Still downloading templates?
There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Privacy is a fundamental human right. And that privacy flows into all aspects of today’s artificial intelligence, too. In a report by Cisco, 64% of people worry they could accidentally share sensitive information when using AI tools.
That’s one of the reasons why offline AI tools are rising in popularity. When the model runs locally, you can write, code, summarize, and create—without uploading everything to the cloud or getting stuck when Wi-Fi drops.
In this list, we’ll cover the best AI tools that work offline, among which is a super app that helps you organize what these tools produce into one cohesive, super secure system.
Offline AI tools are software applications that run large language models (LLMs) on your local device, without any internet connection needed after you download the model. The model’s data is stored directly on your computer, so all the processing, or inference, happens on your own CPU or GPU.
This on-device processing has several key benefits:
Here’s a quick summary of the best offline AI tools available today.
| Tool name | Key features | Best for | Pricing* |
| ClickUp | Offline Mode for tasks and reminders, ClickUp Brain MAX which includes Talk-to-Text, Enterprise Search across connected apps, Docs and Knowledge Management, Automations, plus Integrations and API | Teams that need offline capture plus online execution, governance, and AI context in one workspace | Free forever; Customization available for enterprises |
| GPT4All | Local chat with open models, LocalDocs for private document Q&A, in-app model discovery and downloads, OpenAI-compatible local API server | Privacy-focused users who want a simple offline desktop chatbot with local docs | Free plan available; Paid plans start at $40/user/month |
| LM Studio | Model discovery and downloads, chat UI plus local RAG, OpenAI compatible server or REST API, presets and performance tuning | Developers and power users who want a polished offline model workbench | Free |
| Ollama | One command model, local REST API with streaming, Modelfiles for reusable configs, and embeddings for RAG pipelines | Developers who want a CLI-first local runtime with a strong API layer | Free plan available; Paid plans start at $20/month |
| Jan.ai | ChatGPT-style offline UI, assistants, and MCP support, extensions for added capabilities, and optional OpenAI-compatible providers | Non-technical users who want a clean offline assistant with customization | Free and open source |
| Llamafile | Single executable model packaging, portable distribution across OS, local server mode with web UI and API, minimal dependency runtime | Users who want a zero-install portable AI file they can run anywhere | Free and open source |
| PrivateGPT | Self-hosted document ingestion and indexing, offline RAG Q&A, context filtering by document, modular LLM, and vector store stack | Teams that need offline Q&A over internal files with a controllable RAG pipeline | Free and open source |
| Whisper.cpp | Local speech to text, quantized models for lower resource use, VAD support, optional FFmpeg handling for more formats | Users who need a fully offline transcription they can embed in apps | Free and open source |
| Text Generation Web UI | Browser-based UI for local models, Jinja2 prompt templates, generation controls, chat branching, and message editing | Users who want maximum customization in a local web interface | Free and open source |
| llama.cpp | High-performance inference engine, wide quantization support, local server with OpenAI-style endpoints, embeddings, and reranking support | Developers building custom offline AI apps or backends | Free and open source |
Our editorial team follows a transparent, research-backed, and vendor-neutral process, so you can trust that our recommendations are based on real product value.
Here’s a detailed rundown of how we review software at ClickUp.
Evaluating offline AI tools can feel technical and confusing, leading you to choose a tool that might not even run on your computer. The most important thing to consider is what you want to accomplish. A developer building an AI-powered app has very different needs than someone who just wants a private, offline AI chatbot for writing assistance.
