How Amazon Q Helps with Code Generation

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

The pull request was supposed to be just a few lines to wire an API and a quick test, done before dinner. Instead, it’s 11:47 pm., and the build is failing for reasons buried somewhere in a legacy module no one’s touched in years. The newest engineer is quietly Googling acronyms they were never taught during onboarding.
This repetitive work and tribal knowledge trapped in old repos wear teams down more often than not.
Amazon Q Developer is built to solve such problems. It understands your codebase, services, and context so that writing code feels like a continuation of a conversation you’re already in.
In this article, we’ll explore how Amazon Q helps with code generation, the key features software developers rely on, and the teams it works best for.
As a bonus, we’ll also touch on what happens when code generation alone isn’t enough, and why some teams turn to more complete systems like ClickUp. 🤩
Amazon Q Developer is AWS’s generative AI assistant built to help developers and IT professionals build, operate, manage, and optimize applications on Amazon Web Services.
It brings AI-powered assistance directly into developer tools such as IDEs (VS Code, JetBrains, Visual Studio), the command line, the AWS Console, and even chat apps like Slack and Microsoft Teams.
At its core, it’s an AI-driven collaborator that understands natural-language questions about your code, architecture, project structure, and best practices, delivering relevant, actionable answers. It’s deeply aware of AWS resources and real development workflows, thanks to its foundation on Amazon Bedrock, AWS’s generative AI-powered platform.
🔍 Did You Know? The 1960s ‘software crisis’ refers to the inability of software development to keep pace with rapid hardware advancements, resulting in costly, delayed, unreliable, and complex projects. Coined at the 1968 NATO conference, it highlighted the failure of, e.g., IBM’s OS/360, leading to the birth of software engineering.
Here’s a clear, step-by-step breakdown of how to get started with Amazon Q Developer without changing how you work or learning a new workflow. 👇
Amazon Q Developer works across multiple environments, so you can start wherever you’re most comfortable.
You can use it in:
If you already write code in an IDE or terminal, that’s the fastest place to begin.
Installation takes just a few minutes.
➡️ For IDEs:
➡️ For the command line:
Once installed, Amazon Q becomes part of your editor or terminal, no separate app needed.
🔍 Did You Know? Perfectionism is a significant driver of burnout in software development, often fueled by the binary nature of code: it either works or it doesn’t. This ‘all-or-nothing’ reality, combined with the subjectivity, often traps developers in a cycle of endless refactoring and self-doubt.
After installation, you’ll need to sign in so Amazon Q can personalize responses and access AWS context.
You can authenticate using:
This step securely connects Amazon Q to your AWS environment.
Once authenticated, you can start working immediately.
In IDEs, Amazon Q Developer shows up directly in the activity bar or as a dedicated tool window, depending on the editor you’re using. You can chat with it inline while you work, generate new code, refactor existing logic, or ask questions about your project, specific errors, or AWS services.
In the command line, Amazon Q Developer is available right inside your terminal. You can invoke it directly to generate code snippets, get explanations, or ask for suggestions during code reviews, all without leaving the CLI or interrupting your workflow.
🔍 Did You Know? ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), unveiled in 1946, weighed over 27 tons and contained 18,000 vacuum tubes. Rather than typing code like we do today, early programmers had to plug and unplug cables and set switches to get it to run calculations, a world apart from modern IDEs.
If you spend more time managing infrastructure than writing code, the console is a great entry point.
Inside the console, Amazon Q can also:
This makes architectural and operational decisions faster and easier.
Amazon Q Developer focuses on accelerating day-to-day coding work by embedding AI directly into the development process. Here are some core features of this AI agent for coding:
Amazon Q Developer provides real-time inline code suggestions as you type, helping you write code faster without breaking your coding process. Once you install the Amazon Q extension, these suggestions are enabled by default – you can just start writing code or comments, and Q starts responding.
As you type, Amazon Q looks at:
Based on this context, it provides suggestions that can range from:
You’ll see accurate suggestions inline in your editor, and you can accept them instantly using your keyboard. If a suggestion isn’t what you want, you can keep typing.
