How to Use LLaMA for Chatbots in Your Workflow
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

Most teams exploring open-source AI models discover that Meta’s LLaMA offers a rare combination of power and flexibility, but the technical setup can feel like assembling furniture without instructions.
This guide walks you through building a functional LLaMA chatbot from scratch, covering everything from hardware requirements and model access to prompt engineering and deployment strategies.
Let’s get to it!
Building a chatbot with proprietary APIs often feels like you’re locked into someone else’s system, facing unpredictable costs and data privacy questions. This vendor lock-in means you can’t truly customize the model for your team’s unique needs, leading to generic responses and potential compliance headaches.
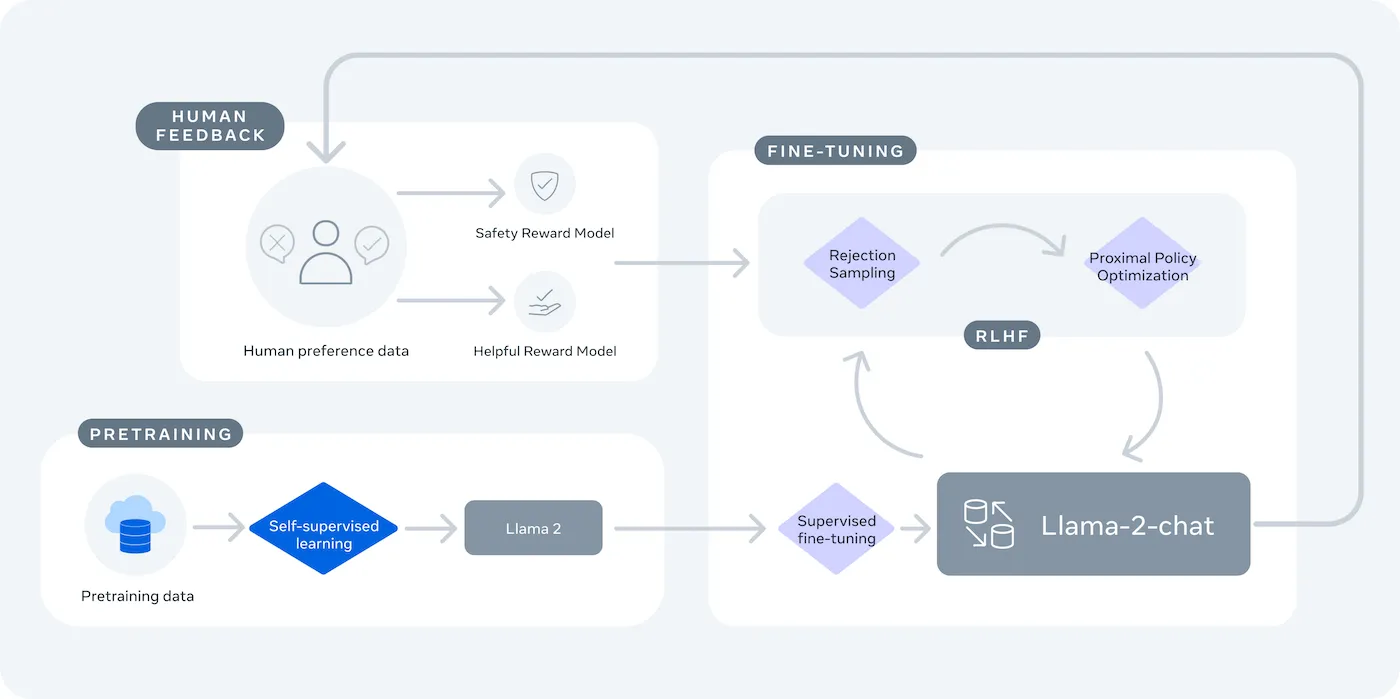
LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) is Meta’s family of open-weight language models, and it offers a powerful alternative. It’s designed for both research and commercial use, giving you the control that closed-source models don’t.
LLaMA models come in different sizes, measured in parameters (e.g., 7B, 13B, 70B). Think of parameters as a measure of the model’s complexity and power—larger models are more capable but require more computational resources.