Here are the key criteria to evaluate:
Here’s a high-level view of the best AI offline tools 👇
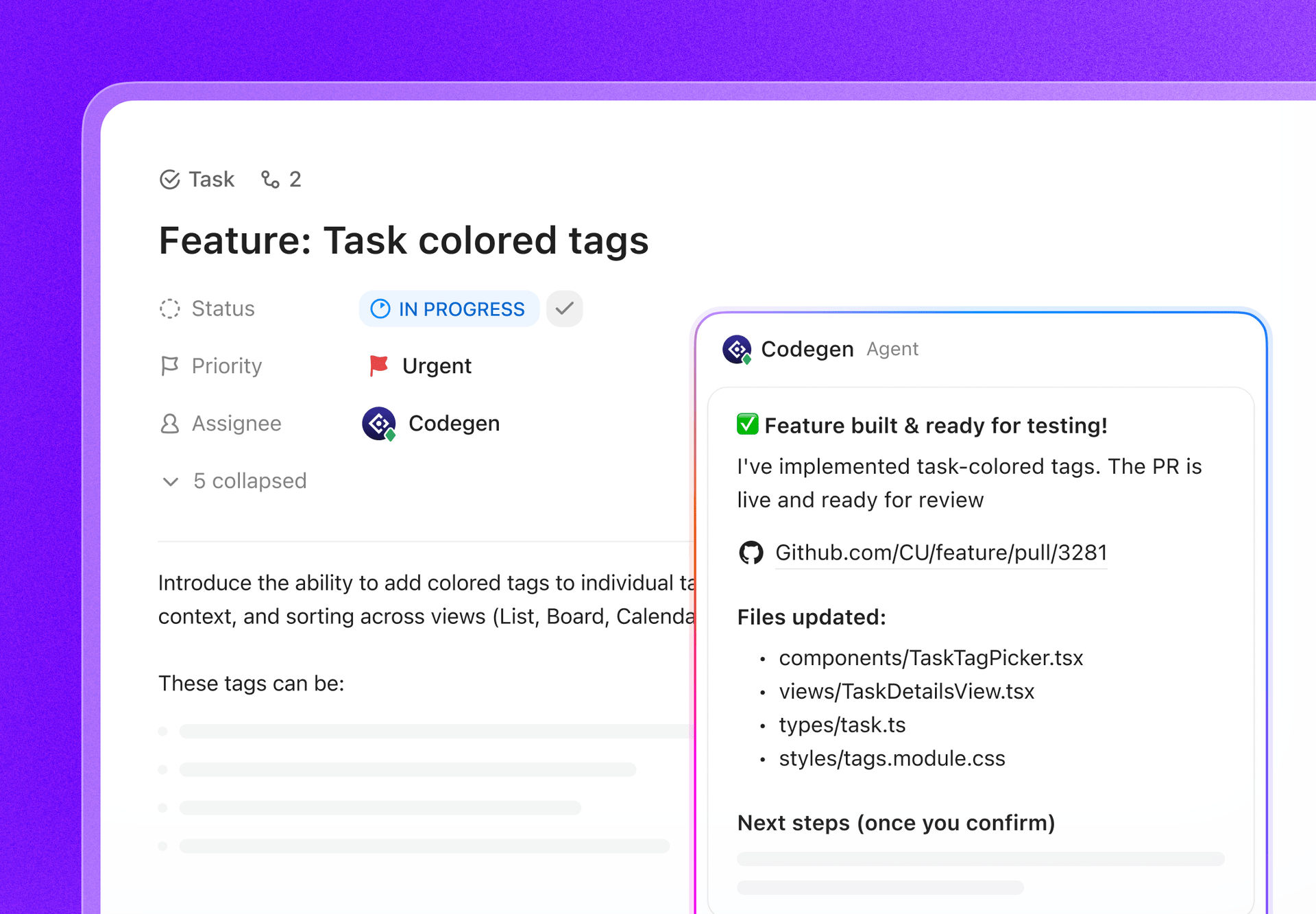
ClickUp, the world’s first Converged AI Workspace, is built on the blocks of ‘offline AI’ that does not stop at generating an answer. That’s because you still need a place where that output becomes a decision, a task, and a next step that does not disappear into files and chats.
And unlike many offline setups that come with lengthy installs and tool stitching, ClickUp gives you a complete execution layer in one place, with AI working on top of the same workspace context.
For starters, you have ClickUp Offline Mode, which automatically turns on and keeps work moving when there’s offline activity. That means all your Tasks, reminders, and notes stay accessible while offline, with the option to add more if needed. Once you reconnect, new tasks and reminders sync back to your Workspace automatically (say goodbye to losing context 👋).
Then there’s ClickUp Brain MAX, the privacy-first desktop AI companion, that can store and search across your entire workspace, connected apps, and even the web.
