Level Up Your Planning: Learn the Difference between Goals & Strategies

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Buzzwords are sprinkled like confetti in the world of business, confusing leaders and eventually setting them up for failure. It’s especially true when they sound no different than everyday words.
Yet, amidst the jargon, one framework stands clear: the GOST business model, representing Goals, Objectives, Strategies, and Tactics.
Businesses go through ever-shifting tactics and mediums. So, mastery of the GOST principles is essential for flourishing in such a dynamic space.
The GOST framework comprises four key ideas:
Whether planning a business, forming a company strategy, or working on a communications strategy, understanding the differences between the components of the GOST framework is key to effective strategy development.
In this article, we’ll explore the GOST model and break down the concepts of goals and strategies. From types and examples to step-by-step approaches and tips, we’ve covered every base so you know how to implement them for your business.
A goal is a specific, measurable target you aim to achieve within a time limit.
For a business, a goal is a big, long-term achievement that is feasible and attainable within a certain time and with the resources available. Goals align with the company’s core values and convey what it wants to achieve.
For example, if a company cares a lot about its consumers, it might aim to improve its customer experience in the next year.
Setting goals you can reach regularly, maybe daily, is crucial. Unrealistic and impossible goals can easily deter you from the path of potential success.
Goals are also important in strategic planning. Let’s see how.
Strategic goals are indispensable. Not only do they give your company a clear direction and purpose, but they also aid the process in the following ways:
Inspiration and willpower might not be enough to make your business goals work. Think about using goal-setting strategies, which help you set goals with direction and focus.
Some of the most common techniques of goal setting are:
Here are some examples of sales, customer service, product development, and marketing goals in different businesses:
Goal: Sell more to make 15% extra revenue this quarter.
Goal: Make customers happy, aiming for a satisfaction rating of 90% or higher, in a year.
Goal: Add two cool features in the next six months to improve the product and stay competitive.
Goal: Get more people to know about you—aim for a 25% increase in brand awareness through social media marketing efforts and partnerships next year.
What does a strategy look like if all these are examples of goals?
A strategy is a plan to reach a goal; it’s how you decide to get from one point to another.
Whether simple or complex, all strategies are built on goals and timeframes, focusing on what you want to achieve and when. For instance, if your business aims to expand into a new market, you’d create a growth strategy to increase market influence and develop new processes.
In the GOST model, strategies fall under the ‘how’ category. They differ from plans, which are more specific and short-term. Strategies serve as blueprints, helping with decisions, resource use, and operations necessary to achieve goals.
A detailed strategy might involve studying the market, researching competitors, and planning product development, marketing, and sales to boost market share or profits.
But how exactly does a business strategy help you reach your goals? It helps you develop:
Yes, the benefits a strategy offers are impressive, but before you start making strategies, you should know that there are various types. Let’s understand each type.
One of the key elements of your business strategy is market segmentation.
Take a look at your audience; what do you see?
Are they all the same age and gender or from the same place? Do they have similar incomes and education levels or face the same problems and desires?
Chances are, your target audience is diverse. Your marketing process might miss the mark if you don’t consider this diversity. This is where the market segmentation strategy comes in.
Segmentation means dividing your large market into smaller groups with specific traits or needs. A market segment is simply a group of people with similar traits in your big group of potential customers.
For example, you have different audiences in the athletic shoe market, such as serious athletes, dog walkers, and style lovers. Then there are older people looking for comfortable, stable shoes.
Knowing these groups helps marketers adjust their plans, making their offers more attractive to specific parts of their larger target audience.
But is that the only kind of strategy out there? Not at all.
Here’s a closer look at the different types of strategies leaders use for different contexts:
Corporate-level strategies focus on the big picture and guide actions, decisions, and resource allocation to move the company in the right direction.
A strategy like this is often framed and set by the C-suite at the corporate level of an organization. It usually focuses on significant matters like mergers, acquisitions, portfolio management, and diversification.
For example, a tech company expanding into new products or markets (like smartphones or smart home devices) different from what they currently offer (computers and laptops).
Operational-level or functional-level strategies focus on specific business departments, such as HR or finance, to help the company succeed.
