You start with a goal, a deadline, and a team ready to get to work. Then reality sets in — tasks pile up, expectations shift, and suddenly, no one’s sure what’s next. That’s when projects stall, budgets stretch, and frustration kicks in.
A project management plan keeps that from happening. It defines the scope, sets clear timelines, and ensures everyone knows their role. Whether you use Agile, Waterfall, or a hybrid approach, a structured plan helps you stay on track and adapt when things don’t go as expected.
In this blog post, we’ll break down what goes into a strong project management plan and how to create a project planning process that actually keeps your project moving. 📊
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- Components of a Project Management Plan
- Executive summary
- Project introduction and objectives
- Project scope and work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Schedule management
- Cost management
- Quality management
- Resource management
- Risk management and mitigation strategies
- Communication plan
- Stakeholder management
- Procurement management
- Change management and closure criteria
- Key Steps to Writing an Effective Project Management Plan
- Step #1: Identify project baselines
- Step #2: Set SMART goals
- Step #3: Determine your project budget
- Step #4: Pinpoint project dependencies
- Step #5: Recognize project stakeholders
- Step #6: Establish project milestones
- Step #7: Assign responsibilities
- Step #8: Implement change management and define closure criteria
- Using Project Management Software and Tools
- Sample Project Management Plan Outline
- Best Practices and Tips for Successful Project Planning
What Is a Project Management Plan?
A Project Management Plan (PMP) is a comprehensive document that outlines how a project will be executed, monitored, and controlled. As a roadmap, it details the project’s scope, objectives, deliverables, timelines, and resource allocations.
The PMP also delegates roles and responsibilities, ensuring every stakeholder understands their specific functions and expectations. Its primary objective is to provide a structured framework that guides the project team from initiation through completion.
A PMP defines:
- The scope, schedule, and cost baselines, collectively known as the performance measurement baseline
- Processes for monitoring project progress
- Roles and responsibilities of the project team and stakeholders
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for managing risks, changes, and quality standards
The project manager, with input from stakeholders and the project team, develops and approves this document. It provides a reference point for decision-making and ensures that baseline deviations are identified and addressed.
If necessary, formal change requests are submitted to realign the project with its objectives.
🔍 Did You Know? The word ‘deadline’ comes from prison. In the 19th century, it referred to a physical line that prisoners couldn’t cross without being shot. Now, missing one just means a stern email.
Project plan vs. a project management plan
Understanding the distinction between a project plan and a project management plan is crucial for effective project execution.
While the terms are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes and encompass varying levels of detail. 📝
| Aspect | Project plan | Project management plan |
| Purpose | Outlines the project’s objectives, scope, and high-level deliverables | Details the processes and methodologies involved in project management and control |
| Focus | Answers the ‘what’ and ‘why’ for the undertaken project | Explains ‘how’ the project will be executed, monitored, and closed |
| Content | Includes tasks, timelines, milestones, resource allocation, and dependencies | Comprises subsidiary plans like scope, schedule, cost, quality, resource, and risk management plans |
| Detail level | High-level overview with broad objectives | In-depth guidance with specific procedures and protocols |
| Usage | Provides detailed guidance with specific procedures and protocols | Acts as a comprehensive guide for the project team to manage execution |
🌟 Template spotlight: The ClickUp Project Planner Template gives you a ready-made framework to build your project management plan, saving time and keeping everything organized from the start.
It’s perfect for outlining the project scope, defining milestones, and setting a budget. The template helps you:
- Track all project plans in one place for easy access
- Visualize progress with ClickUp Board View to see your tasks in motion
- Align team members and resources, ensuring maximum efficiency across all stages
Components of a Project Management Plan
A project management plan consists of multiple components to ensure alignment, efficiency, and control throughout the project lifecycle.
With the application of proven project management techniques, each component addresses a specific facet of planning and execution, offering clarity to project managers, coordinators, and team leaders.
Below are the distinct components that form a solid foundation for an effective project management plan. 📂
Executive summary
The executive summary offers a high-level project overview by concisely summarizing its purpose, objectives, scope, and key deliverables. This section is a snapshot for stakeholders, enabling rapid understanding of the project’s intent and strategic value.
For example, the executive summary for a project aimed at launching a new software tool might highlight:
- Anticipated market impact
- Projected timelines
- Critical milestones
With the essential information in a brief format, the executive summary supports swift decision-making and sets the tone for more detailed planning.