Over time, these suggestions can be customized to match your team’s internal libraries, proprietary logic, and preferred coding style. Auto-completion feels less generic and more aligned with how your codebase actually works, enhancing developer productivity.
🧠 Fun Fact: In 1953, John W. Backus and his team at IBM developed Speedcoding (or Speedcode) to alleviate the immense difficulty of programming the IBM 701 computer using raw machine code. That tension between ease of development vs efficiency is one of the earliest documented pushes toward automation in coding.
Amazon Q Developer also lets you write code using plain English. Instead of starting from a blank file or searching for examples, you can describe what you want to build, and Q translates that intent into working code.
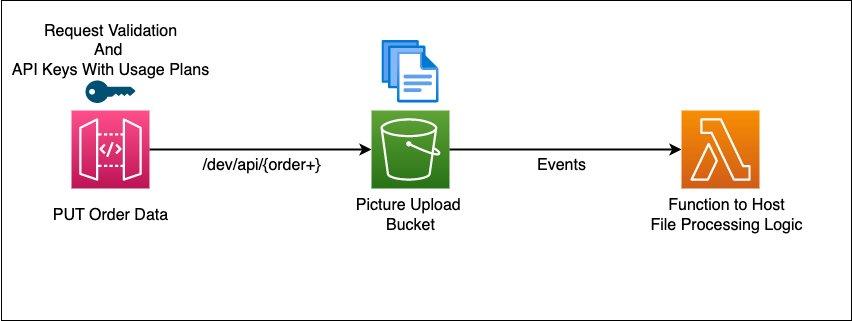
You can do things like:
For example, you might write a comment like ‘Create an S3 bucket and store user uploads’, and Amazon Q can generate the required code, imports, and AWS SDK calls based on that description.
This natural language approach also works for more structured tasks:
By default, AI tools give you generic suggestions. However, Amazon Q Developer goes a step further by letting you customize its code generation and chat responses using your own private codebase. This means Q knows how to write code and learns how your team writes code.
Code customization is available as part of the Amazon Q Developer Pro tier and is set up by an administrator.
The process follows a clear flow:
The model is periodically updated to reflect changes in your codebase, so recommendations stay current as your system evolves.
❗️ Note: All code used for customization stays private to your organization. It’s not used to train AWS foundation models, and customized suggestions are only visible to authorized developers within your account.
Amazon Q Developer isn’t limited to suggesting code or answering questions. It can also act as an agent, meaning it can plan, reason, and execute complex, multi-step tasks on your behalf with minimal back-and-forth.
You describe the goal in natural language, and Amazon Q figures out how to get there. It breaks the request into logical steps, decides which tools to use, performs the actions, and keeps iterating until the task is complete.
It includes purpose-built agents, each focused on a specific part of the software development lifecycle. Here are some of them to help you use AI in software development efficiently:
When you’re ready to build a new feature or patch a bug, this is the agent you turn to first. It helps implement features or fix bugs across multiple files. You describe the change in plain language, and the agent analyzes your existing codebase, creates a step-by-step plan, and shows you what it intends to modify.
This is especially useful for changes that span multiple layers, like updating APIs, business logic, and configuration together.
🧠 Fun Fact: The iconic ‘Hello, World!’ program became famous in the 1970s as the standard first program for beginners, cementing its place in programming culture through the work of Brian Kernighan at Bell Laboratories.
Once the code is in place, testing is the next obvious step, and the agent takes it from there, focusing on improving test coverage. It identifies what needs to be tested, generates unit tests (including edge cases and failure scenarios), creates mocks where required, and runs the tests inside your IDE.
Before anything gets merged, you’ll want a second set of eyes. That’s where the review agent comes in. It acts as an automated code reviewer, scanning your code for security risks, quality issues, and violations of best practices such as exposed credentials, unsafe queries, or weak error handling.
And once everything’s ready to ship, documentation often becomes the last-mile problem. The documentation agent handles that by generating or updating project documentation through codebase analysis.
It can create or refresh README files, explain APIs, and document key components, so you don’t have to write everything manually.
From speeding up feature development to simplifying cloud-native workflows, Amazon Q Developer is designed for teams building and maintaining applications on AWS.