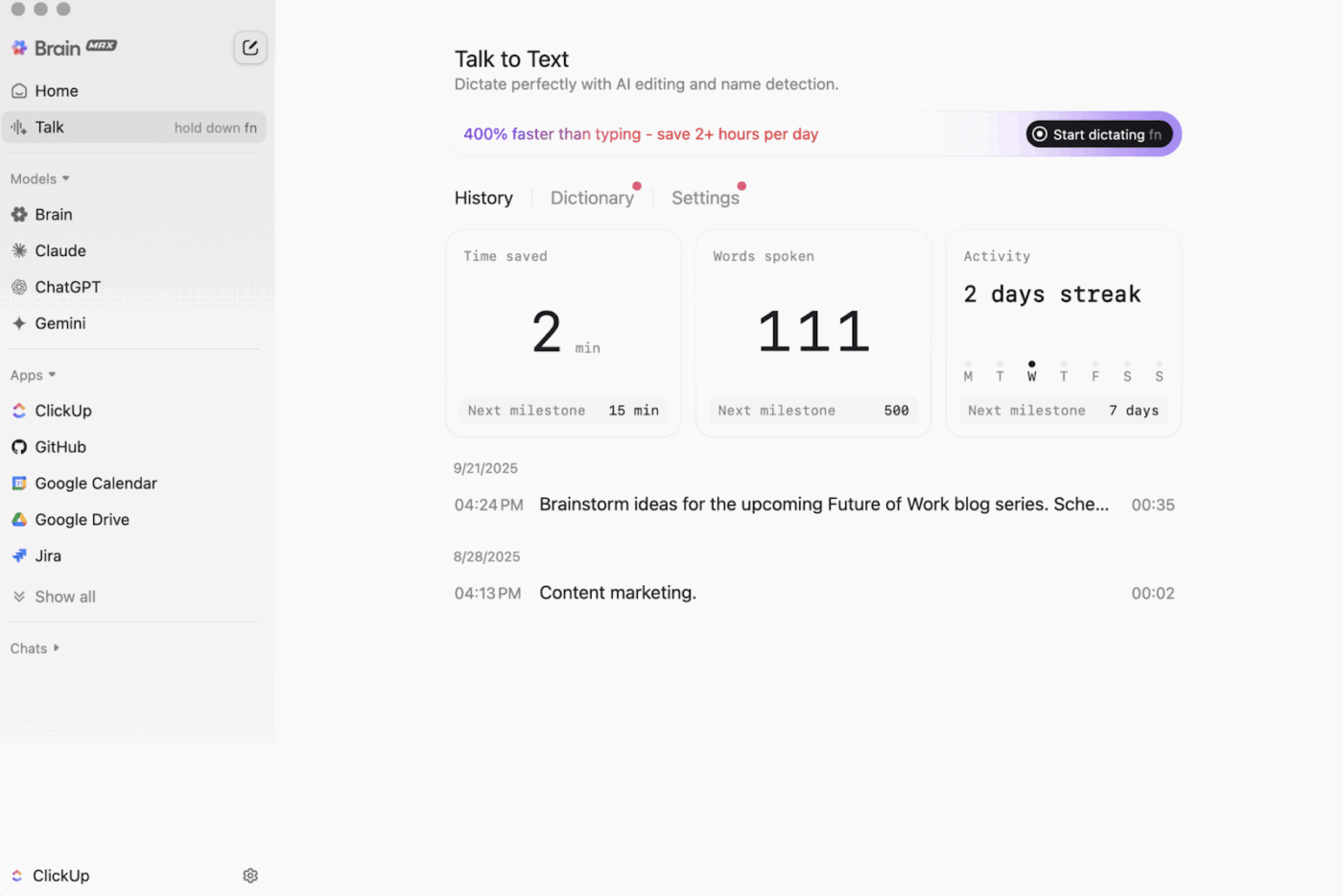
With Talk-to-Text in the mix, Brain MAX can convert your voice into text hands-free. That includes drafting an email, writing a doc, or capturing a quick update while you are on the run.
Brain MAX also gives you Universal AI, built for chatting with the latest AI models for coding, writing, complex reasoning, and more. That means you get to ask questions to top AI models in one place, including ClickUp Brain plus options like OpenAI, Claude, and Gemini, minus the tool toggling.
Even more, ClickUp Security adds guardrails that offline tools frequently skip. Think encryption, granular permissions, and admin controls like SSO, provisioning, and audit logs, all designed for teams that need enterprise-grade security.
ClickUp AI Knowledge Management helps big time in the ‘offline to online’ handoff. It gives your team a hub to store different resources in Docs and wikis, then uses ClickUp Brain to draw instant answers from across your entire workspace, so the right context is available the moment work resumes.
🎬 Agents in action: Use Super Agents to turn synced work into next steps!
ClickUp Super Agents are AI-powered teammates you can create and customize to run multi-step workflows inside your ClickUp Workspace. You can configure specific triggers, instructions, and tool access to ensure they act within the boundaries you set.
For example, after offline tasks sync back in, a Super Agent can scan the new items, summarize what changed, pull out action steps, draft an update, and route it to the right owner for review.
And because Super Agents are governable, you can control what they can access with permissions and audit what they do. 🔐
A G2 reviewer says:
Agile boards, integrations, and customization. Also, I like the fact that I can just go offline and still work on tasks. Additionally, I can send e-mails to any of the lists and get tasks automatically created. The text editor is fabulous, working in both MD mode and with shortcuts, letting you preview the content inline.
