How to Implement Secure Coding Using Amazon Q in ClickUp
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

According to a Consortium for Information & Software Quality study, software defects cost the US economy $2.41 trillion annually, with security vulnerabilities accounting for a significant portion of that waste—a problem that persists as 45% of U.S. companies still report quality issues costing them $1-5 million annually.
This article walks you through implementing secure coding practices using Amazon Q Developer’s AI-powered scanning directly in your IDE. You’ll also learn how to track and remediate those vulnerabilities in ClickUp to close the loop between finding issues and actually fixing them.
Your team is shipping code, but security scans happen so late in the process that they feel like an afterthought. By the time a vulnerability is flagged, the code has been committed, reviewed, and maybe even deployed.
The ClickUp Software Development Template is built for product, design, engineering, and QA teams to plan, build, and ship in one collaborative space. Scrum or Kanban? It’s all here.
This forces your developers to stop what they’re doing, dig through old code they barely remember writing, and try to fix a problem that should have been caught days ago. This constant context switching kills momentum and creates friction between development and security teams.
This is the problem that secure coding with Amazon Q Developer solves. It’s an approach that uses AI-assisted tools to identify and fix security vulnerabilities directly in your integrated development environment (IDE) as you write the code.
This matters for any team shipping production code, whether you’re building internal tools or customer-facing applications. Manual code reviews can’t scale, and standalone security tools often generate noisy, generic alerts that developers quickly learn to ignore.
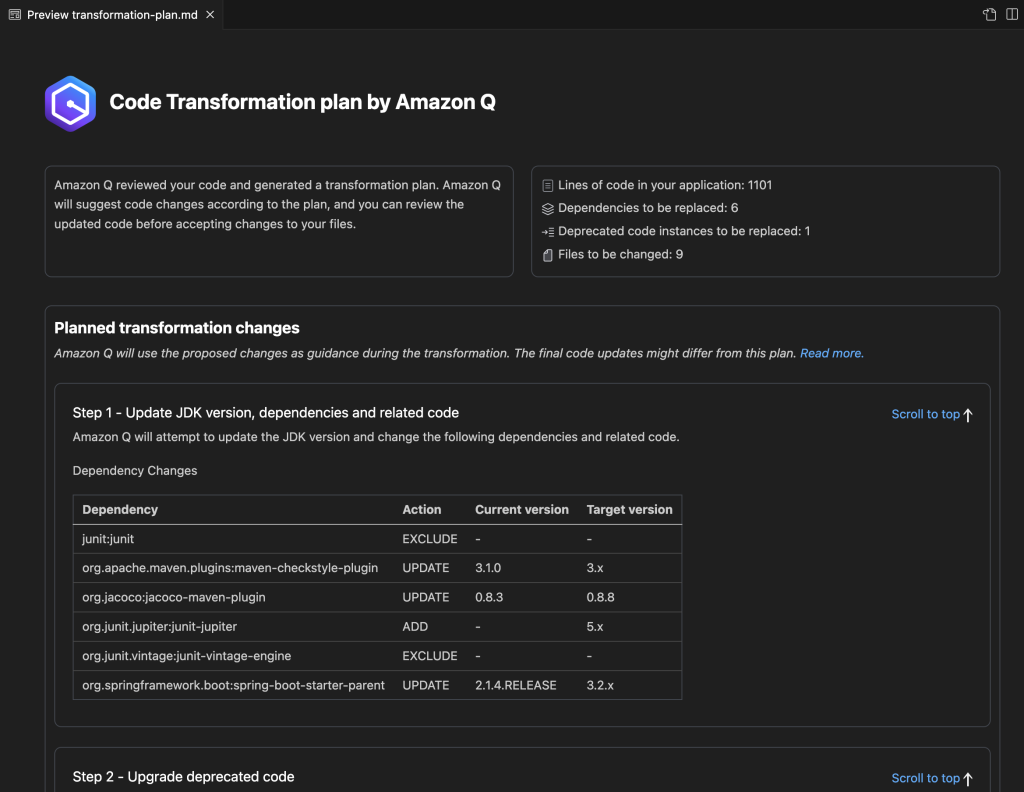
Amazon Q Developer integrates static application security testing (SAST) directly into your coding workflow. It analyzes your code in real-time, flagging common but dangerous issues before they ever get committed.