These use cases show where it fits best in real engineering workflows, how teams apply it beyond basic code suggestions, and how leveraging these AI-assisted practices can help you become a better programmer.
With Amazon Q Developer, writing unit tests stops being a slow, manual task and becomes part of your everyday workflow. Instead of crafting test cases by hand, you trigger the unit test agent with a simple /test prompt inside your IDE.
📌 How it works in practice:
You can highlight a function or run /test directly in the Amazon Q chat. Q analyzes your codebase, understands its surrounding context, and automatically generates relevant unit tests. This includes common paths, edge cases, and error scenarios that are easy to miss.
⚡️ What makes it useful:
Before anything is added, Amazon Q asks for your approval. You review the changes, accept what you want, and stay entirely in control.
The result is faster test coverage, more reliable code, and more time spent building features instead of writing repetitive tests.
Legacy code often slows teams down with complex logic, outdated patterns, and risky changes. Amazon Q Developer helps you clean this up safely, right inside your IDE.
📌 How to refactor with Amazon Q:
Open the file, highlight the code you want to improve, and ask Amazon Q to refactor or optimize it using a simple prompt like ‘simplify this logic’ or ‘optimize for performance.’
Amazon Q first presents a clear, step-by-step plan explaining:
You can ask questions, refine the approach, or stop altogether. Once approved, the updated code can be inserted with a single click. In many cases, Q also updates or generates tests so you can validate changes immediately.
Onboarding usually means digging through unfamiliar code, outdated docs, and lots of questions. Amazon Q Developer speeds this up by acting like a built-in guide inside the IDE.
📌 Here’s how it helps:
📖 Also Read: Software Development Templates
Amazon Q Developer works best when you treat it like a smart pair programmer. Here are some practices that help you get accurate, usable output while keeping your codebase under control.
Amazon Q Developer is powerful, but even the best code editors come with their own limitations. You should be aware of the tool’s quotas, technical boundaries, and operational constraints to plan usage realistically and avoid surprises as adoption scales.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 12% of respondents say AI agents are hard to set up or connect to their tools, and another 13% say there are too many steps just to get simple things done with Agents.
Data has to be piped in manually, permissions have to be redefined, and every workflow depends on a chain of integrations that can break or drift over time.
Good news? You don’t need to “connect” ClickUp’s Super Agents to your tasks, Docs, chats, or meetings. They are natively embedded in your Workspace, using the same objects, permissions, and workflows as any other human coworker.
Because integrations, access controls, and context are inherited from the workspace by default, agents can act immediately across tools without custom wiring. Forget configuring agents from scratch!
Amazon Q Developer works well when your primary need is IDE-level code assistance, especially inside the AWS ecosystem. But as teams scale, many run into its limits and the reality that shipping software involves far more than just writing code. Modern software development needs an all-in-one system, without forcing developers to stitch together five different tools.
This is where ClickUp for Software Teams comes in as the world’s first Converged AI Workspace that connects planning, execution, documentation, collaboration, and code in one place. It covers the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC), with AI built directly into every layer of work, eliminating Work Sprawl.
That means ClickUp understands the full project context: what the task is, why it matters, who owns it, where it sits in the sprint, and what documentation already exists.
Let’s look at how the platform goes beyond IDE-level assistance to become a true alternative to Amazon Q Developer! 💁
LLMs are great at understanding language. But without real context, they’re still guessing.
ClickUp Brain is a context-aware AI tool that ties everything together in your workspace. It pulls together ClickUp Tasks, Docs, conversations, and project history so its responses reflect what’s actually happening, not just what was typed into a prompt.

Here’s what teams can do with this AI for software teams:
For instance, if you’re exploring an idea for a mental wellness app, you can ask ClickUp Brain to help validate product-market fit. It pulls from your Docs, research notes, and conversations, grounding responses in your actual project context.
🧠 Fun Fact: The 1969 Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) operated with just 72 kilobytes of memory (often cited as 64KB+ in common parlance). This minimal, hand-woven magnetic-core memory was less than the data needed to store a single high-resolution photo on a modern smartphone.