2. GPT4All (Best for private, offline AI chat with local LLMs)
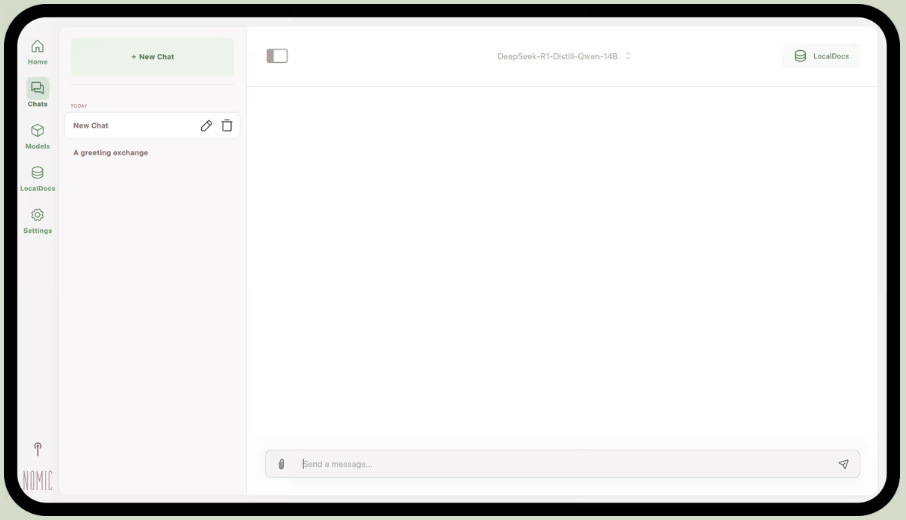
Part of Nomic.ai, GPT4All is a desktop app that lets you run open-source large language models directly on your computer, so you can chat with an AI assistant without relying on internet access or cloud API calls. It’s built for people who want a ‘local-first’ setup, where prompts, responses, and files stay on-device.
Its best feature is LocalDocs, which uses a form of retrieval-augmented generation to let you chat with your own documents privately. You can point the app to a folder of PDFs or text files, and it will create a local knowledge base that you can ask questions about.
GPT4All also includes a curated library of popular models like Llama and Mistral, which you can download directly through the app.
A Reddit user says:
This is the best one I’ve tried with RAG, beats everything, and even LM Studio in simplicity. I like the way you map it to a folder, and it tracks and handles the changes for you. Still early in its maturity, like the rest, but this is going to be my default for the short term.
via LM Studio
LM Studio is a local AI desktop app built around finding, testing, and running open-source models in a UI, without having to rely on a terminal. It’s geared toward experimentation, like picking a model, running it locally, and iterating on prompts and settings with a tighter feedback loop than most CLI-first setups.
It also supports chatting with documents entirely offline (local RAG), where you attach files to a conversation and reference them during responses. That makes it ideal for offline research, study notes, or internal docs workflows where uploads are not an option.
LM Studio also gives you elaborate control over how the AI runs, with options to adjust temperature, context length, and GPU usage.
A Reddit user says:
It’s great. It just works, super easy to get up and start. Has the nicest-looking UI out of all the competitors.
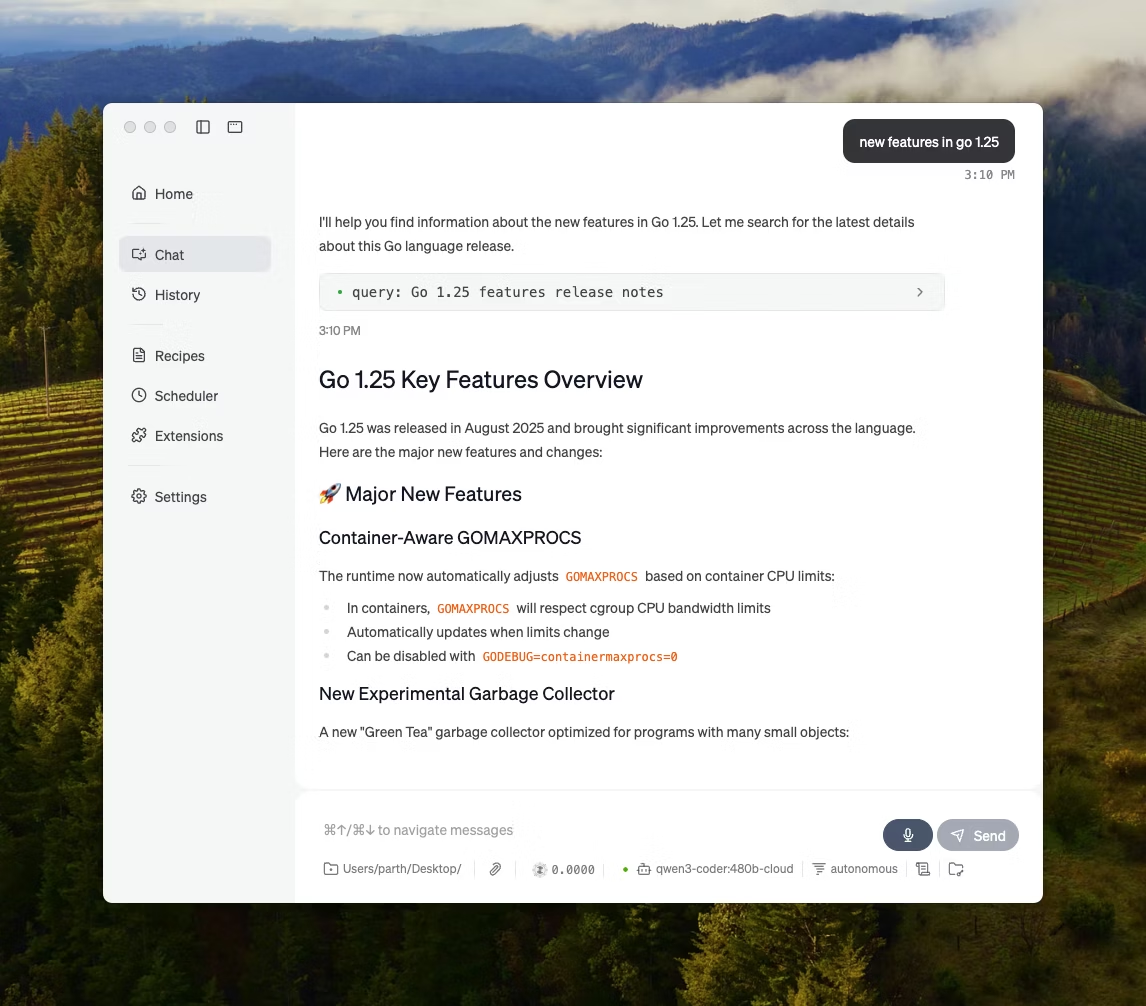
Ollama is a local model runner that behaves more like an LLM runtime than a standalone chat app. It’s terminal-first, designed to pull and run open models with quick commands (like, ollama run llama3), then expose them through a local service that other interfaces can sit on top of.
The strength of Ollama lies in its REST API. Once Ollama is running in the background, any application can communicate with it through simple HTTP requests. This helps build AI features into your own software.
Ollama also offers a library of popular models that can be downloaded with one command, and you can create custom model configurations, which are like Dockerfiles for AI.
A Producthunt reviewer says:
Easy to deploy and manage. Ollama makes running local LLMs so easy. Pair it with OpenWebUI for the ultimate experience.
🧠 Fun fact: Speech-to-text started as ‘digits only.’ Bell Labs’ AUDREY (1952) recognized the digits 0–9, and one account notes it worked best when spoken by its inventor.
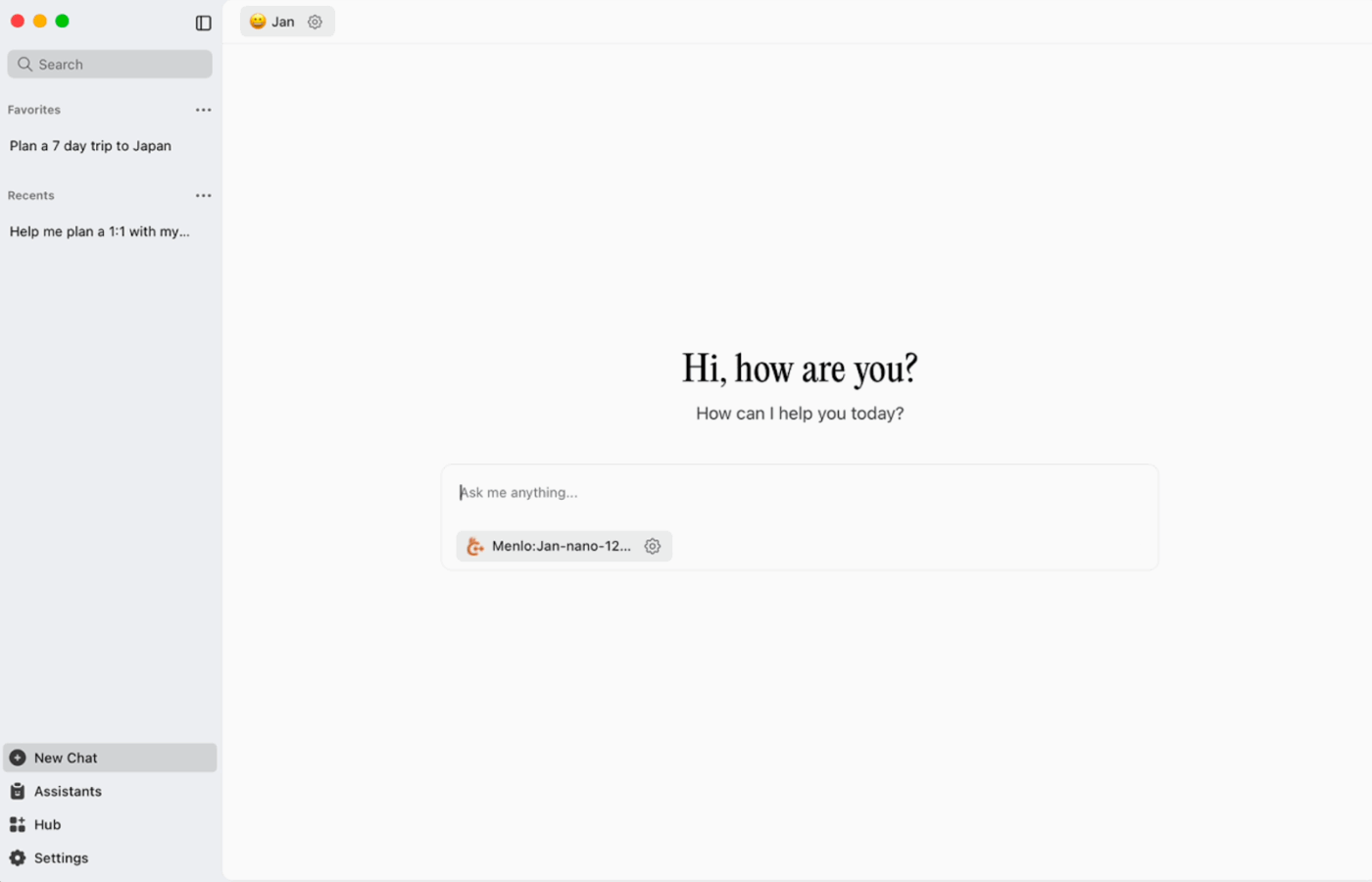
Jan.ai is an open-source desktop assistant that brings a ChatGPT-like chat experience to macOS, Windows, and Linux, with local-first usage as the default. It runs on-device when you want it to, while conversation history and usage data are stored locally and don’t leave your computer.
It supports running open-source models locally and also allows optional connections to remote providers like OpenAI-compatible APIs, which makes it flexible when offline use is the priority, but cloud access is sometimes needed.
A Reddit user says:
Jan.ai is my go-to local LLM app. It’s great.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 88% of our survey respondents use AI for their personal tasks, yet over 50% shy away from using it at work. The three main barriers? Lack of seamless integration, knowledge gaps, or security concerns. But what if AI is built into your workspace and is already secure? ClickUp Brain,
