
The Constructivist Learning Theory states that we construct knowledge or learnings by reflecting on our experiences. This theory is largely based on metacognition, which refers to ‘reflecting on our thinking.’
Metacognition involves analyzing our thoughts or being self-aware of how we process our thoughts. By improving our metacognition skills, we can identify gaps in our prior knowledge, enhance our learning, and cultivate a growth mindset.
Whether you’re a student preparing for an exam or a professional looking to accomplish your career goals, metacognition skills can help you grow significantly in both aspects of life.
Let’s look at what metacognition skills are and how you can develop these skills to achieve success.
What are Metacognition Skills?
Metacognition skills is an umbrella term for several techniques that enhance self-awareness abilities; to identify and improve your current thinking process. It focuses on how we channel our thinking to set goals, solve problems, and achieve objectives through self-directed learning processes.
Think of metacognition as the science behind our thinking process where we intentionally monitor and try to understand our thoughts.
It involves three simple steps:
- Planning: Focus on a specific problem and figure out the best strategy to solve it
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor your progress as you implement various strategies
- Evaluating: Review your learnings and achievements after completing the task
Elements and components of metacognition
Two vital elements contribute to your metacognition process. They are:
Metacognitive knowledge
It tells you about your cognitive abilities and thought processes—whether you are good at memorizing complex concepts, how much time you take to read and understand a page, how long you can focus before your attention drifts, whether or not you struggle with decision-making, etc.
Applying metacognitive knowledge to a task helps you learn about your strengths, weaknesses, and thinking patterns and how you can leverage them to finish the task effectively.
Metacognitive strategies
Metacognitive strategies involve monitoring and managing your cognitive processes to ensure you are on the right track to meet your objectives. You can practice these metacognitive strategies to improve efficiency and achieve your goals:
- Create to-do lists to prioritize your tasks and break them into subtasks
- Design elaborate project plans with milestones, resources, and deliverables to deliver successful projects
- Learn new skills to enhance your knowledge
Varying learning styles
Metacognition skills develop based on different learning styles and how you take in and process the information. There are four predominant learning styles educators use to help students develop metacognitive skills:
- Visual learning: It uses visual elements like graphs, pictures, and charts to display information and teach new concepts
- Auditory learning: The auditory learning technique involves lectures and group discussions as a part of learning
- Reading/Writing learning: Such learning styles use reading plenty of books and writing down key concepts in your own words
- Kinesthetic learning: It’s the most engaging learning style which promotes learning through doing
10 Metacognition Skill Examples
Let’s see the 10 metacognition examples to improve your productivity and enhance your cognitive processes:
1. Goal setting
Goal-setting is one of the vital habits of highly effective people. When you set goals, you intentionally focus on your ambitions and plan steps, processes, or milestones to achieve your objectives. This gives you clarity on the possible challenges and helps you find the most effective strategies for success.
But goal setting is not coming up with some random plan of attack. You need to set goals that are:
- Specific: Articulate your goals clearly so you know exactly what you need to focus on
- Measurable: Make your goals quantifiable to keep yourself motivated
- Achievable: Set achievable goals that you know you can achieve
- Relevant: Define goals that are relevant to your learning objectives or business outcomes
- Time bound: Set timelines to achieve your goals to stay disciplined
2. Problem-solving
Sometimes, you may feel stuck with a work problem, unable to find a way out. That’s probably because you’re assessing the issue at the surface level, trying to find band-aid solutions. However, metacognition skills make you consciously think of your problems, find their root cause, and devise the best possible way to solve them.
3. Reflection
Taking time to reflect upon past actions and thoughts helps you gain meaningful insights. In metacognition, reflection is a three-step cyclical process:
- You finish a task
- Reflect upon how you did
- Evaluate and look for areas of improvement
Once you become good at self-reflection, you become flexible, and it becomes easier to adapt to new and appropriate cognitive strategies while working on a task.
4. Planning
The planning phase is one of the best examples of metacognitive skills for educators and leaders. You assess available resources and implement the best methods of learning or leading.