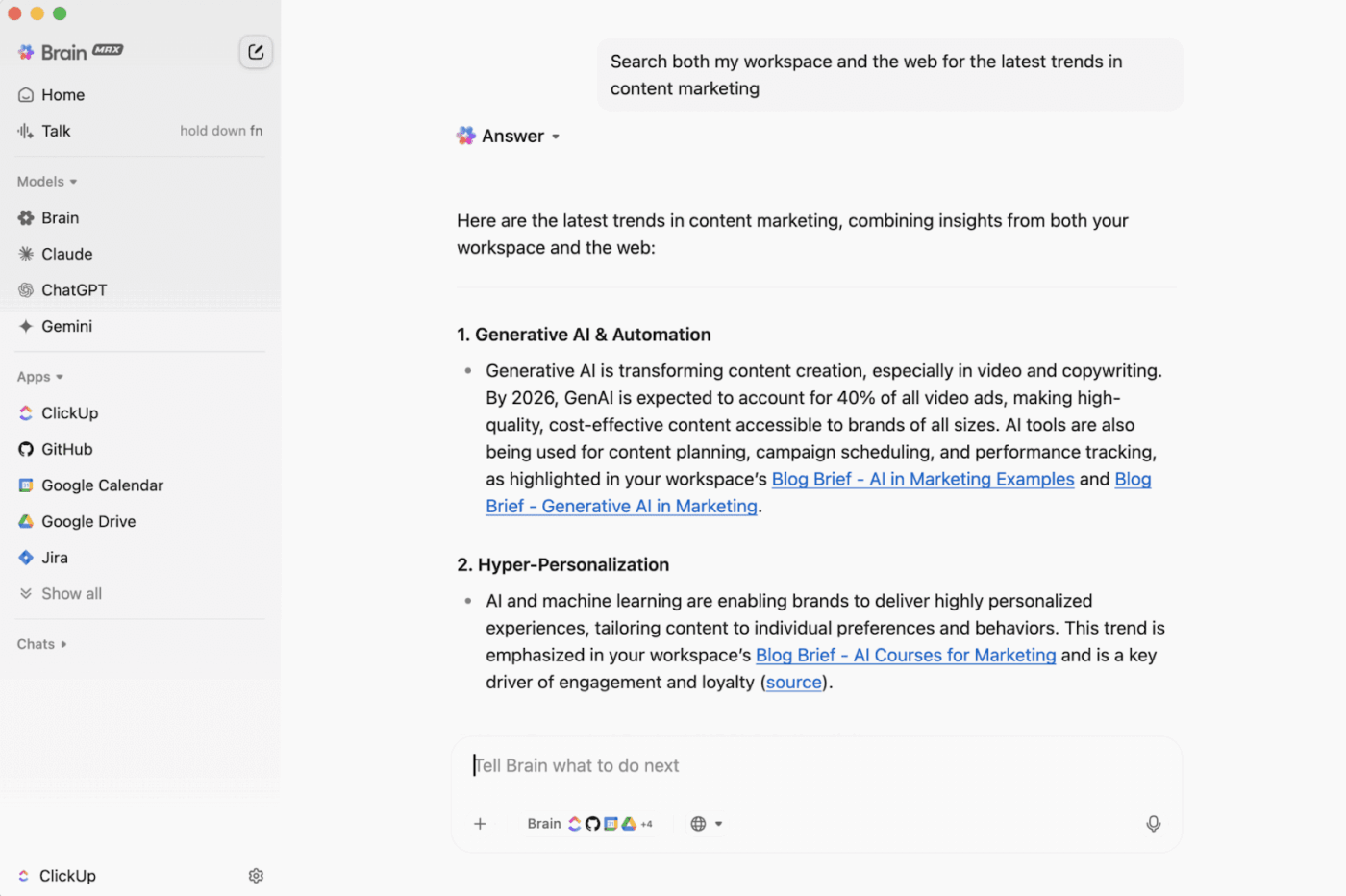
ClickUp Enterprise AI Search works behind the scenes to make every file, note, and integration instantly discoverable. It connects all your tools, such as Docs, tasks, chats, meetings, and even external apps like Drive, Slack, Gmail, and Notion, into a single AI-powered search layer.