💡 Pro Tip: Utilize project overview templates to keep your executive summary sharp and stress-free. A good template does the heavy lifting — just plug in the details, and you’re ready to impress.
📮 ClickUp Insight: 92% of knowledge workers risk losing important decisions due to scattered documentation.
That’s a problem for project managers who need quick access to updates, approvals, and key decisions. ClickUp keeps everything in one place, so no one has to dig through emails or track down scattered files. It makes it easy to connect meeting notes, strategy documents, and action items with real work.
Project introduction and objectives
Here, the context behind the project is elaborated, explaining the background, rationale, and specific goals of the project. It explains why the project is being undertaken and clearly articulates the desired outcomes.
For example, an IT modernization effort might aim to reduce system downtime by 30% over a 12-month period, thereby setting a clear benchmark for success.
💡 Pro Tip: As the project evolves, keep revisiting the core strategic objective behind it. Periodically ask, ‘Why are we doing this?’ to ensure the project is still aligned with the company’s shifting priorities.
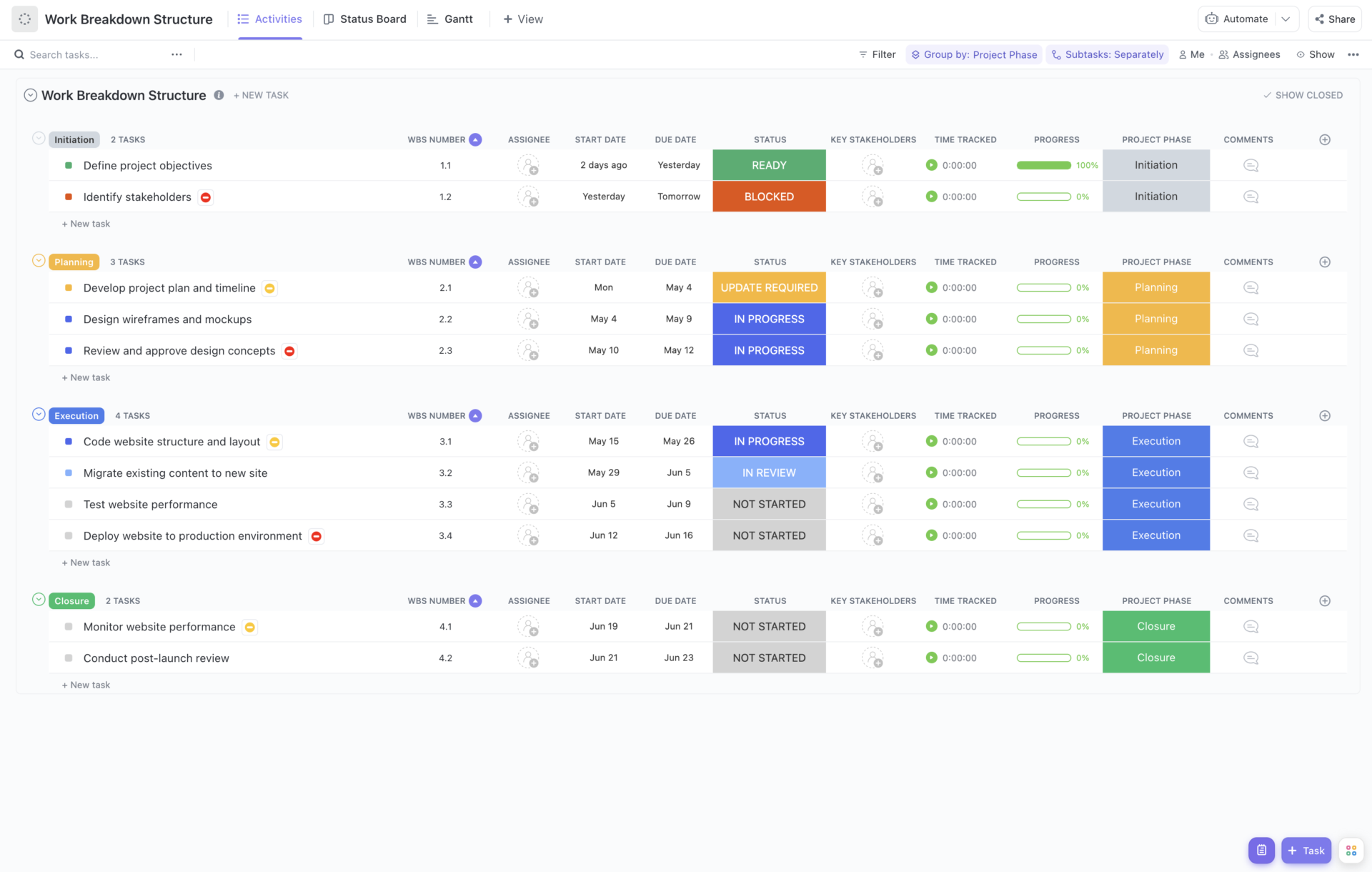
Project scope and work breakdown structure (WBS)
Defining the project scope is essential for establishing what is included and excluded, thereby preventing scope creep. A project scope statement details the project’s boundaries, deliverables, and constraints.