When you prepare a clear roadmap for project management or learning, you anticipate potential growth opportunities and challenges and can act on them to achieve your goals faster.
5. Self-assessment
Self-assessment is the foundation for analyzing one’s strengths and weaknesses, an idea central to the metacognition strategy.
Knowing your strengths and weaknesses helps you enhance your performance and overcome challenges easily.
You can use a SWOT analysis for self-assessment. It stands for:
- Strength: Identify your core capabilities
- Weakness: Find skills or processes that you can improve
- Opportunity: Identify opportunities you can pursue based on your strengths
- Threats: Identifying potential risks that can restrict your personal or professional growth
6. Self-questioning
Asking questions to yourself while learning new concepts involves self-awareness and reflective thinking skills, which makes it a perfect metacognition example.
Self-questioning piques curiosity and interest and helps you analyze concepts better.
7. Monitoring
How do you assess whether you are on track to achieving your goals? By continuous observation and analysis.
It’s one of the classic metacognition examples involving self-assessment, analyzing strengths and weaknesses, and self-regulating activities.
Using reflective questions to monitor your thinking, you can identify factors that are holding you back from new learnings and find ways to overcome them.
8. Active reading
Active reading is more than just reading for pleasure. It involves monitoring your comprehension abilities and requires total concentration. You can improve your reading strategies by summarizing chapters or finding deeper connections between different chapters.
9. Concentration
Concentration is about ‘saying no to everything’ to ‘say yes to the one thing.’ It helps you build self-discipline keeping aside the mental discomfort caused by it.
However, concentration doesn’t mean only focusing on a specific task. It also requires continuous self regulation of your attention, which is a metacognition skill.
10. Testing
Self-testing is slightly different from self-assessment. In assessment, you analyze your strengths and weaknesses. In self-testing, you challenge yourself with questions to review your learning.
How to Develop and Strengthen Your Metacognition Skills
Here are the top three ways to enhance your metacognition skills:
1. Self-reflection and self-questioning
Introduce questions into your learning process to help process thoughts consciously. When you ask yourself questions like, “What was my thought process behind learning this?” or “How can I improve my approach next time?” you are prompting yourself to reflect upon your knowledge and strategies.
This stimulates deeper thinking of our mental states and helps to make adjustments for further exploration.
Self-reflection, on the other hand, involves consciously thinking about your past experiences to gain meaningful insights and improve future performances.
Journaling is an excellent reflective practice that involves recording your feelings and observations. It enhances self-awareness, allowing you to understand your cognitive process and change it accordingly.
2. Active reading and active listening strategies
Active reading requires a more strategic approach than just skimming through the texts. Use these simple techniques to make reading more fun and fast:
- Highlight important texts: Underline key phrases and points to identify what’s important without repeating the whole text. However, avoid too much underlining as it can create confusion
- Take notes: Take notes as you read to identify key ideas and retain information easily
- Use Feynman technique: This is an excellent four-step technique to improve learning capabilities. It focuses on ditching memorization and learning concepts. Feynman technique involves:
- Selecting a concept to learn
- Explaining or teaching what you’ve read to yourself and others
- Referring back to the original source if you are unable to understand something
- Simplifying the topic explanations by using analogies
3. Setting goals and planning ahead
Setting goals gives you clarity and helps overcome mental blocks before starting a new project.
However, set realistic time-bound goals so that you can monitor their progress effectively.
For instance, learners who plan ahead by developing study schedules and checklists tend to stay more focused and manage their time wisely.