You can ask direct, high-level queries like ‘What are our top customer issues this month?’ or ‘Which features are blocking this sprint?’ and get answers grounded in live workspace data.
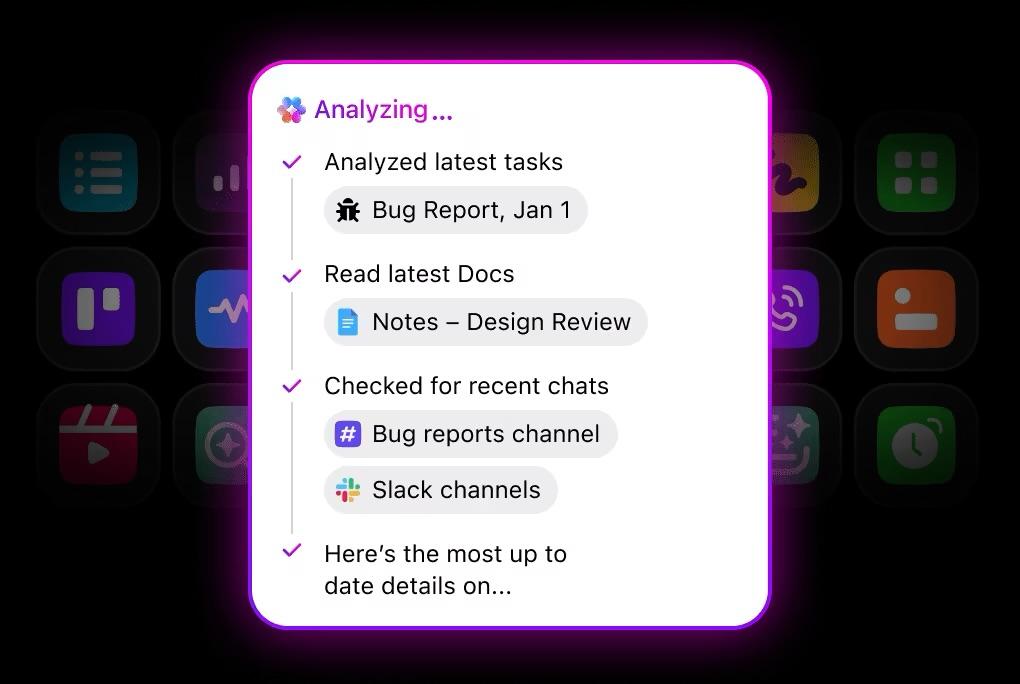
🚀 ClickUp Advantage: If you’ve ever stopped mid-debug just to dig through old tickets, Docs, GitHub threads, or meeting notes, you know how quickly context-switching kills momentum.
ClickUp Brain MAX fixes that. It gives you a desktop AI companion that works across your ClickUp Workspace, external AI orchestration tools, and the web. You can chat with premium AI models such as Brain, Claude, Gemini, OpenAI, and more, to reason through bugs, review code, summarize requirements, or generate documentation.
When blockers come from ‘Where was this discussed?’ or ‘What’s the latest spec?’ Brain MAX’s Universal Search pulls context from tasks, Docs, GitHub, files, and conversations in one place.
Wondering how to use AI to automate tasks? You’ve come to the right place.
ClickUp Super Agents are AI-powered teammates that operate within your workspace; they can be tagged, assigned work, or triggered automatically. These agents also perform reasoning across multiple steps rather than providing single responses.

Unlike traditional AI assistants or rule-based bots, ClickUp Agents have:
This makes them fundamentally different from IDE-bound agents or automation scripts.