Amazon Q doesn’t just identify problems—it generates specific remediation code you can review and accept with a single click. Security becomes a natural, helpful part of the development process instead of a frustrating roadblock. Your team can now write more secure code from the start, reducing the time and cost of fixing vulnerabilities later. ✨
Before diving into Amazon Q Developer specifically, it’s helpful to understand the broader landscape of modern coding tools that can enhance your development workflow. This video provides an overview of various vibe coding tools that developers find valuable for improving their productivity and code quality.
Running a scan is the first step, but knowing when and how to scan is what makes the process effective. The goal is to catch issues before they ever reach version control, making your entire development lifecycle more secure.
Amazon Q offers multiple scanning modes to fit your workflow, whether you prefer on-demand checks, continuous background analysis, or automated pipeline gates.
These scans work across a variety of popular programming languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#, Go, Ruby, C/C++, PHP, Kotlin, and Scala, with varying depth of analysis.
First, ensure you have the necessary prerequisites: an AWS account or a free AWS Builder ID for authentication, a supported IDE (such as VS Code, a JetBrains IDE like IntelliJ or PyCharm, or Visual Studio), and properly configured AWS credentials with the permissions required to run security scans.
With those in place, follow these steps to get started:
If you find that scans aren’t triggering as expected, first check that the file’s programming language is supported by Amazon Q. Next, verify that your AWS credentials are correct and have the necessary IAM permissions for security scanning.
📚 Also Read: How to Build DevOps Workflows Using Amazon Q
Amazon Q gives you two primary ways to scan your code locally: project scans and auto-scans. Each serves a different purpose in your workflow.
Project scans are manually triggered analyses of your entire codebase or specific directories you select. Think of these as a comprehensive check-up for your code. They are perfect to run before you create a pull request or commit a large set of changes, ensuring you haven’t introduced any new vulnerabilities.
To run a project scan:
Auto-scans (available with Amazon Q Developer Pro) provide continuous, real-time feedback by scanning files in the background every time you save them. This catches issues the moment they’re written, preventing them from ever becoming part of a larger problem.
You can enable this feature in your settings to get instant alerts without interrupting your flow. If you find the alerts too noisy during heavy development, you can adjust the sensitivity to only show high-priority findings.
Finding a vulnerability is only half the battle; you also need to understand and fix it. Amazon Q makes this easy by providing rich context for every finding. Each alert includes:
When you’re ready to apply a fix, simply click on the finding to review the detailed explanation and the proposed code change. If the suggestion looks good, you can accept it to apply the fix automatically. For more complex issues related to your specific business logic, you might need to modify the suggestion slightly.
Use the AI-generated code as a reliable starting point, not always the final answer. After applying the fix, you can re-scan the file to confirm the vulnerability is resolved. 🛠️
🎥 Watch this video to learn how to create an effective code review checklist.
While local scans are great for catching issues early, integrating security into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline creates an essential security gate. This automated check ensures that no vulnerable code makes it into your main branch or gets deployed to production, which is a cornerstone of any modern AWS DevOps security strategy.
You can add an Amazon Q scanning step to any major build pipeline, including AWS CodePipeline, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins. The key is to configure it to run automatically on pull requests and commits to your main branch.
Here’s a common configuration:
| Pipeline Stage | Scan Type | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Pull Request | Incremental Scan | Block the merge if any critical or high-severity vulnerabilities are found |
| Main Branch Commit | Full Project Scan | Block the build on critical findings, and send warnings for medium-severity ones |
| Scheduled (Nightly) | Comprehensive Scan | Generate a full code scan report for compliance and trend analysis |
When setting this up, you need to balance security thoroughness with build speed. Running a full project scan on every single commit can slow down your CI process. A good compromise is to use faster incremental scans on pull requests and reserve full, comprehensive scans for merges to the main branch or for scheduled nightly builds.
Finally, configure your pipeline to export the scan reports in a standard format like SARIF for your compliance and audit trails.
📮ClickUp Insight: 1 in 4 employees uses four or more tools just to build context at work. A key detail might be buried in an email, expanded in a Slack thread, and documented in a separate tool, forcing teams to waste time hunting for information instead of getting work done.
ClickUp converges your entire workflow into one unified platform. With features like ClickUp Email Project Management, ClickUp Chat, ClickUp Docs, and ClickUp Brain, everything stays connected, synced, and instantly accessible. Say goodbye to “work about work” and reclaim your productive time.
