Prompt Engineering Examples, Techniques, and Practical Applications
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

You wouldn’t call a pizzeria and place an order for a “pizza.” To receive the dinner you desire, you’d specify your choice of crust, toppings, spices, accompanying drink, and anything you might be allergic to.
Moral of that story is: The more detailed your instructions, the closer the pizza is to your preference. This applies to using generative AI tools like Open AI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini.
In this blog post, we show you how to give clear instructions and ask specific questions of gen AI tools—a process also known as prompt engineering.
Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining the input text given to AI models, especially language models, to elicit the most accurate, relevant, and creative responses.
Generative AI is growing to be one of the most powerful and impactful tools across a wide range of applications—from content writing to architectural modeling. McKinsey finds that up to 30% of hours currently worked across the US economy could be automated by 2030 with Gen AI-based technologies.
To make the best use of Gen AI, you need to master prompt engineering.
Accelerating interactions: Prompt engineering serves as the primary interface between human intent and machine output. For the machine learning (ML) model to understand your natural language query, you need to know prompt engineering.
Fostering AI creativity: The differentiating factor of Generative AI is that it ‘generates’ i.e., creates text, images, or data in response to prompts. To get creative responses, you need to input clear prompts.
Eliciting accurate responses: A big challenge in Gen AI has been hallucination—a phenomenon where the AI model produces incorrect or misleading information based on wrong assumptions or inherent biases. To eliminate this, you need good prompt engineering skills.
Maximizing returns: Generative AI is made of large language models, processing extraordinary amounts of data. To leverage the best of a model’s capabilities—and circumvent its limitations—good prompt engineering is fundamental.
Improving relevance: Anything generated by the AI needs to be relevant to the intended audience. For instance, you can improve the relevance of your AI-generated social media post for your audience by specifying their demographics, interests, needs, challenges, etc.
To reap these benefits, you need to understand how you can use prompt engineering to get your desired results from generative AI. Let’s begin with some examples
There are a lot of do’s and don’ts, best practices, and AI prompt templates around to help you get it right. But before we get into any of the AI hacks, the best way to learn a skill as practical as prompt engineering is to see it in action.
Here are some examples of prompt engineering across areas of work.
Whether you’re programming, fixing bugs, or writing documentation, AI tools for developers can make your work much simpler. Here’s how.
“Generate a code review checklist for a robotic process automation (RPA) application built using Python. Especially focus on readability and enterprise security.”
“Write a comprehensive guide on implementing OAuth 2.0 in a web application using Node.js. Include step-by-step instructions and code snippets for each stage.”
“Describe a systematic approach for identifying and fixing memory leaks in a Java application, including tools to use and common areas to check.”If you’re a beginner finding this a bit too complex, we’ve brought help. Use ClickUp’s ChatGPT prompts for engineering to generate ideas, process plans, and much more.
Agile software development teams are often short of product managers who can clarify the roadmap and drive progress. The AI tools like ChatGPT can be of help.
“Using the RICE scoring model (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort), prioritize the following features for our upcoming project management tool: Kanban boards, real-time collaboration, automated reporting, and third-party integrations.”
“Develop a detailed user persona for a fitness tracking app targeting busy professionals who are beginners in personal fitness. Include demographic details, goals, challenges, and how they might use the app.”
“Outline a 6-month product roadmap for an e-commerce platform expansion, focusing on integrating AI for personalized shopping experiences. Detail the phases, key milestones, and expected outcomes.”Or choose from the 130+ ClickUp ChatGPT prompts for product management and get started right away.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 37% of our respondents use AI for content creation, including writing, editing, and emails. However, this process usually involves switching between different tools, such as a content generation tool and your workspace. With ClickUp, you get AI-powered writing assistance across the workspace, including emails, comments, chats, Docs, and more—all while maintaining context from your entire workspace.
You can ask Gen AI to create a project plan, which you can customize. Or just take help optimizing parts of it. We’ll see both below.
“Draft a detailed project plan for launching a new online marketplace, including phases such as market research, design and development, testing, and go-live strategy. Specify key activities, resources needed, and timelines for each phase.”
“Analyze the current resource allocation for a software development project and suggest optimizations to ensure timely delivery without compromising quality. Consider factors like skill sets, workload distribution, and critical path tasks.”
190+ ChatGPT prompts for project management curated exclusively for you by ClickUp.

Learn more about ClickUp Brain here:
The best AI content creation tools can help improve your marketing outcomes significantly. Try the following to see for yourself.
