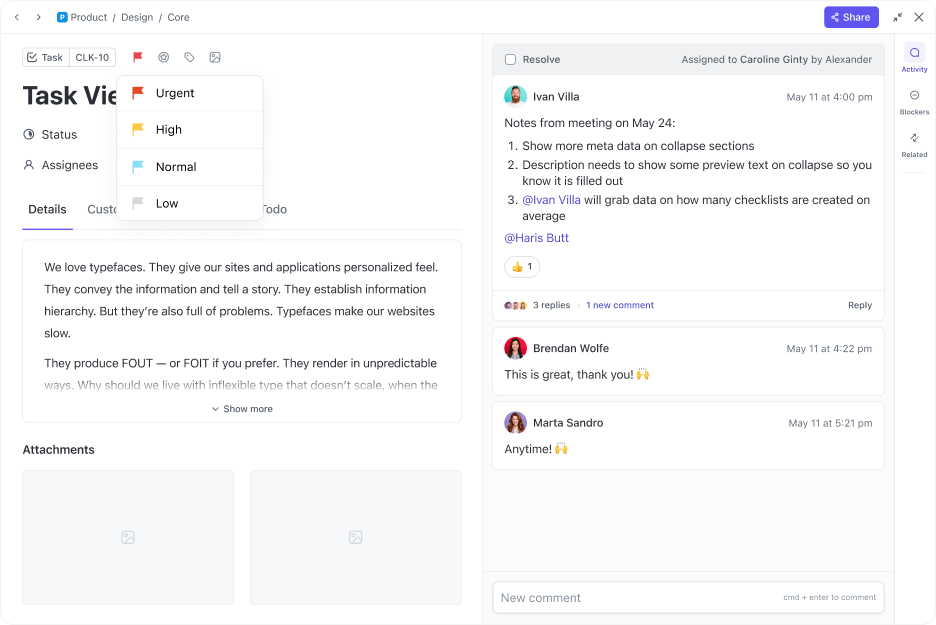
If you’re tired of maintaining spreadsheets and paper files for all your patients’ personal and medical records, switch to ClickUp Docs for a centralized digital document hub.
With Docs, your team can easily create, share, and update documents in real time, ensuring everyone is always on the same page (literally).

📮 ClickUp Insight: 74% of employees use two or more tools just to find the information they need—while jumping between emails, chat, notes, project management tools, and documentation. This constant context-switching wastes time and slows down productivity. As the everything app for work, ClickUp unifies all your work—email, chat, docs, tasks, and notes—into a single, searchable workspace, so everything is exactly where you need it.
What if you could discuss patient care, track tasks, and share resources all within the same conversation?
ClickUp Chat lets you send messages and create tasks out of conversations without juggling multiple apps or losing context midway.
Using AI, Chat automatically suggests replies, answers questions, creates tasks, summarizes threads, and more. You can have live video calls with interdisciplinary teams, share documents, and reduce time to action, making IPC quicker and smoother.
Pharmacy Mentor, a pharmacy marketing company, faced challenges managing client projects and communication. Adopting ClickUp as a centralized platform helped the team streamline project management and communication.
ClickUp’s CRM features and automation tools boosted client response rates from 20% to 80%, reduced project revisions by 20%, and enabled time-zone-independent communication.
ClickUp has helped our business become much more productive—saving time, reducing the need for pointless meetings, and vastly increasing employee and client satisfaction.
In time-sensitive situations, when comments need action, ClickUp Assign Comments lets you direct comments to the right person—whether it’s you or someone else on the virtual team.
This ensures that no task, big or small, gets overlooked.

Interprofessional skills don’t always come naturally. Many healthcare organizations now offer workshops and training programs on active listening, role clarity, and collaborative problem-solving.
Here are some well-regarded American educational programs and workshops that focus on developing interprofessional skills:
Without a doubt, interprofessional collaboration is enhancing patient care, but implementing the framework into your organization or medical procedures comes with challenges.
These are some common obstacles. 🚧
Language and cultural differences often hinder effective communication.
These barriers can prevent your team from clearly understanding each other’s perspectives, leading to fragmented care, late actions, and errors in patient treatment.
✅ Solution: Use simple, inclusive language. Avoid jargon, clarify information as needed, and seek feedback to ensure mutual understanding. Digital tools and regular check-ins help keep everyone informed and connected.
In a healthcare system, overlapping or poorly defined roles can lead to duplicated efforts, missed tasks, and friction between team members.
Role confusion can occur when responsibilities aren’t clearly outlined, causing some professionals to take on tasks outside their expertise while leaving other areas unattended.
✅ Solution: Establish clear role definitions and boundaries from the start. Use ClickUp Tasks and Assign Comments to delegate each team member’s responsibilities and prevent misunderstandings. Clearly outlined roles create a smooth, coordinated workflow.
Biasness created due to experience, status, or authority creates power imbalances within healthcare teams. The survey previously mentioned also revealed that:
This can discourage open communication, with less-experienced members potentially feeling undervalued or hesitant to contribute. Power imbalances can impact team interactions and patient care.
✅ Solution: Encourage equal contributions to promote an environment of mutual respect. Actively recognize each team member’s value and invite patient input where appropriate to promote inclusivity and an open dialogue policy.
Conflicting values and principles can lead to ethical conflicts among healthcare professionals, especially regarding patient autonomy, confidentiality, and resource allocation.
When team members have different values or principles, it can create tension and make shared decision-making difficult, particularly in complex cases where ethical considerations are paramount.
✅ Solution: Create a framework for ethical decision-making by consulting relevant guidelines and discussing dilemmas openly with the team. Engage in constructive dialogue to reach consensus or compromise, helping to align team values for patient-centered care.
Personal factors, such as a lack of motivation, limited time, or inadequate understanding of team roles, can impede effective collaboration.
When team members struggle to engage fully due to individual constraints, it can lead to missed connections and reduced team effectiveness.
✅ Solution: Promote a culture of shared learning and professional development. Offer regular training on teamwork and collaboration best practices to build motivation and understanding. Flexible scheduling can also provide space for collaborative efforts without overwhelming individual workloads.
Institutional challenges, such as a productivity-focused culture, lack of resources, or inadequate prioritization of teamwork, can stifle collaboration in the workplace. When organizations emphasize individual productivity over team success, it may lead to fragmented efforts and reduced quality of care.
✅ Solution: Advocate for policies that support interprofessional teamwork by prioritizing teamwork in organizational goals. Allocate resources for team-building activities and training, and shift the focus from productivity to a balanced approach that values collaborative care.
Policy and administration are the foundation for creating a healthcare environment that fosters interprofessional collaboration among healthcare workers.
Here’s how:
📖 Also Read: How to Effectively Overcommunicate at Work
Interprofessional collaboration is essential for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. It breaks down the age-old silos and allows healthcare professionals to work together to deliver more comprehensive services.
ClickUp empowers this collaboration with tools like tasks for organizing responsibilities, docs for shared knowledge, and chat for real-time communication, keeping everyone aligned.
For healthcare teams especially, these resources foster a culture of teamwork that ultimately benefits both your team and your patients. Sign up to ClickUp for free today.

© 2026 ClickUp