Here’s why you might use a LLaMA chatbot:
The main tradeoff is convenience for control. LLaMA requires more technical setup than a plug-and-play API. For production chatbots, teams typically use LLaMA 2 or the newer LLaMA 3, which offers improved reasoning and can handle more text at once.
Jumping into a development project without the right tools is a recipe for frustration. You get halfway through, only to realize you’re missing a key piece of hardware or software access, derailing your progress and wasting hours of your time.
To avoid this, gather everything you need upfront. Here’s a checklist to ensure a smooth start. 🛠️
| Model Size | Minimum VRAM | Alternative Option |
|---|---|---|
| 7B parameters | 8GB | Cloud GPU instance |
| 13B parameters | 16GB | Cloud GPU instance |
| 70B parameters | Multiple GPUs | Quantization or cloud |
If your local machine doesn’t have a powerful enough Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), you can use cloud services like AWS or GCP. Inference platforms like Baseten and Replicate also offer pay-as-you-go GPU access.
For this guide, we’ll use the LangChain framework. It simplifies many of the complex parts of building a chatbot, like managing prompts and conversation history.
Connecting all the technical pieces of a chatbot—the model, the prompt, the memory—can feel overwhelming. It’s easy to get lost in the code, leading to bugs and a chatbot that doesn’t work as expected. This step-by-step guide breaks down the process into simple, manageable parts.
This approach works whether you’re running the model on your own machine or using a hosted service.
First, you need to install the core Python libraries. Open your terminal and run this command:
pip install langchain transformers accelerate torch
If you’re using a hosted service like Baseten for inference, you’ll also need to install its specific software development kit (SDK):
pip install baseten
Here’s what each of these packages does:
If you’re running the model locally on a machine with an NVIDIA GPU, make sure you have CUDA installed and configured correctly. This allows the model to use the GPU for much faster performance.
Before you can download the model, you need to get official access from Meta through Hugging Face.
meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfhuggingface-cli login and paste your token to authenticate your machineApproval is usually quick. Make sure you choose a model variant with “chat” in the name, as these have been specifically trained for conversational tasks.
Now you can load the model into your code. You have two main options depending on your hardware.
If you have a powerful enough GPU, you can load the model locally:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer model_name = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf" tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name) model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="auto")
If your hardware is limited, you can use a hosted inference service:
from langchain.llms import Baseten llm = Baseten(model="llama-2-7b-chat", api_key="your-api-key")
The device_map="auto" command tells the transformers library to automatically distribute the model across any available GPUs.
If you’re still running out of memory, you can use a technique called quantization to shrink the model’s size, though this may slightly reduce its performance.
LLaMA chat models are trained to expect a specific format for prompts. A prompt template ensures your input is structured correctly.
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
template = """<s>[INST] <<SYS>>
You are a helpful assistant. Answer questions clearly and concisely.
<</SYS>>
{user_input} [/INST]"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["user_input"], template=template)
Let’s break down this format:
<<SYS>>: This section contains the system prompt, which gives the model its core instructions and defines its personality[INST]: This marks the beginning of the user’s question or instruction[/INST]: This signals to the model that it’s time to generate a responseKeep in mind that different versions of LLaMA might use slightly different templates. Always check the model’s documentation on Hugging Face for the correct format.
Next, you’ll connect your model and prompt template into a conversational chain using LangChain. This chain will also include memory to keep track of the conversation.
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt,
memory=memory,
verbose=True
)
LangChain offers several types of memory:
For testing, ConversationBufferMemory is a great place to start.
Finally, you can create a simple loop to interact with your chatbot from the terminal.
while True:
user_input = input("You: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit"]:
break
response = conversation.predict(input=user_input)
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
In a real-world application, you would replace this loop with an API endpoint using a framework like FastAPI or Flask. You can also stream the model’s response back to the user, which makes the chatbot feel much faster.
You can also adjust parameters like temperature to control the randomness of the responses. A low temperature (e.g., 0.2) makes the output more deterministic and factual, while a higher temperature (e.g., 0.8) encourages more creativity.
You’ve built a chatbot that gives answers, but is it ready for real users? Deploying an untested bot can lead to embarrassing failures, like providing incorrect information or generating inappropriate content, which can damage your company’s reputation.