“Design a social media campaign for an upcoming eco-friendly shampoo launch. Include 3 different Instagram posts and 3 different Twitter posts. Add relevant hashtags for each platform.”
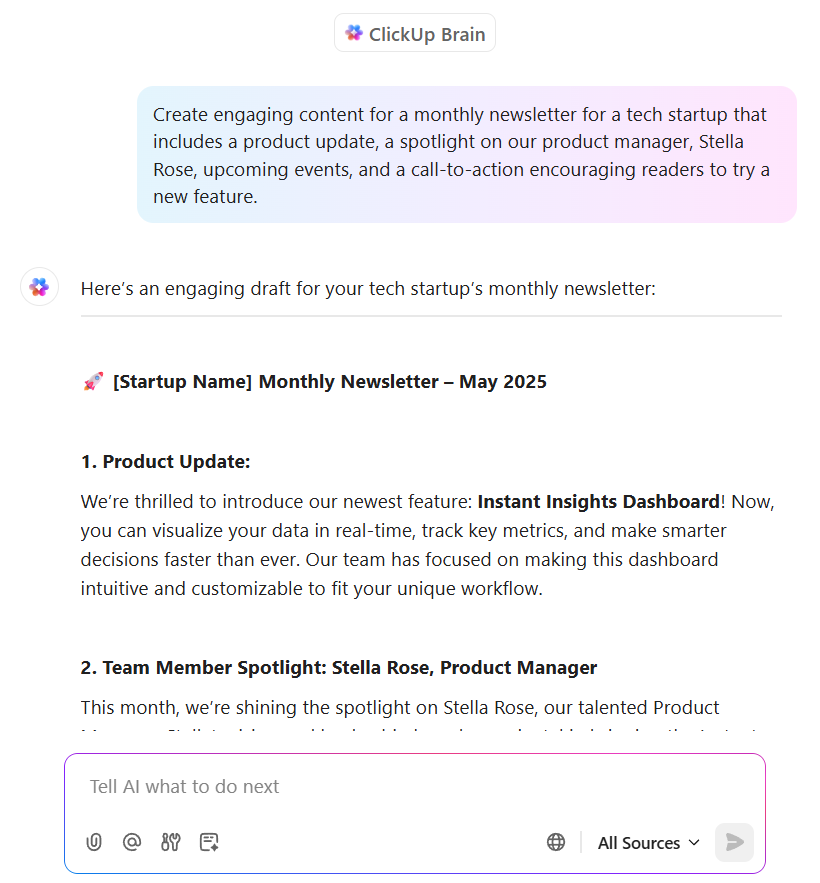
“Create engaging content for a monthly newsletter for a tech startup that includes a product update, a spotlight on a team member, upcoming events, and a call-to-action encouraging readers to try a new feature.”
You can also give more details about the product update or a team member to get precise output. Example below.
“Create a spotlight on a team member. His name is Jake, he’s a fabulous developer. He completes one year this month. In his time, he has helped solve some of the biggest client problems. A client once said, “Without Jake, we’d have been stuck in a loop of confusion. He did great work by helping us hit two birds with one stone.”

Use ClickUp Brain as your writing assistant, perform spell checks, summarize longer documents, create tables, templates, transcripts, and more.
Do remember that most businesses don’t yet favor AI-generated content, which has given rise to several AI detection tools. The best way to use Gen AI for content would be as a brainstorming tool or a starting point that eliminates the blank-page-problem.
Technically speaking, ChatGPT or Google Gemini is a chatbot we’re talking to. It understands our input and produces responses. It is trained on large language models with a plethora of data.
You can take these models and further train them with proprietary or industry-specific information to enable nuanced, context-aware, personalized conversations with the user. In this case, the customer might just ask questions like, “how much does this backpack cost?”
However, a good customer service chatbot can draw from organizational data around shopping history, location, preferences, past complaints, etc., to provide answers and upsell products, significantly enhancing user experience.
Prompt engineering can help a developer to generate specific code snippets in various programming languages.
“Write a Python function to connect to an SQL database and perform a SELECT query based on parameters passed to the function.”
Integrating AI in version control workflows provides recommendations for code review based on commit history, suggests areas of the codebase that may require refactoring, and automates routine version control tasks, improving code quality and team productivity.
Prompt engineering, especially with models like DALL-E, unleashes unprecedented capabilities in generating imaginative and intricate visuals from textual descriptions.
For instance, a game developer could use a prompt like “Generate an image of a high street, with fashion stores lining either side, at dusk, in modern architectural styles and cool colors.” The results enable rapid visualization of game environments without requiring extensive manual drawing.