Complementing the scope is the WBS, which deconstructs the project into manageable tasks and sub-tasks.
For a marketing campaign, the scope might include social media ads and email outreach but exclude influencer partnerships and print media.
A WBS could break it down into:
- Content creation: Ad copy, graphics, and video production
- Campaign execution: Scheduling posts, launching email sequences
- Performance tracking: Analyzing engagement, adjusting strategy
The WBS helps create a high-level project plan by clarifying task dependencies and resource allocations. It ensures each component is clearly assigned and tracked, reducing ambiguity and improving control over project progress.
Schedule management
Schedule management outlines the timeline for project activities, highlighting key milestones, deadlines, and dependencies. This section describes the methods and tools used to plan, monitor, and control the project schedule.
A visual tool like a Gantt chart is often employed to map out phases, such as design, development, testing, and launch, with specific date ranges attached.
For instance, the schedule management for a marketing campaign might look like this:
| Phase | Timeframe | Key milestone | Dependencies |
| Content development | June 1-15 | First draft completed | Requires finalizing content strategy |
| Review | June 16-20 | Feedback incorporated | Relies on content completion |
| Deployment | June 21-30 | Campaign goes live | Demands approved content and review completion |
🧠 Fun Fact: The Y2K bug was basically a scheduling disaster waiting to happen. Early programmers used two-digit years (99 instead of 1999), which meant computers couldn’t process the year 2000 correctly. Companies spent billions fixing it because one small scheduling oversight can cause huge problems down the line.
Cost management
The temporary nature of a project calls for a clearly defined budget that is actively managed to prevent unnecessary expansion. Cost management includes estimating costs, setting budgets, and monitoring expenses to ensure adherence to financial constraints. This component details software, staffing, and marketing allocations.
For example, in a mobile app development project, the budget might allocate:
- $50,000 for development tools and cloud services
- $30,000 for developer salaries
- $20,000 for marketing and user acquisition
Regular expenditure tracking through variance analysis (comparing actual project performance against planned expectations) helps detect deviations early, allowing for prompt corrective action.
💡 Pro Tip: Customize your project budget templates to include a timeline for financial reviews. Regularly updating the budget according to project milestones helps maintain financial control and prevents running over budget.
Quality management
Quality management focuses on ensuring that project deliverables meet predefined performance standards and stakeholder expectations.
This section outlines quality assurance and quality control measures, including periodic inspections, testing procedures, and adherence to industry standards like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
For example, in a software development project, quality management might involve code reviews, automated testing, and user acceptance testing to catch defects early.
Adhering to ISO 25010 standards ensures the final product is reliable and meets stakeholder expectations.
🔍 Did You Know? Toyota once recalled nine million cars due to a sticky accelerator pedal. The cost? $1.2 billion — a painful lesson in why quality management can’t be an afterthought.
Resource management
Resource management involves strategically allocating and utilizing human, material, and technological resources essential to the project’s success. This component outlines team roles, hiring strategies, and equipment and material scheduling.
For instance, a customer support system upgrade might designate specialized teams for software configuration, training, and ongoing maintenance, ensuring that the right expertise is applied at the right time.
💡 Pro Tip: Create a project dashboard with live metrics (e.g., task completion, resource usage, financial health) for quick decision-making and adjustments. A dip in task completion can signal a bottleneck needing attention.