ClickUp’s built-in AI assistant, makes this a reality. It understands prompts in plain language, solving all three AI adoption concerns while connecting your chat, tasks, docs, and knowledge across the workspace. Find answers and insights with a single click!
Llamafile is a Mozilla-led project that bundles a full open-source LLM into one executable file. Instead of installing a runtime, managing dependencies, or wiring up a separate UI, you download one file and run it like an app.
The core idea is distribution. A ‘llamafile’ includes the model weights plus a compiled runtime, built to run across multiple operating systems with minimal setup. It’s especially handy when an offline tool needs to be shared with teammates, students, or customers who won’t troubleshoot installs.
🧠 Fun fact: The first website is still visitable. CERN literally hosts it at info.cern.ch, calling it the ‘home of the first website.’
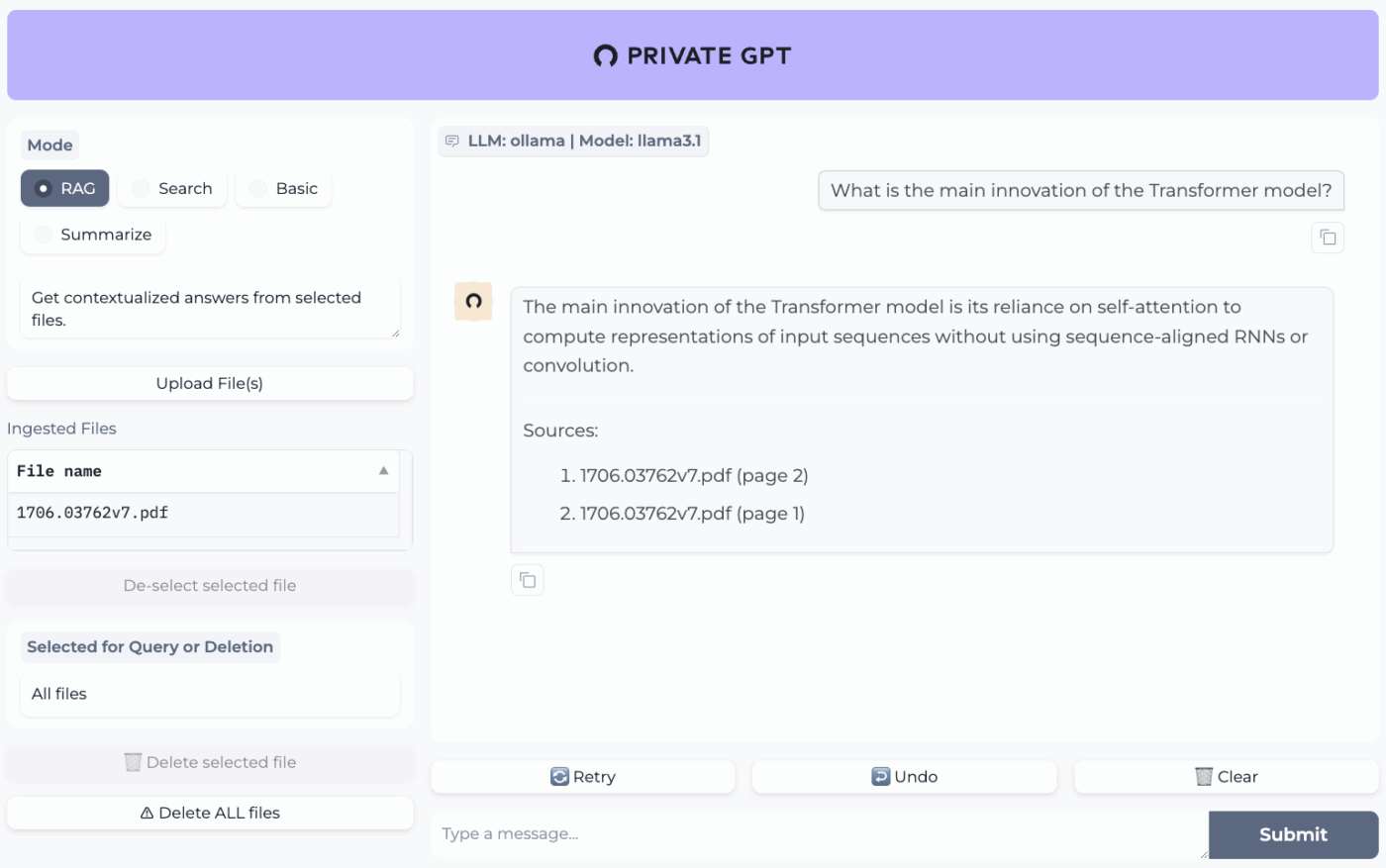
PrivateGPT is a production-ready, self-hosted project built for ‘chat with your documents’ workflows. It ingests local files, indexes them, and answers questions by retrieving relevant context from your own content instead of relying on a cloud chatbot’s memory. The project is designed to run fully offline, with the claim that data stays inside your execution environment.
What makes it different from general-purpose offline chat apps is the modular architecture. In other words, you can mix and match the LLM, embedding provider, and vector store based on your hardware and privacy constraints, then run everything behind a local API + UI.
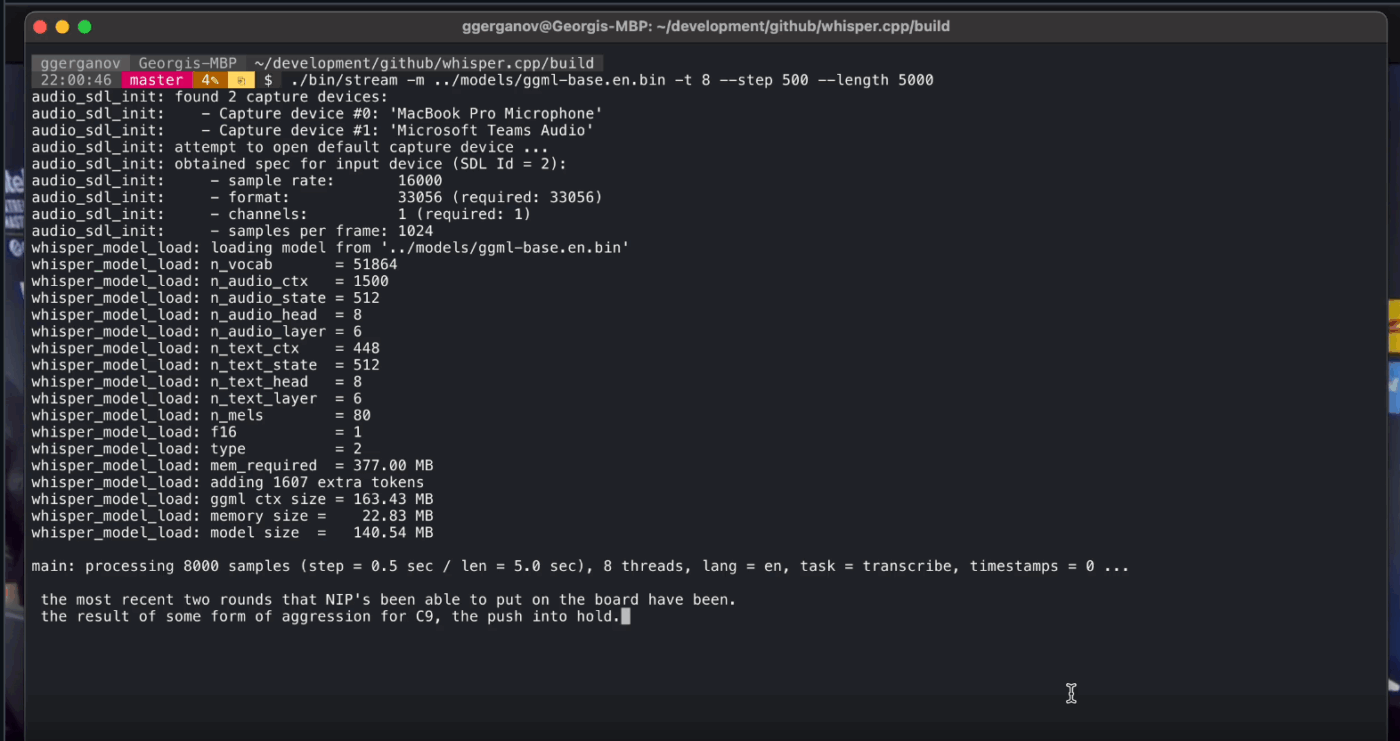