💫 Real Results: Teams are able to reclaim 5+ hours every week using ClickUp—that’s over 250 hours annually per person—by eliminating outdated knowledge management processes. Imagine what your team could create with an extra week of productivity every quarter!
📚 Also Read: DevOps vs Agile: Ultimate Guide
Finding vulnerabilities with a scanner is a great first step, but it’s useless if those findings get lost in a spreadsheet or a separate ticketing system.
When security alerts live in one tool, development tasks in another, and team communication in a third, you create context sprawl—where teams waste hours hunting for information across disconnected apps. This disconnect is where vulnerabilities fall through the cracks, deadlines are missed, and your security posture weakens.
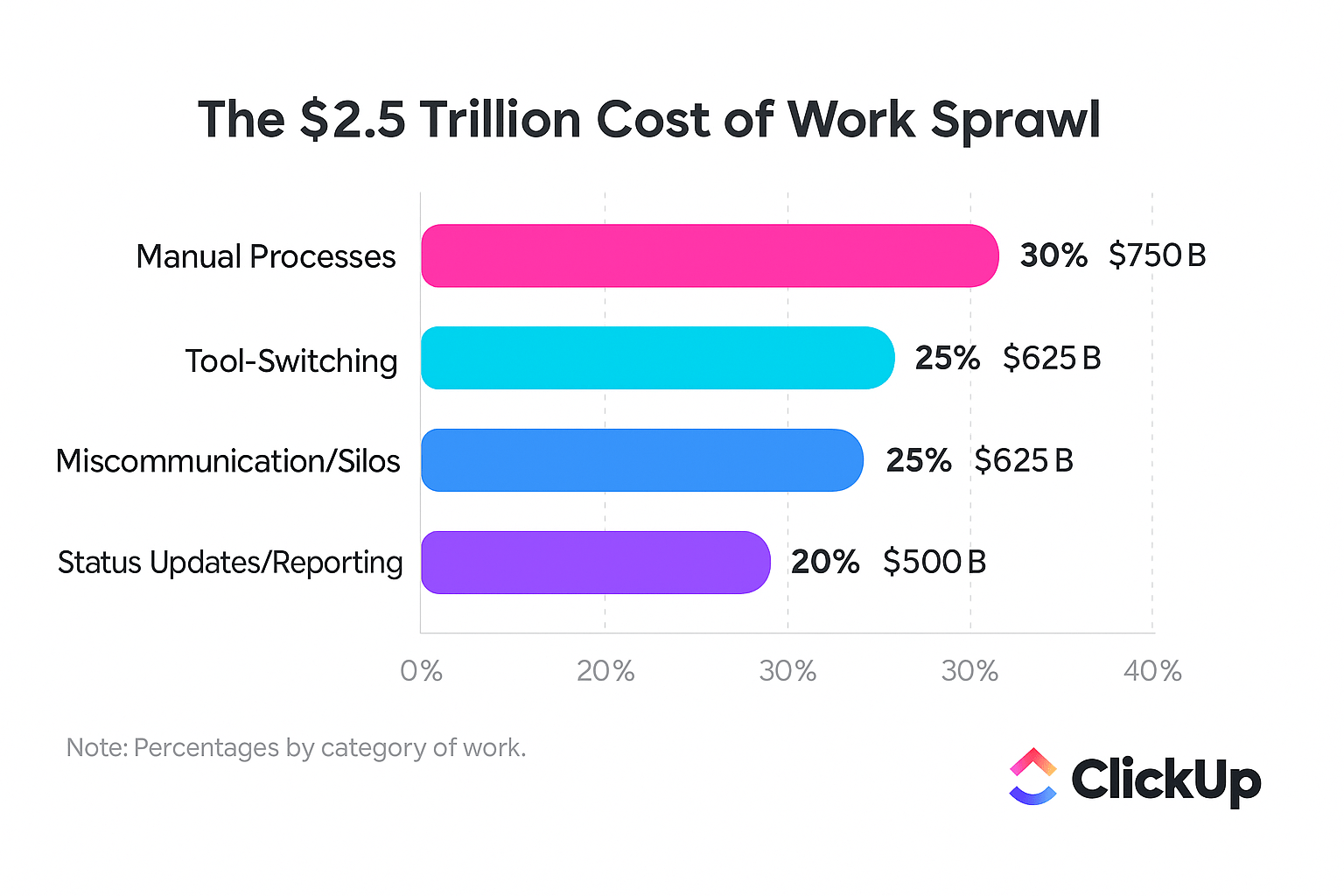
Eliminate this work sprawl by consolidating your entire vulnerability remediation workflow in ClickUp. This provides a single source of truth where you can turn scan results into actionable tasks with clear ownership, priorities, and deadlines.