Typically, extracting information from databases requires someone with SQL knowledge to write complex programming language queries. Generative AI has changed this, enabling you to write your queries in natural language to retrieve data from unstructured or semi-structured data sources.
“Be a data scientist and write code to clean and pre-process my data for analysis. My dataset contains shopping information of all customers for the last 30 days.”
Here, you can ask Gen AI to do specific cleaning tasks such as eliminating empty rows, removing rows with cart values less than 50$, and so on.
“Write code in Python to visualize my dataset. My dataset contains shopping information of all customers over the age of 50 in the last 30 days.”
Give additional specifications for visualization and fine-tuning, such as “show me shopping trends,” or “organize by category.”
Sentiment analysis is immensely popular in online user-generated content, especially from social media posts. Your prompt to understand customer sentiment about your product can be as follows.
“Based on my dataset containing social media posts mentioning [brand], classify them as positive, negative, or neutral. Identify the specific features/aspects associated with each sentiment.”
If you’ve learned the basics of how prompt engineering works, it’s time to see its larger applications and implications.
You see from the examples above that you can do basic data analysis or sentiment analysis across all industries. However, generative AI and prompt engineering are delivering special value in data-driven sectors and applications. Here’s how.
Good prompt engineering helps educators create accurate, relevant, engaging, and personalized content at scale. Some of the most high-potential use cases for Gen AI in education are:
Personalized learning experiences: Creating lessons and plans based on each individual student’s preferences, proficiency and interests at a fraction of the time.
Automated content creation: Rapid generation of supporting materials, such as summaries, quizzes, and reading comprehension questions.
Language learning and practice: Generating conversational practice scenarios, grammar exercises, and vocabulary drills aligned with the learner’s current level.
Tutoring and support: AI-powered tutoring to address specific student questions or areas of difficulty, offering explanations, resources, and practice problems.
By crafting precise and contextually relevant prompts, researchers leverage AI models to sift through vast data, generate novel hypotheses, and even simulate experimental outcomes.
Prompt engineers can help researchers design the right input to get accurate results at scale. Some scenarios in which this can be valuable are:
Literature review: Performing comprehensive literature reviews, identifying relevant studies, key findings, and gaps in the current knowledge base.
Data mining: Uncovering patterns, correlations, and anomalies in large datasets.
Hypothesis generation: Generating multiple hypotheses within the same research area to explore multiple paths.
Experiment simulation: Simulating experiments or model outcomes, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming physical experiments.
Prompt engineering improves the ability of AI models to interpret complex medical data, provide diagnostic support, personalize patient care, and facilitate research and training.
Prompt engineers can help medical professionals gain better insights from their data in the following scenarios.
At its core, generative AI can create content in three forms: Text, image, and audio/video. Some of the most effective AI use cases across these three forms are as follows.
This is the most popular use case for generative AI today. From journalists and marketers to shy developers, users across the spectrum are using AI text generators for their needs.
Popular use cases are:
There are also AI tools for meeting notes that can transcribe video calls into text notes or summarize text notes to identify key points, action items, etc.
Though still not as widely used as text, image generation presents incredible opportunities for creativity. Popular use cases include:
Audio and video generation through prompt engineering has significant entertainment, education, and virtual assistance applications. Some practical use cases for AI content creation tools include:
The impact of generative AI is extraordinary—influencing every sector, industry, geography, and business type. Over the next decade, prompt engineering might define one’s ability to learn and comprehend things, in a way that ‘Googling’ is today.
Even as generative AI is rapidly evolving, here are some foundational methods you can use to get started with prompt engineering.
Before we get into technical terms, remember that the main advantage of generative AI is that you can give your input in natural language. So, go ahead and speak to ChatGPT or Google Gemini or Microsoft Copilot like you would naturally.
Observe responses and fine-tune your input as you go along. Here are some concepts that might help you along the way.
Providing the AI with a task without prior examples or context is called zero-shot prompting. It is characterized by the following.
Example prompt: “Identify the primary programming language used in the following code snippet: print(‘Hello, World!’).”
Giving the AI model a few examples of the task at hand before presenting the actual task is called few-shot prompting.
Example prompt: “Given the input and output pairs: Input: 5 * 5, Output: 25; Input: 8 + 2, Output: 10; calculate the output for Input: 7 – 4.”
Prompting the model to generate intermediate steps or reasoning paths leading to the final answer or desired output is called chain-of-thought (COT) prompting.