Insights into ClickUp Super Agents:
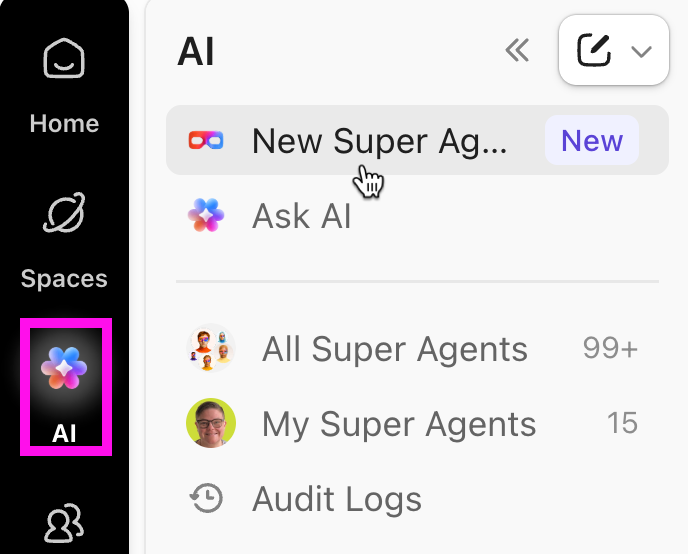
📌 Option 1: Create a Super Agent using the Natural-Language Builder
This is the fastest way to get started and is recommended for most teams. Here’s how it works:
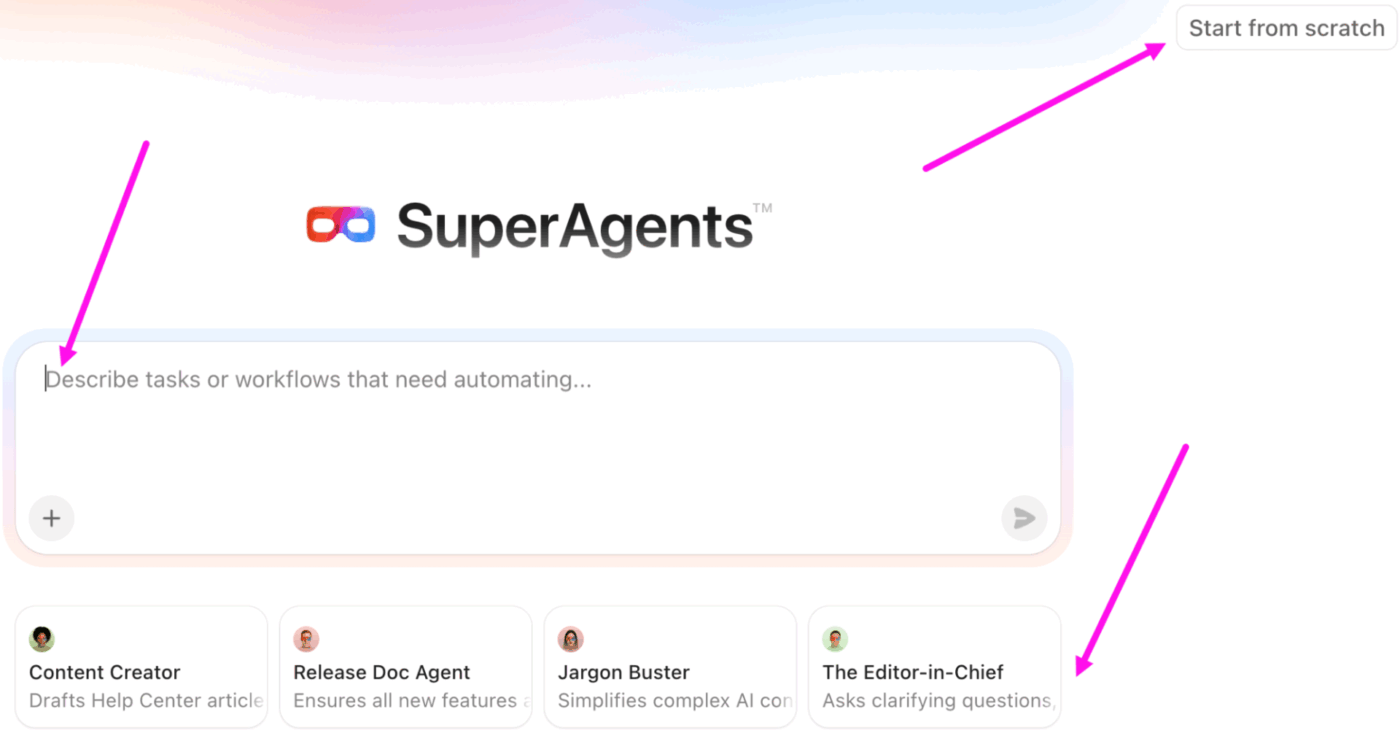
📌 Option 2: Create a Super Agent from scratch
This option gives you complete manual control. All you need to do is:
❗️ Note: Before rolling an Agent into active workflows, you can test and improve it. You can either start a DM to ask questions, give feedback, or adjust behavior, or simply trigger it manually to see how it behaves on a schedule. Iterate as needed, tuning prompts, permissions, and tools until the Agent behaves exactly as you want.