Start by creating a dedicated ClickUp List or ClickUp Folder for all security issues. This keeps them organized and visible to the entire engineering and security teams.
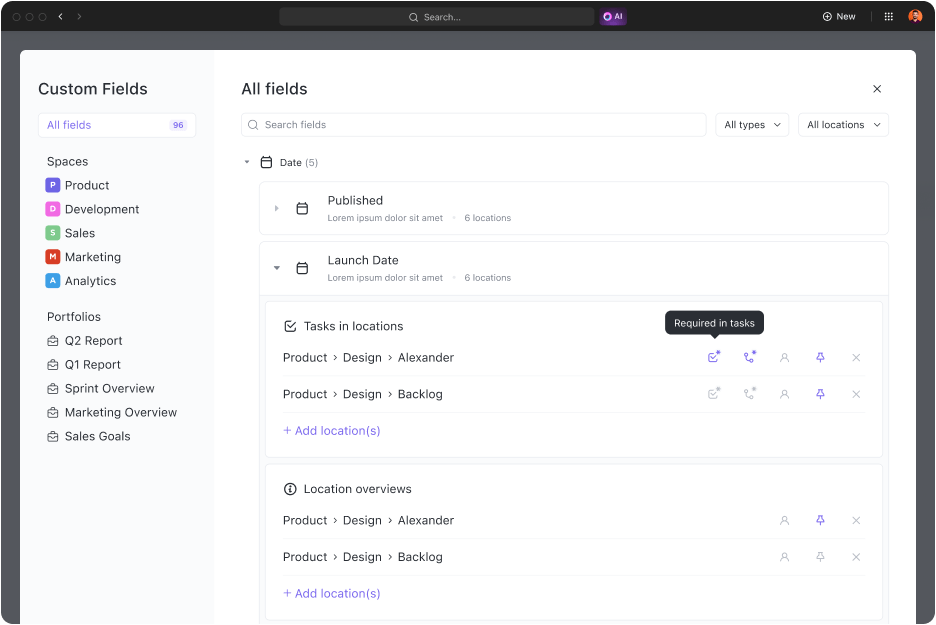
Stop wasting time manually copying and pasting data between tools. Use ClickUp Custom Fields to capture all the critical information for each vulnerability. You can create fields to track:
Next, put your triage process on autopilot with ClickUp Automations. Instead of a manager manually assigning every new ticket, build rules that do it for you.
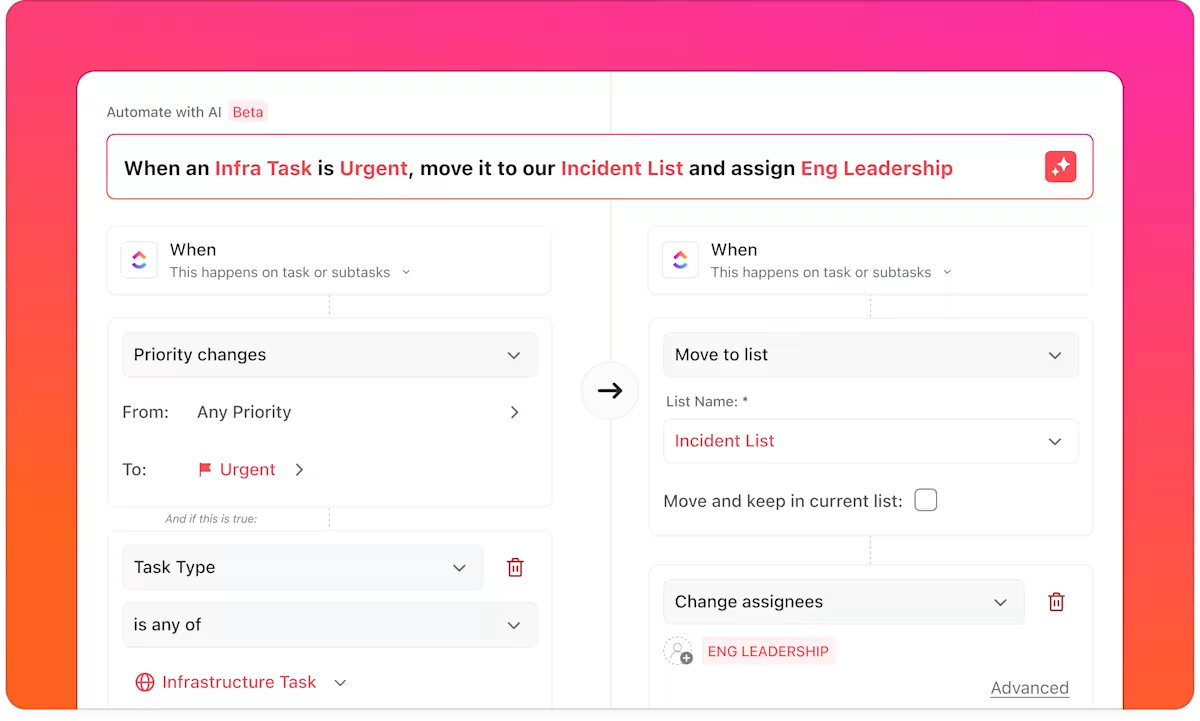
For example, an Automation can be triggered whenever a new task is created: if the severity is “Critical,” the task is automatically assigned to a senior developer with an urgent due date. If it’s “Medium,” it can be added to the next sprint’s backlog.