Usually, different departments, like marketing or operations, create strategies that align with the overall business goals. When these plans work together well, the company achieves its objectives.
Operational strategy acts like the muscles behind the business plan. It fine-tunes daily activities by making operations smoother, using better technology, and improving supply chains for efficiency.
For example, Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy aims to build emotional bonds with customers using its well-known branding and storytelling.
Business-level strategies zoom in on how a company competes in the market, making decisions about products and customer segments and standing out from competitors.
This strategy ensures the company makes clever moves to succeed and achieve long-term goals, impacting every department and aspect of the organization. It involves making clear choices about how to gain a competitive advantage, whether through differentiation, pricing, or market expansion.
An example of this is the cost leadership strategy. In this strategy, the company aims to be the lowest-cost producer in your industry. For instance, Walmart offers low prices daily, aiming to be the most cost-effective brand in retail.
Now that you know all about strategies, the next big question is: how do you plan one?
Strategic planning creates a clear and practical framework for your company by answering three main questions: Where are you now? Where do you want to be? How will you get there?
It includes reviewing your organization’s mission and goals and examining the competition to create a strategic plan. This plan is then shared with everyone in the company and implemented. Without one, you might spend time and resources on things that won’t help your company.
An ideal strategic plan covers all important areas, lets you measure success, and allows adjustments when needed. This way, your company can always be ready for the future with a strategy that matches its vision and mission.
The strategic planning process consists of seven main components that work together to create clear plans for your business goals:
If not understood carefully, these elements might sound the same to leaders and confuse them, ultimately leading to a botched strategic plan and incomplete goals.
You can avoid that with this 5-step approach to simplify the strategic planning process:
Strategies vs. goals still sound a little confusing. We’ve got you. The key differences between goals and strategies are:
| Goals | Strategies |
| Goals are like destinations—the desired outcomes your company aims to reach. | Strategies are how you achieve your goals. |
| Goals are open-ended and flexible, changing with circumstances and adjusting to your needs. | Strategies are specific and detailed, leaving less room for changes. |
| Unlike a manual, goals don’t come with step-by-step instructions. | Strategies are logical, step-by-step processes that should be executed in order. |
| Goals motivate and give your business a sense of purpose and direction. Meaningful goals drive us to work harder and stay energized. | Strategies are practical and analytical. They help assess situations, spot obstacles, and create doable action plans for goals. |
| Just setting a goal doesn’t ensure success. | Unlike goals, strategies ensure the plan is executed correctly and moves things forward. |
| Goals lay the groundwork for creating strategies. | Strategies are based on the goals you’ve set. |
We understand that setting outcome-oriented goals and planning strategies can be stressful. And nobody wants unrealistic goals or ineffective strategies. So, here are some tips to make things simpler for you:
Trusted by teams worldwide, ClickUp is a highly-rated project management software that combines goal-setting and strategic planning features in one place.
It offers a complete set of tools for teams to plan and prioritize tasks and handle projects. With visual templates for goal-setting and strategic planning, project managers can easily kickstart the creation process.
Whether scheduling goals on a dynamic calendar or brainstorming business strategies on customizable whiteboards, this all-in-one platform can boost your planning success.
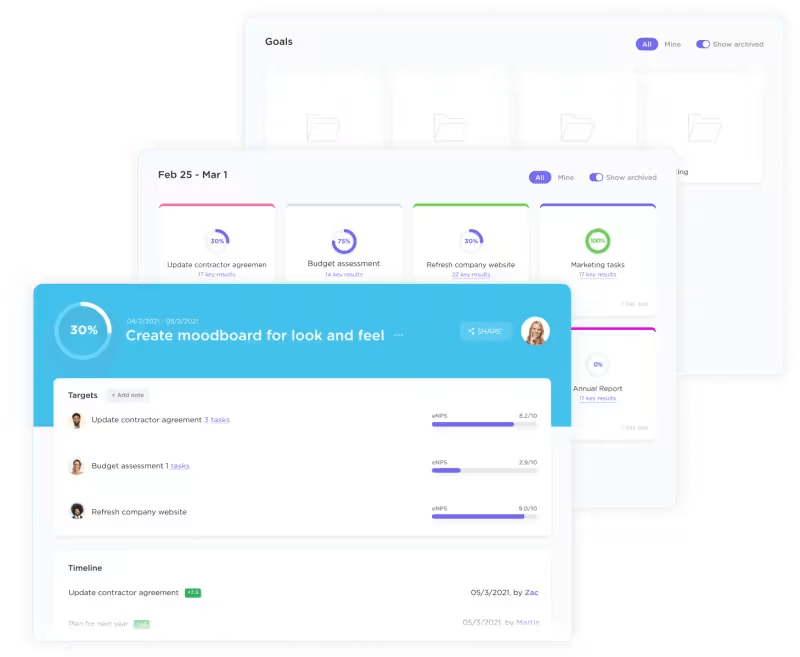
With ClickUp Goals, you can create goals connected to your business vision and mission, ensuring you and your team have a clear path to success.