Risk management and mitigation strategies
Every project is susceptible to uncertainties, making risk management a crucial component. This component identifies potential threats that could derail the project and establishes strategies to mitigate their impact. It includes a thorough risk assessment, prioritization of identified risks, and contingency plan development.
For example, a network infrastructure upgrade might flag risks such as hardware failures or cybersecurity breaches and establish immediate response protocols to address these issues.
Utilizing risk matrices and periodic reviews, this section ensures that emerging issues are addressed proactively.
🧠 Fun Fact: The Leaning Tower of Pisa was a 199-year-long project fail. It took centuries to build, but no one accounted for the soft ground — hence the tilt. It’s now a global icon of poor planning.
Communication plan
The communication plan defines how project information will be shared among team members, stakeholders, and external parties. It outlines project management collaboration tools, reporting frequencies, and documentation procedures to ensure transparency.
For example:
| Recipients | Frequency | Medium | Contents |
| Project team members | Weekly (Every Wednesday) | ClickUp Chat or Slack | Task progress, upcoming deadlines, blockers |
| Clients | Biweekly (Every 15th and 30th) | PDF via email | Project milestones, risks, next steps |
| Senior management and executives | Monthly (First Monday) | Presentation | Key achievements, budget updates, risks |
💡 Pro Tip: Host ‘role clarity’ workshops to define roles, responsibilities, and expectations, ensuring everyone knows their duties and reducing misunderstandings.
Stakeholder management
Engaging the right stakeholders and gathering their feedback are pivotal to project success. This section identifies all parties impacted by the project and details strategies for regular interaction, such as structured feedback sessions, surveys, or one-on-one consultations.
For example, in a product launch project, stakeholders might include marketing teams, sales representatives, and end users.
Regular interaction could involve monthly strategy meetings with marketing, sales surveys to refine positioning, and beta testing sessions to gather user feedback before release.
You can also try the ClickUp Project Management Template to complement your project planning. It’s ideal for complex projects requiring detailed task tracking, risk monitoring, and stakeholder communications.
💡 Pro Tip: Set regular feedback checkpoints with stakeholders for consistent input and course adjustments, ensuring the project stays aligned with their expertise.
Procurement management
Procurement management addresses selecting, contracting, and overseeing external vendors, contractors, and suppliers. It specifies the required external products and services, criteria for their selection, and methods for performance monitoring.
For example, in a manufacturing project, procurement might involve sourcing specialized machinery with strict quality and delivery standards outlined in a Statement of Work (SOW) and Request for Proposal (RFP).
This component ensures that external contributions align with project quality and timeliness requirements, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns.
🔍 Did You Know? The Sydney Opera House was a massive project management failure. Originally planned to take four years and cost $7 million, it ended up taking 14 years and costing $102 million— 15 times over budget!
Change management and closure criteria
As projects evolve, managing modifications effectively becomes imperative. This section outlines formal procedures for handling change requests. It details how alterations to the project’s scope, timeline, or budget are evaluated and approved.
This component also specifies the criteria for project closure, including final deliverable acceptance, performance evaluations, and post-project reviews.
For example, a system upgrade project might require a formal sign-off from all key stakeholders before transitioning to maintenance mode. This way, all changes are documented and the project is wrapped up systematically.
🧠 Fun Fact: Pirates had their own version of project management. They followed strict codes of conduct, elected captains, and even had compensation plans for injuries.
Key Steps to Writing an Effective Project Management Plan
Writing a project management plan ensures smooth project execution, accountability, and risk management.
But writing one that’s actually useful (and not just a document that gets ignored) takes more than listing tasks. Here’s how to write one that actually works. ✅
Step #1: Identify project baselines
Project baselines serve as the benchmarks against which you measure project performance. Think of them as the ‘rules of the road’ that keep everything aligned.
Without them, it’s easy to veer off course, blow past deadlines, or watch costs spiral. Set these baselines early, and you’ll have a solid foundation to measure progress and adjust when needed.
This involves:
- Scope baseline: Define project deliverables and exclusions
- Schedule baseline: Outline key deadlines and milestones
- Cost baseline: Set initial budget estimates
For example, an e-commerce website project might include product listings, checkout functionality, and a mobile-responsive design, but exclude third-party integrations at launch.