Gain immediate insight into your team’s security debt—a problem affecting 50% of organizations according to recent research—without digging through hundreds of tasks by visualizing your security data in real-time with customizable ClickUp Dashboards.
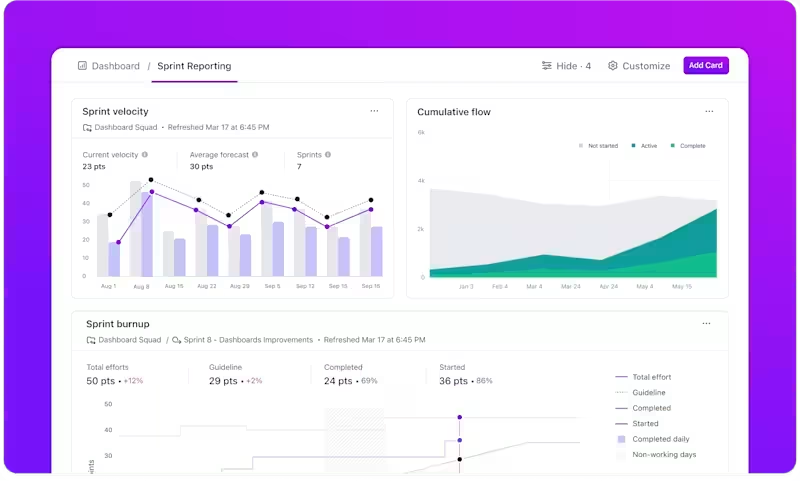
You can build charts showing open vulnerabilities by severity, the average age of open tickets, or which team members have the most assigned fixes. This gives engineering managers the high-level view they need to spot trends and allocate resources effectively.
To ensure developers have all the information they need, use ClickUp Task Dependencies. When Amazon Q flags an issue, create a ClickUp Task and link it back to the original finding. You can paste the file path, line number, and suggested fix directly into the task description. This gives developers full context without forcing them to switch between tools.