ClickUp Codegen is an external AI Agent that completes tasks, builds features, and answers code-related questions using natural language. It’s designed to help software teams release features faster, reduce errors, and even create production-ready pull requests.
Here’s how Codegen works in ClickUp:
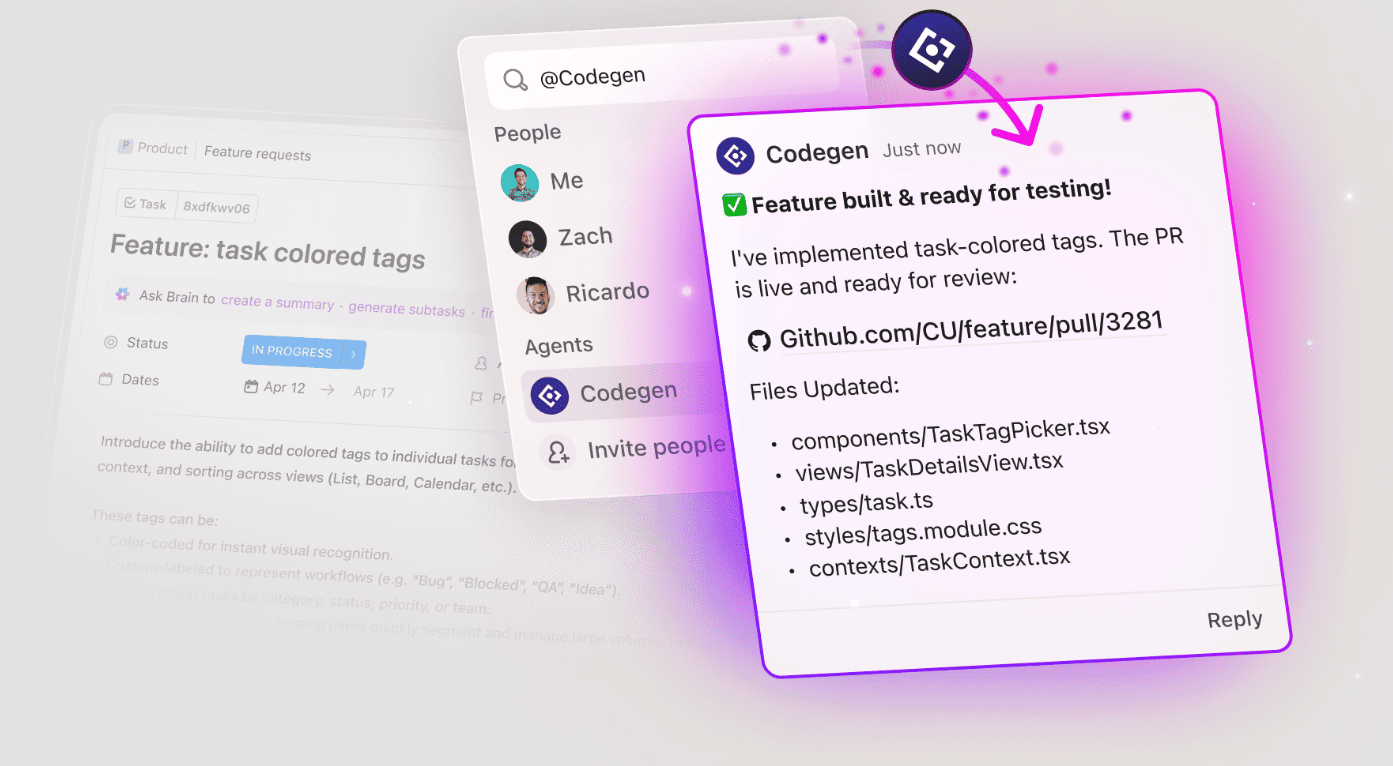
To use Codegen, a workspace admin or owner needs to connect it from the App Center, and users must have a Codegen account. Once set up, any workspace member can interact with the Codegen Agent.