Once baselines are set, document them in your project plan and communicate them clearly with your team. Any changes down the line should be carefully evaluated against these benchmarks to maintain control and avoid unexpected delays or budget overruns.
🔍 Did You Know? Burj Khalifa’s construction was so fast, it added a new floor every three days. With meticulous scheduling and resource management, it became the world’s tallest building in just six years.
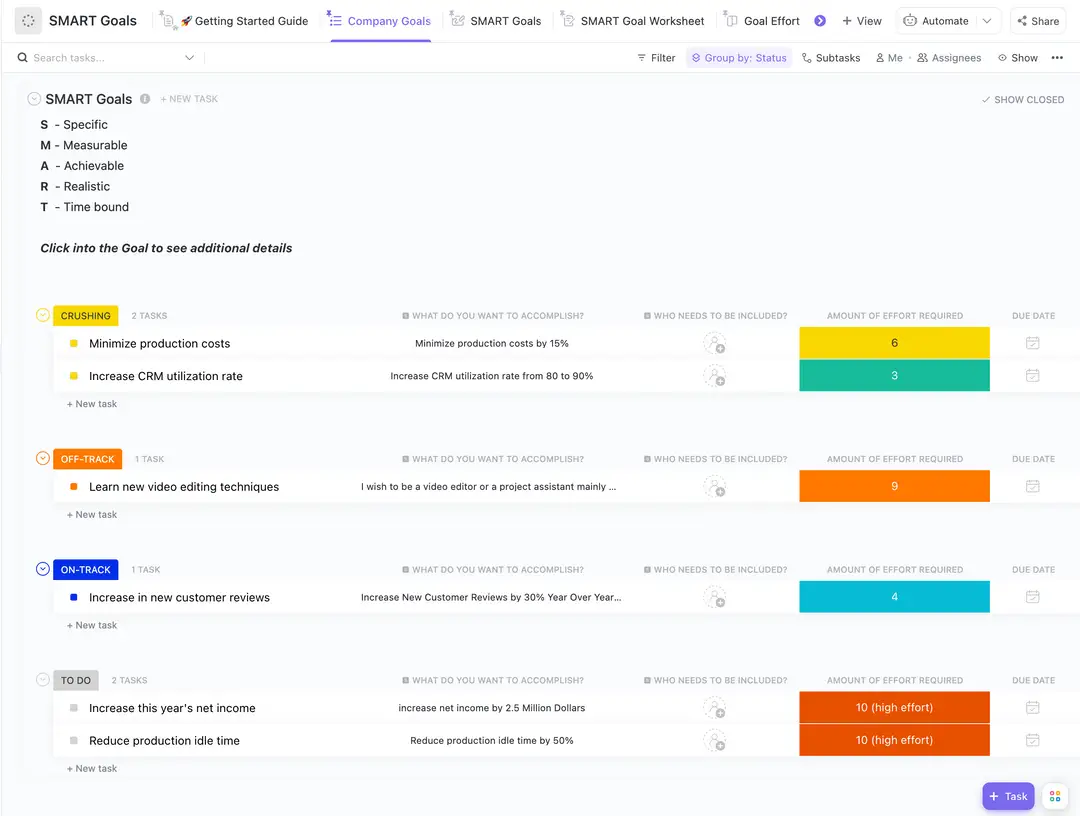
Step #2: Set SMART goals
Setting SMART goals is crucial for translating your vision into actionable targets. Use this framework to ensure goals are:
🎯 Specific: Clearly define what success looks like
🎯 Measurable: Use quantifiable metrics
🎯 Achievable: Align with available resources
🎯 Relevant: Contribute to broader business goals
🎯 Time-bound: Include deadlines
For instance, rather than stating, ‘Improve user engagement,’ a SMART goal would be, ‘Increase user engagement by 20% over the next six months by optimizing app notifications and user interface design.’
This step helps define clear performance metrics and create a project timeline that motivates the team to deliver results within set deadlines.
💡 Pro Tip: Use goal setting templates to break large objectives into smaller, actionable tasks with deadlines. This will help prioritize efforts, track progress, and keep your team focused on the most impactful actions.
Step #3: Determine your project budget
Accurate budgeting lays the financial foundation for your project. A WBS organizes work into hierarchical sections.