Example prompt: “To reverse a given string ‘hello,’ first, split the string into individual characters. Second, reverse the order of these characters. Finally, join these characters back into a string. What is the final output?”
Let’s get into a couple of more complex and advanced prompt engineering techniques.
Zero-shot chain-of-thought (COT) combines the two methods to tackle complex problems without prior examples in the training data.
Imagine using a generative AI model to debug a piece of software code it has never encountered before.
Using zero-shot COT, the model would articulate its understanding of the problem, logically deduce causes, and articulate potential solutions, step by step, despite not having been trained on this specific issue.
What if AI could prompt AI to find the right answers? Well, that’s automating prompt engineering.
Using algorithms and techniques to automatically generate or optimize prompts for interacting with AI models is called APE. In this model, the algorithm analyzes a corpus of successful and unsuccessful attempts to automate similar tasks.
Then, it incorporates keywords, structures, and instructions identified as most likely to result in a successful output. As the AI generates scripts, the APE system evaluates their effectiveness, refines the prompt based on what it learns, and iteratively improves the process.
Irrespective of the method you use, you are likely to face a few challenges in your journey to effective prompt engineering.
As an emerging field, Gen AI is going through its own ups and downs. On the other hand, users are trying various prompts and styles to get the output they need. A technology in such rapid motion is bound to have challenges.
Some of the biggest limitations of prompt engineering and ways to overcome them.
Model dependency: A prompt that works well with one model might not yield the same results with another.
Keep an eye out for differences in the model. Make adjustments and optimizations as you go along.
Complexity and specificity: Effective prompts often require a deep understanding of the model’s language and capabilities.
Find the balance between too vague and too specific to make the most of your large language models.
Bias and sensitivity: AI models can inherit biases from their training data, which you may amplify inadvertently through prompt engineering. Moreover, hallucination, bias, insensitivity, etc., can lead to harmful, misleading, or unethical outputs.
Build systems for careful consideration and ethical oversight of AI usage.
Scalability: As the scope of tasks grows, manual engineering prompts for each unique scenario become impractical.
Consider automatic prompt generation or optimization for future needs.
Interpretability: Lack of interpretability can make it hard to iteratively improve prompts or diagnose issues.
Use chain-of-thought methods and insist on seeing the AI’s logical reasoning for important output.
Overfitting and underfitting: Overfitting occurs when a prompt is too tailored to specific examples, making it less effective for general cases. Underfitting happens when a prompt is too broad, leading to generic or irrelevant outputs.
Well, find the balance.
Cost and resource constraints: High-quality prompt engineering, especially in a commercial setting, can require significant computational resources and expert time.
Focus on practical applications and return on investment.
What’s the name of that Taylor Swift song? How much cheese should I put in my pasta? Is this dataset clean for analysis? What medication is this patient allergic to? What tasks from this sprint are yet to be assigned?
The scope of generative AI models is constantly expanding. As a result, prompt engineering is emerging as a must-have skill among professionals across industries.
Your ability to speak the LLM’s language determines how successful you are eliciting the best outcomes—a skill encapsulated in ‘prompt engineering.’
You could try your hand at prompt engineering with any of the free LLMs such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, DALL-E etc. Try asking it to create a remix of your favorite songs for your next birthday party or look at your credit card statements to visualize your biggest expenses.
Make work faster and more effective with ClickUp Brain. ClickUp integrates AI into the platform for knowledge management, project management, and writing.
What’s more? ClickUp Brain also comes with inbuilt prompts and hundreds of templates to make sure you start on the right foot.See what generative AI can do for your project management. Try ClickUp for free today!
Crafting input for generative AI models like ChatGPT to guide them in producing specific or desired output is called prompt engineering.
When a software developer wants to use a language model like GPT-4 to generate a Python script for a web scraper that collects news headlines from a specific website.
Prompt: “Generate a Python script using Beautiful Soup library to scrape the latest news headlines from ‘example-news-site.com.’ The script should handle pagination and store the headlines in a list.”
Any input you give a generative AI model is a prompt. With good prompt engineering, you can improve your output significantly, making it more useful, relevant, accurate, and engaging.
A good example of a prompt is: “Generate a 150-word product description for a bamboo fiber towel set that emphasizes its eco-friendly benefits, durability, and softness. Include a call-to-action encouraging eco-conscious living and promoting the brand’s commitment to sustainability.”
The best way to start prompt engineering is to try it for yourself. Interact with it in natural language and understand the model. In parallel, you can:
Stay updated with advancements in AI and natural language processing technologies, as these can affect how prompts should be structured.
© 2026 ClickUp