Techniques for boosting critical thinking & creativity
Here are a few effective techniques you can use to sharpen your critical thinking and creativity:
- Brainstorming: It’s a time and-tested ideation technique where you generate as many rough ideas as possible and combine them to find an ideal solution
- Mind-mapping: It’s a visual technique that enhances your critical thinking as you establish a relation between multiple ideas
- First-principles thinking: Elon Musk suggested this mental model as one of the best ways to stimulate critical thinking and creativity. It involves breaking down a problem into smaller, most basic segments to find unique solutions
- Role-playing: Role-playing exercises allow you to step into different shoes and adopt a different thinking approach. This boosts your creativity and helps find unique and innovative solutions. At the same time, it also encourages you to consider their implications and challenge your critical thinking abilities
- Six-Thinking Hats: Six-thinking hats is a transformative concept introduced by Edward De Bono to enhance creativity and decision-making in a group where everyone adopts a different style
Potential obstacles in developing metacognition skills and how to overcome them
Beware of these potential obstacles that can be a roadblock in developing metacognition skills:
- Negative or no feedback: Negative criticism blocks the metacognitive skill growth. It doesn’t provide learners the chance to assess their knowledge and mistakes
- Narrow mindset: The idea that people are born with certain skills and abilities that can’t be changed. This mindset is a red flag to developing metacognitive awareness
- Being ignorant: Being rigid and refusing to acknowledge your strengths and weaknesses hinders the growth of metacognitive skills.
- Rote learning: Over-reliance on memory without understanding impedes metacognitive development. Introduce active learning strategies like brainstorming to improve metacognition skills
Role of constructive feedback in deepening metacognitive skills
Constructive feedback plays a vital role in developing metacognition skills. We can better analyze and improve our learning strategy and management processes by receiving specific feedback about our performance and strategies.
The Role of Technology in Boosting Metacognitive Skills
Technology has transformed our learning and work processes, making them more personalized and automated.
We can use tools to plan our days, set task reminders, collaborate with others, and monitor our progress. This helps us build focus and achieve our objectives.
With ClickUp, an all-in-one project management tool, you can simplify goal setting.
Whether you’re managing personal or team goals, ClickUp can help you break down problems into an actionable plan and apply metacognitive strategies. It helps you improve all three aspects of metacognition: planning, monitoring, and evaluation.
Setting realistic goals is key when working with metacognition strategies. ClickUp Goals can help you set high-level goals and break them down into smaller targets, which you can then use to track progress. This helps build a productive mindset. When implemented in a work scenario, this empowers your coworkers to track their progress and evaluate whether they’re on the right path.
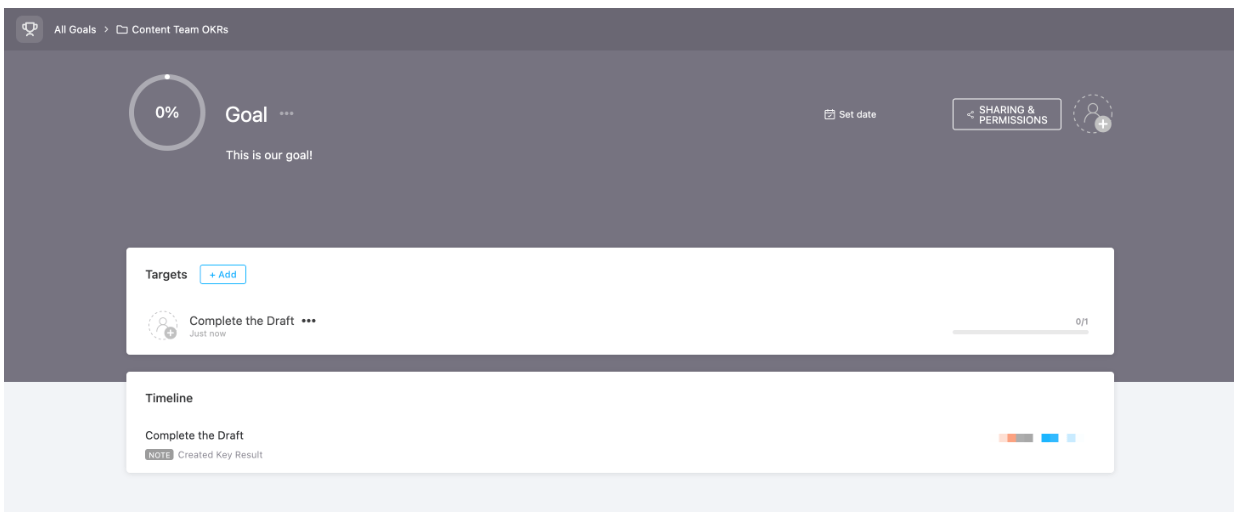
If you want to apply metacognition strategies at a project level, try ClickUp’s Personal Project Management Software to plan and prioritize your projects using tasks and sub-tasks, and streamline workflows. From planning out each individual step to staying on track and monitoring progress, ClickUp can help build metacognition strategies into your personal projects.