Whisper.cpp is a high-performance C/C++ implementation of OpenAI’s Whisper automatic speech recognition model, built to run locally without heavyweight runtime dependencies. It’s popular for offline transcription pipelines where you want a small, portable binary or a C-style library you can ship inside your own product.
It’s also flexible across environments, with official support spanning desktop, mobile, WebAssembly, Docker, and even Raspberry Pi-class hardware, which makes it a suitable fit for offline tools that need to run in more than one place.
The ‘cpp’ in its name signifies its focus on performance. This implementation is significantly faster and uses less memory than Python-based alternatives, making real-time transcription possible on modern computers without needing a powerful GPU.
Text Generation Web UI (often called ‘oobabooga’) is a Gradio-based web interface for running local models with a heavy emphasis on control and experimentation. It behaves more like a full workbench: multiple model backends, multiple interaction modes, and lots of knobs for generation behavior.
It also leans into ‘writer/dev’ workflows that many offline tools skip, with features like prompt-format automation, notebook-style generation, and conversation branching. For offline setups that still need a web UI, it’s one of the most configurable frontends in this category.
Llama.cpp is a C/C++ inference engine and toolchain for running LLMs locally with minimal dependencies and strong performance across a wide range of hardware. It’s less of a ‘chat app’ and more of a local runtime where you build workflows around, whether that’s a CLI, a local HTTP server, or an embedded library inside your own product.
While not an end-user application itself, Llama.cpp is the engine that powers many of the tools on this list, including GPT4All and LM Studio. It introduced the GGUF model format, which has become the standard for running large models on consumer hardware by efficiently reducing their size.