A systematic testing plan is the solution to this uncertainty. It ensures your chatbot is robust, reliable, and safe.
Functional testing:
Quality evaluation:
Performance testing:
Also, watch out for common LLM issues like hallucinations (confidently stating false information), context drift (losing track of the topic in a long conversation), and repetition. Logging all test conversations is a great way to spot patterns and fix issues before they reach your users.
Once you move past the mechanics of fine-tuning and deployment, LLaMA becomes most valuable when it’s applied to everyday team problems—not abstract AI demos. Teams typically don’t need “a chatbot”; they need faster access to knowledge, fewer manual handoffs, and less repetitive work.
By fine-tuning LLaMA on internal documentation, wikis, and FAQs—or pairing it with a RAG-based knowledge base—teams can ask natural-language questions and get precise, context-aware answers. This removes the friction of searching across scattered tools while keeping sensitive data fully internal, rather than sending it to third-party APIs.
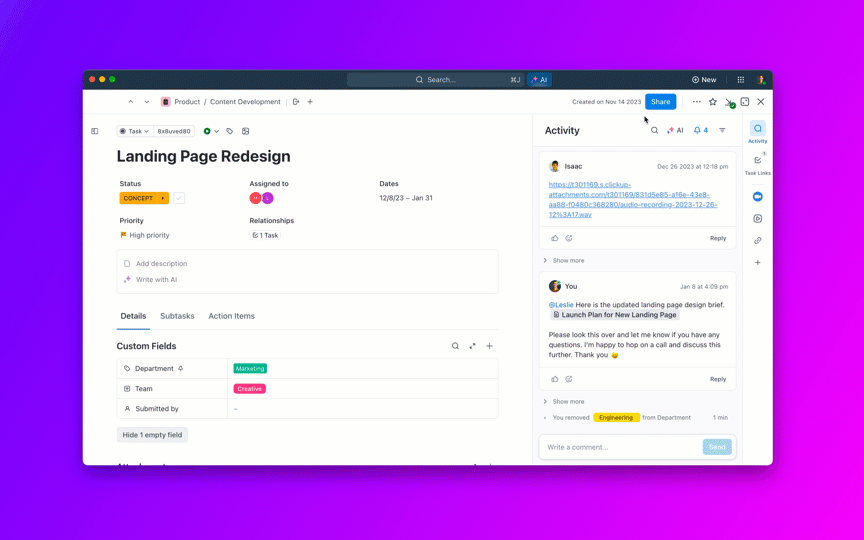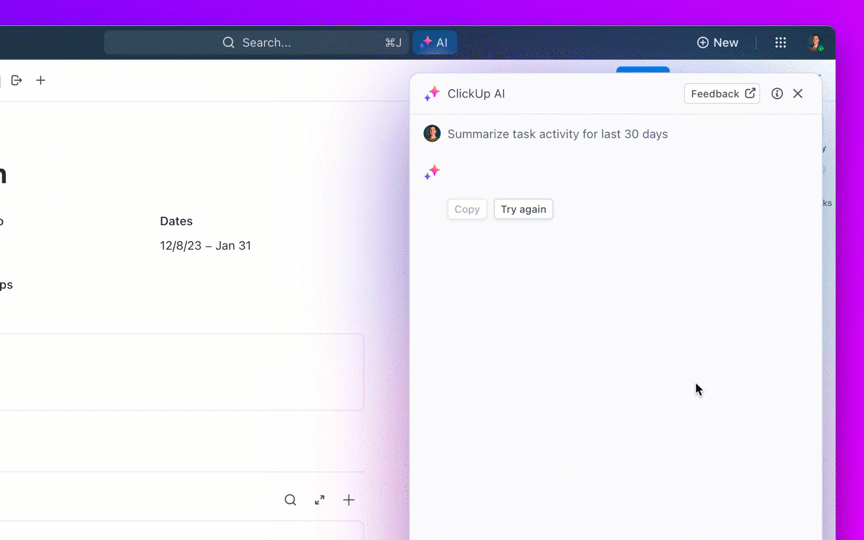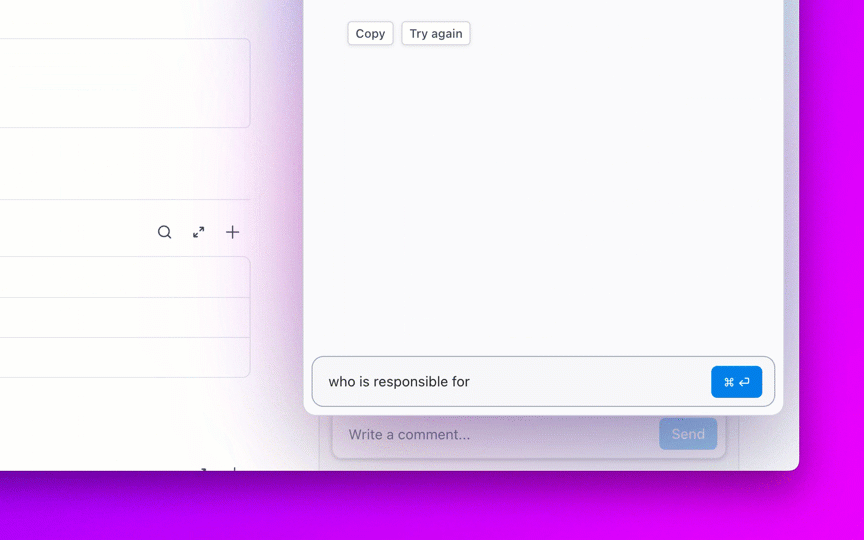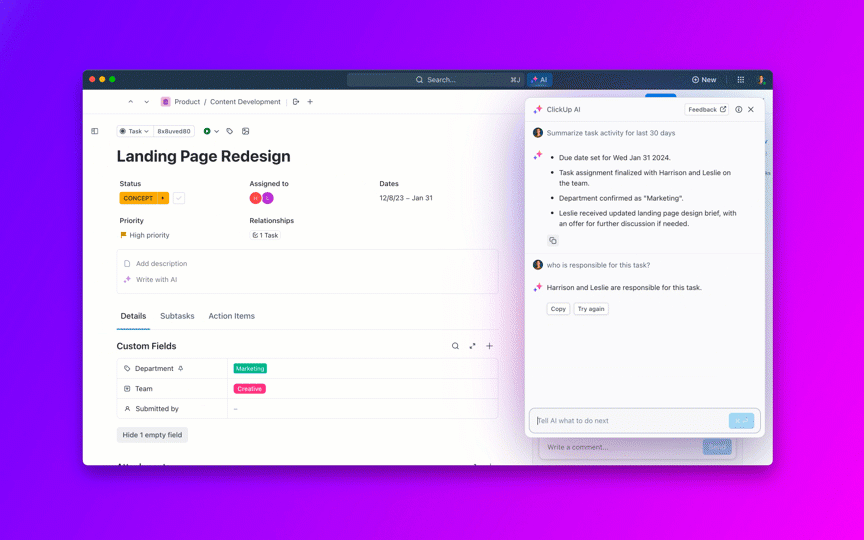
🌟 Enterprise Search in ClickUp, and the pre-built Ambient Answers agent, provide detailed contextual answers to your questions using knowledge within your ClickUp workspace.
When trained on your own codebase and style guides, LLaMA can act as a contextual code review assistant. Instead of generic best practices, developers get suggestions that align with team conventions, architectural decisions, and historical patterns.
🌟 A LLaMA-based code review helper can surface issues, suggest improvements, or explain unfamiliar code. ClickUp’s Codegen goes one step further by acting inside the development workflow—creating pull requests, applying refactors, or updating files directly in response to those insights. The result is less copy-paste and fewer broken handoffs between “thinking” and “doing.”
LLaMA can be trained for intent classification to understand incoming customer queries and route them to the right team or workflow. Common questions can be handled automatically, while edge cases are escalated to human agents with context attached, reducing response times without sacrificing quality.
You could also just build a Triage Super Agent using natural language within your ClickUp workspace. Learn more
Using meeting transcripts as input, LLaMA can extract decisions, action items, and key discussion points. The real value emerges when these outputs flow directly into task management tools, turning conversations into tracked work.