If you often run into blockers at work because your documents are scattered across different workflows. Use ClickUp Docs to access all the information in one place, spot any critical gaps and collaborate with your team members in real time.
When combined together, these three ClickUp features can help you practice metacognition in your personal and professional lives. Whether you need to improve your goal-setting skills or monitor your strategies better, we’ve got you covered.
Pro tip: Try our ready-to-use goal setting and tracking templates for some inspiration.

The Benefits & Limitations of Metacognitive Skills
Let’s see how metacognitive skills impact different aspects of our lives:
Metacognitive skills & academic achievement
Several studies show that students with high metacognitive skills achieve greater academic excellence.
The metacognitive process includes self-awareness and self-evaluation, both of which are essential for academic growth. This helps students understand their cognitive process, leading to improved attention and comprehension abilities.
Role of teacher in developing metacognitive skills
In an academic setting, metacognition is all about students taking charge of their own learning process. However, the role of a teacher is undeniable in helping them develop those particular strategies.
Defining learners’ levels is the foremost step in developing metacognition skills. To assess their intellectual thinking and problem-solving skills, give them challenging tasks slightly beyond their reach. Performing difficult tasks encourages students to expand their knowledge and indulge in higher-order thinking, which reflects their metacognitive abilities.
Once you’ve determined their learning abilities, you can devise a lesson plan that encourages your students to develop metacognitive skills.
Real-life advantages of metacognition skills
Metacognition examples are not limited to academia. It’s one of the fundamental life skills that offers several real-life advantages that result in:
- Better social interaction: Practicing metacognition examples like active listening and self-awareness helps understand other’s viewpoints, resulting in better social interaction
- Mental well-being: Evaluating your own thinking processes also makes you learn more about what makes you happy or what bothers you. Understand your preferences to make better choices and improve your overall well-being
- Fulfill personal goals: Whether you want to take a new hobby or start a new habit, monitoring your progress on the go makes you think clearly, increasing the chances of success
- Better professional life: Problem-solving and critical thinking are the cornerstone of success in the business world. Incorporating metacognition examples into your life empowers you to perform better at work
Potential drawbacks of using metacognitive skills
Actively engaging in metacognition examples improves your cognitive capabilities. However, it’s not always as helpful as you would think.
Here are four potential drawbacks of using metacognitive practices that you should know:
- Leads to burnout: Constantly engaging in self-monitoring and analyzing processes can be overwhelming and lead to burnout
- Interferes with actual tasks: Continuous reflection and adjusting actual learning strategies can sometimes interfere with the task performance
- Time-consuming: Engaging in metacognitive strategies can be time-consuming, leaving little time for the completion of the task
- Over-critical: Repeated involvement in self-evaluating processes can make learners over-critical about themselves, leading to poor mental health
Dunning-Kruger effect
The Dunning-Kruger effect is a cognitive bias that explains why low-ability people often claim they’re the smartest in a room. The theory explains that low-ability people don’t possess the necessary metacognition skills to evaluate their and others’ strengths and weaknesses. That’s why they overestimate their capabilities and skills and underestimate others. This can mislead people into thinking they have superior abilities.
Use ClickUp to Improve Metacognitive Thinking
The greatest advantage of learning metacognition skills is that once you learn them, you can apply them in all walks of life, whether it’s education, professional development, or personal growth.
However, learning metacognitive skills requires consistent practice. Self-reflection ain’t easy! You can start by writing down your thoughts and ideas to process them better, set goals, manage tasks, and monitor progress. ClickUp helps you do all of this and a lot more. It provides a wide range of tools and templates to plan, assess, and track your tasks, enabling you to achieve your goals faster.
Sign up for ClickUp for free to enhance your metacognitive skills!