It also offers bindings for popular programming languages like Python and Rust, and its server mode can provide an OpenAI-compatible API.
A Sourceforge reviewer says:
Awesome. Democratizing AI for everyone. And it works great!
Picking the right offline AI tool is really about matching the tool to the job.
If you’re here, you’re probably optimizing for three things: privacy, no internet dependency, and freedom from being locked into yet another subscription.
The tools on this list deliver on that front in different ways. Meaning, some are better for writing and coding, others for search, notes, or creative work.
But for teams, the bigger challenge is not just running AI locally. It’s turning AI output into real workflows.
With ClickUp’s AI capability layered into your tasks, docs, and knowledge, you can easily surface next steps in the same place where work happens (all with enterprise-grade security).
Try ClickUp for free and see what it looks like when AI and execution finally live together. ✨
Yes, after an initial download of the model files, many AI tools can run entirely on your device with no internet required. This makes them perfect for handling sensitive data or working in locations with poor connectivity.
Local LLMs process all data on your personal device, so your information never leaves your machine, while cloud-based AI sends your prompts to remote servers for processing. Local tools are generally free to use after setup, whereas cloud AI often involves subscription fees but may offer more powerful models.
Smaller models with 1-3 billion parameters can run on most modern laptops with 8GB of RAM. Larger, more capable models with 7 billion or more parameters perform best with 16GB or more of RAM and a dedicated GPU, with Apple Silicon Macs and NVIDIA GPUs providing significant performance boosts.

© 2026 ClickUp

There’s an easier way. Try a free AI Agent in ClickUp that actually does the work for you—set up in minutes, save hours every week.