🌟 ClickUp’s AI Meeting Notetaker doesn’t just take meeting notes; it drafts summaries, generates action items, and links meeting notes to your documents and tasks.
Teams can use LLaMA to generate first drafts of reports, proposals, or documentation based on existing templates and past examples. This shifts effort from blank-page creation to review and refinement, speeding up delivery without lowering standards.
🌟 ClickUp Brain can quickly generate drafts for documentation, keeping all your workplace knowledge in context. Try it today.
LLaMA-powered chatbots are most effective when they’re embedded into existing workflows—documentation, project management, and team communication—rather than operating as standalone tools.
This is where integrating AI directly into your workspace makes all the difference. Instead of building a separate tool, you can bring conversational AI to where your team already operates.
For example, you may create a custom LLaMA bot to act as a knowledge assistant. But if it lives outside your project management tool, your team has to switch contexts to ask it a question. This creates friction and slows everyone down.
Eliminate this context-switching by using an AI that’s already part of your workflow.
Ask questions about your projects, tasks, and documents without ever leaving ClickUp using ClickUp Brain. Just type @brain in any task comment or ClickUp Chat to get an instant, context-aware answer. It’s like having a team member who has perfect knowledge of your entire workspace. 🤩
This transforms the chatbot from a novelty into a core part of your team’s productivity engine.
Building a LLaMA chatbot can be empowering, but teams often get blindsided by hidden complexities. The “free” open-source model can end up being more expensive and difficult to manage than expected, leading to a poor user experience and a constant, resource-draining maintenance cycle.
It’s important to understand the limitations before you commit.
Self-hosted models also typically have higher latency than highly optimized commercial APIs. These are all operational burdens that managed solutions handle for you.
📮ClickUp Insight: 88% of our survey respondents use AI for their personal tasks, yet over 50% shy away from using it at work. The three main barriers? Lack of seamless integration, knowledge gaps, or security concerns.
But what if AI is built into your workspace and is already secure? ClickUp Brain, ClickUp’s built-in AI assistant, makes this a reality. It understands prompts in plain language, solving all three AI adoption concerns while connecting your chat, tasks, docs, and knowledge across the workspace. Find answers and insights with a single click!
LLaMA is just one option in a sea of AI models, and it can be overwhelming to figure out which one is right for you.
Here’s how the landscape of alternatives breaks down.
Other open-source models:
Commercial APIs:
You can build it yourself with an open-source model, pay for a commercial API, or use a converged AI workspace that offers a pre-integrated solution with different types of AI agents.
📚 Also Read: How to Use a Chatbot for Your Business
Building a chatbot with LLaMA gives you incredible control over your data, costs, and customization. But that control comes with the responsibility for infrastructure, maintenance, and safety—all things that managed APIs handle for you. The goal isn’t just to build a bot—it’s to make your team more productive, and a complex engineering project can sometimes distract from that.
The right choice depends on your team’s resources and priorities. If you have ML expertise and strict privacy needs, LLaMA is a fantastic option. If you prioritize speed and simplicity, an integrated tool might be a better fit.
With ClickUp, you get a Converged AI Workspace with all your tasks, documents, and conversations in one place, powered by integrated AI. It cuts context sprawl and helps teams work faster and more effectively, with the right information at their fingertips through customizable Super Agents and contextual AI.
Stop wasting time on infrastructure and get the benefits of a context-aware AI assistant today without building anything from scratch. Get started for free with ClickUp.
The cost depends entirely on your deployment method, and project forecasting can help you estimate it. If you use your own hardware, you’ll have an upfront cost for the GPU but no ongoing per-query fees. Cloud providers charge an hourly rate based on GPU and model size.
Yes, the licenses for LLaMA 2 and LLaMA 3 allow for commercial use. However, you must agree to Meta’s terms of use and provide the required attribution in your product.
LLaMA 3 is the newer and more capable model, offering better reasoning skills and a larger context window (8K tokens vs. 4K for LLaMA 2). This means it can handle longer conversations and documents, but it also requires more computational resources to run.
While Python is the most common language for machine learning due to its extensive libraries, it’s not strictly required. Some platforms are beginning to offer no-code or low-code solutions that allow you to deploy a LLaMA chatbot with a graphical interface. /
© 2026 ClickUp