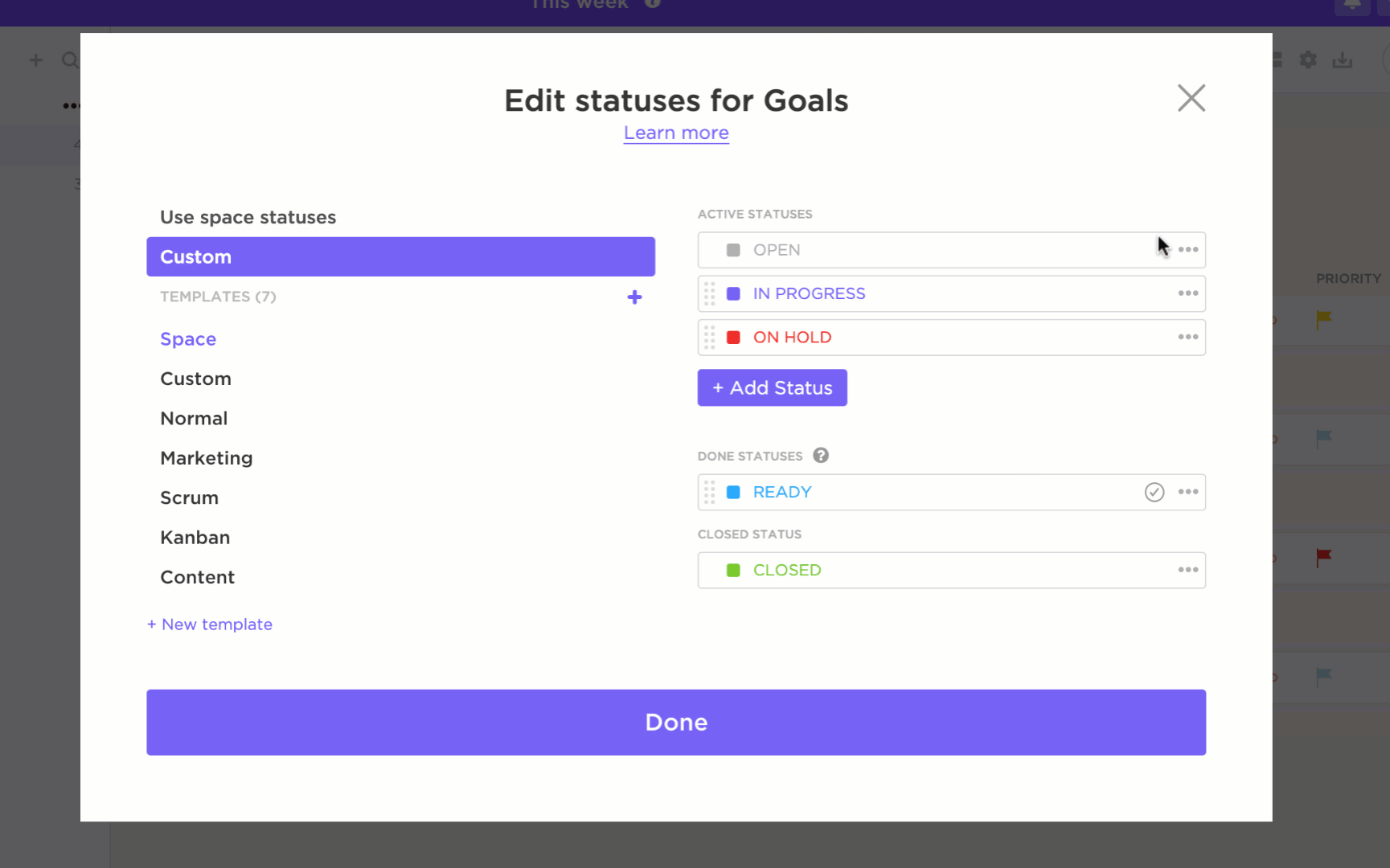
Finally, track the complete lifecycle of a vulnerability with ClickUp Custom Statuses. A typical workflow might be: New → In Review → In Progress → Fixed → Verified. By adding a final “Verified” step, you ensure that a second scan is run to confirm the fix works before the task is officially closed, creating a closed-loop process where nothing is left to chance. 🙌
And with ClickUp Brain, the integrated, contextual AI within ClickUp, your team doesn’t have to keep searching for information. Just ask Brain a question, and it’ll search your tasks, files, chats, and connected apps to surface the info you need!