With easy-to-understand timelines, measurable targets, and automatic progress tracking, achieving your objectives becomes faster and more straightforward. ClickUp Goals also allows you to measure success using various targets such as numbers, money, yes/no, and task-related goals.

Keep everything organized in user-friendly folders, whether sprint cycles, OKRs, or weekly employee scorecards. Easily track progress by grouping related goals and setting deadlines to stay on schedule.
However, if you’re short on time, simply use the ClickUp SMART Goals Template to get started. It comes with ready-made, customizable statuses for your goals, up to 12 fields for recording different goal attributes (due dates, people involved, targets to be achieved, etc.), and five views to give you a complete picture of your goals and their progress.
The Getting Started Guide provides step-by-step instructions for implementing the template. The SMART Goals View lets you create and organize your goals. Using this template, you can also measure the effort required for each goal and track team goals.
The template has plenty of room to brainstorm and store all of your ideas with the SMART Goal Worksheet view.
ClickUp simplifies the creation of business strategies with its huge library of strategy templates and whiteboards.
ClickUp’s Project Strategy Template defines your OKRs, manages corresponding tasks, and helps you track important project segments such as timelines, costs, and resources.
The template offers custom statuses (think sections for Completed, In Progress, and Not Yet Started), custom fields (like Completion Rate, Project Phase, etc.), and views to help you visualize and manage your projects better.
Use this template to:

However, if you want to start from scratch, head to ClickUp Whiteboards. Sit down with your team, brainstorm ideas, jot important points down on a free-flowing, creative canvas, and collaborate on strategies in real-time.
You’ll have access to features like sticky notes, text boxes, shapes, highlights, and more. You can also complement your text-heavy discussions with multimedia elements like images for greater visual clarity and understanding.
Once your ideation is done, immediately turn your discussions and strategies into trackable goals, actionable tasks, and more—all on the Whiteboard.
Clear goals and smart strategies lay the path to success in any company. If you want your team to understand the ABCs of goals, objectives, strategies, and tactics, use the GOST framework.
However, juggling everything all at once with too many platforms can often lead to confusion and, ultimately, failure. This is where ClickUp helps.
It’s an all-in-one project management platform that brings goals, objectives, and strategies together within a single, collaborative workspace.
With 1000+ integrations and a comprehensive suite of tools to manage projects, tasks, and goals, ClickUp is the only tool you need to supercharge your planning process and bring transformative results.
Sign up to ClickUp today for free and achieve your business goals!
Goals typically come before strategies in the planning process. Goals are the desired outcomes an organization aims for, setting the direction. Once goals are established, strategies are developed as detailed plans outlining how to reach those goals. In essence, goals provide the destination, and strategies are the routes.
An example of a goal is a company aiming to increase sales by 20% within a year. The strategy to achieve this goal might involve launching a targeted marketing campaign, expanding into new markets, and optimizing pricing strategies. Goals specify what the organization wants to achieve, and strategies outline the specific actions and plans to make those goals a reality.
A strategic vision is a big picture of where a company wants to go, while a goal is a specific, measurable target to achieve within a certain timeframe. The vision is broader, guiding overall direction, while goals are more specific and actionable.
© 2026 ClickUp