📌 Example: A production bug gets reported right after a release. A task is created in ClickUp with error logs, user impact, and links to the related feature work. Instead of switching tools, you can assign the task to the ClickUp Codegen Agent to kick off the investigation.
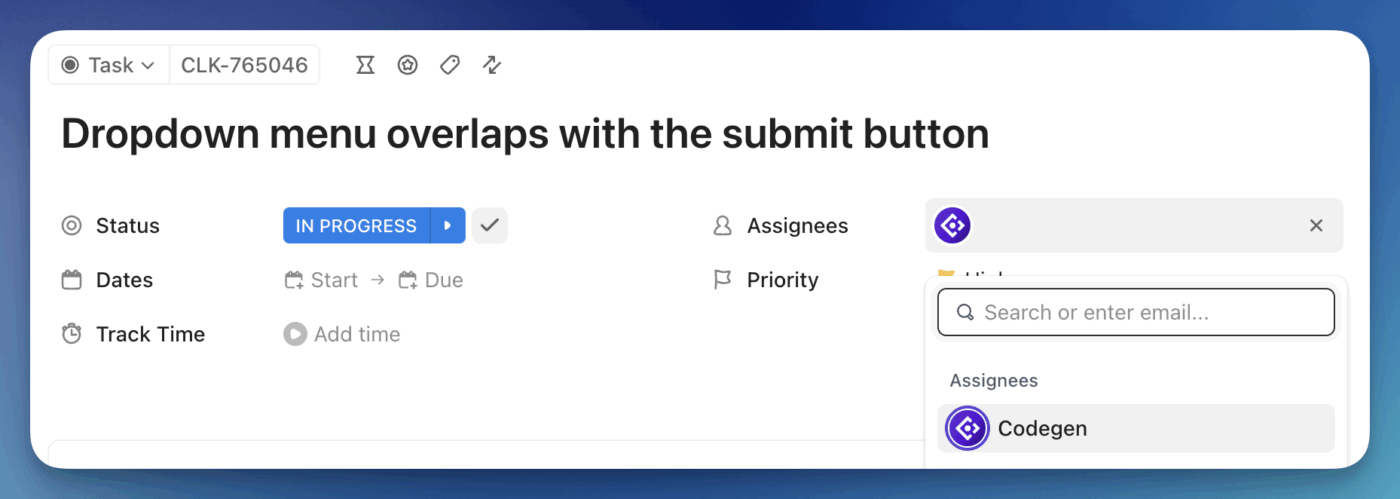
Codegen reads the full task context, traces the relevant parts of the codebase, and identifies the edge case causing the failure.
Once the issue is clear, Codegen generates a fix that follows your existing code patterns and standards. It can update or add unit tests to cover the failing scenario and ensure the bug doesn’t regress.
Here’s what Abraham Rojas, Delivery Team Manager, Pattern, had to say about using ClickUp:
We use ClickUp to track our software development projects in-house; managing multiple projects and teams makes things easier for me, this is one of the best tools I have used so far for handling my scrum and modern agile projects.
AI-generated code works best when it aligns with how developers already work. And Amazon Q Developer does this well inside the IDE, helping engineers understand existing code, refactor safely, and ship faster, especially in AWS-focused stacks.
But its scope stops at the code. It can’t see the planning discussions, support context, or documentation that explain why something exists.
When that context lives elsewhere, developers still have to piece the story together.
ClickUp approaches this differently. ClickUp Brain understands tasks, Docs, and conversations, while ClickUp Super Agents act on that context as work evolves. And ClickUp Codegen ties code changes directly to real requirements. Together, they provide a unified workspace that keeps context intact from planning through shipping without breaking flow. Sign up to ClickUp for free today! ✅
© 2026 ClickUp