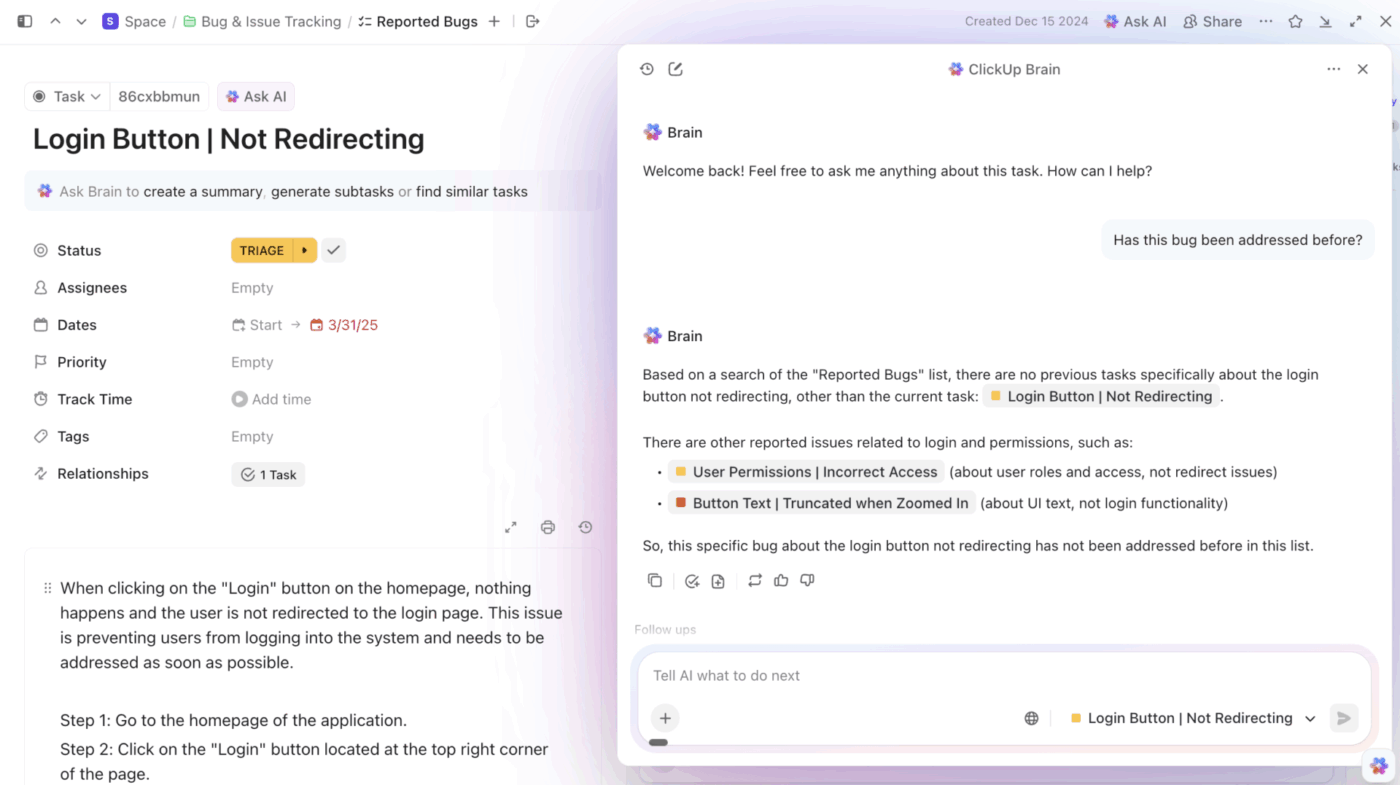
💡 Pro Tip: ClickUp’s Codegen AI Agent can help identify issues in code without you needing to move out of your Workspace. It can:

Even the best security tools will fail if your team doesn’t have the right habits and workflows in place. If developers ignore findings, or fixes are allowed to pile up in an endless backlog, your investment in scanning tools is wasted. Building sustainable practices makes security a natural part of your team’s daily routine.
Here are some best practices to build a strong, secure coding workflow:
💡 Pro Tip: Enforce these best practices consistently using ClickUp.
Secure coding isn’t a one-time task or a separate phase of development—it’s a continuous practice that should be woven into the fabric of how your team writes, reviews, and ships code. By bringing vulnerability scanning directly into the IDE with Amazon Q Developer, you catch issues at the earliest possible moment, when the code is still fresh in a developer’s mind. The AI-generated fix suggestions turn security from a chore into a collaborative part of the creative process.
This approach works best when scanning happens in the IDE where developers already work. By connecting all your work in a converged workspace like ClickUp, you create a closed-loop system where nothing falls through the cracks. Automation handles the repetitive, administrative parts of the process, like triggering scans and routing findings. This frees your team to focus on the high-impact judgment calls that require human expertise.
Teams that build security into their daily workflow spend less time fixing urgent issues and more time building new features.
Ready to close the loop between finding and fixing? Get started for free with ClickUp to build your secure coding workflow. ✨
Amazon Q supports many major languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, and C#, but the depth of security analysis can vary depending on the language and its known vulnerability ecosystem.
Use suppression rules within the tool for confirmed false positives, and be sure to document the reasoning in your ClickUp Task so the decision is clear to future team members.
A common best practice is to configure your pipeline to block builds on critical and high-severity findings. Show warnings for medium and low issues to balance security with development velocity.
Review open vulnerabilities weekly as part of your sprint planning. Conduct a deeper audit of suppressed findings and overall security trends on a quarterly basis./
© 2026 ClickUp