To start, your budget should cover three key aspects:
💰 Total project costs: Includes labor, materials, and equipment
💰 Resource allocation: Divides budgets by deliverables
💰 Project timeline: Outlines when funds will be spent on each deliverable
Begin with a detailed cost breakdown using techniques such as bottom-up estimation or analogous estimating to ensure that every expense is accounted for. For example, in a software development project, the WBS might include a:
- Design phase
- Wireframes
- UI/UX prototyping
- Development phase
- Backend development
- Frontend development
- Testing phase
- User testing
- Bug fixes
Step #4: Pinpoint project dependencies
Understanding project dependencies is essential for sequencing tasks and managing workflow. Dependencies describe how tasks relate to one another — whether one must be completed before another can start (finish-to-start) or if they can run concurrently.
Follow these key steps:
- Map out task sequences to identify critical paths
- Analyze both internal dependencies (within project tasks) and external dependencies (influences from outside projects or vendors)
For example, in event planning, securing a venue must happen before invitations are sent, but catering arrangements and stage setup can happen simultaneously.
In a software development project, backend architecture must be built before integrating user authentication, but UI design can progress alongside coding.
🧠 Fun Fact: Mount Rushmore was originally supposed to show full bodies. Budget constraints forced the project to scale back, so we got giant faces instead. Classic case of scope reduction.
Step #5: Recognize project stakeholders
Identifying and understanding stakeholders is vital to the success of your project. A stakeholder analysis includes:
- Influence and interest levels: Who needs frequent updates, and who prefers only major milestones?
- Communication preferences: Does your sponsor want detailed reports, quick email summaries, or regular check-ins?
- Potential risks and support: Who has the power to accelerate approvals, and who might delay progress with conflicting priorities?
Once you know who’s involved, get ahead of their expectations. Set up clear communication, address concerns before they turn into roadblocks, and keep everyone aligned so there are no surprises.
The better you manage stakeholder relationships, the fewer unexpected twists your project will face.
Step #6: Establish project milestones
Milestones are the significant markers that denote progress throughout your project. Define milestones that represent critical phases such as project initiation, design approval, prototype completion, and final delivery.
Plus, set milestone dates that reflect realistic timelines while utilizing time tracking reporting to stay on track.
For a mobile app development project, key milestones might include:
📌 Project kickoff: Finalizing requirements and assembling the team
📌 Design approval: Stakeholders sign off on UI/UX mockups
📌 Prototype completion: A functional version is ready for initial testing
📌 Beta launch: Limited user testing begins
📌 Final release: The app goes live on app stores
Regular milestone reviews ensure smooth progress.
🔍 Did You Know? 86% of organizations now have one or more PMOs, up from 71% in 2016. In the last five years, PMOs have focused more on project assurance and managing enterprise PM solutions, while status reporting remains the most common activity, with benefits tracking being the least prioritized.
Step #7: Assign responsibilities
Clearly assigned responsibilities maintain accountability and ensure smooth execution. A common technique is to use the RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) to define roles.
Key considerations include:
- Identifying individual or team strengths and matching them with task requirements
- Clearly outlining the scope of responsibility for each role
- Setting up regular check-ins to monitor progress and address issues promptly
For a product launch project, a RACI matrix could look like this:
- Market research: Research team (Responsible), Marketing lead (Accountable), Sales team (Consulted), Executive team (Informed)
- Product development: Engineering team (Responsible), Product manager (Accountable), Design team (Consulted), Customer support team (Informed)
- Go-to-market strategy: Marketing team (Responsible), Head of marketing (Accountable), Sales and product teams (Consulted), Company leadership (Informed)
- Launch event and promotions: Events team (Responsible), Marketing director (Accountable), PR team (Consulted), Entire company (Informed)
Step #8: Implement change management and define closure criteria
Even the most well-planned projects face changes along the way. A structured change management process ensures that adjustments are intentional, controlled, and aligned with project goals — rather than last-minute surprises that derail progress.
Define clear protocols for who can request changes, how they will be evaluated, and the approval process. If this isn’t in place, minor tweaks can snowball into full-blown scope creep, stretching timelines and budgets beyond control.
Equally important is defining closure criteria to ensure the project wraps up properly.
Establish what needs to be completed before calling the project ‘done’. This might include:
- Meeting all deliverables
- Securing stakeholder sign-off
- Finalizing documentation
- Conducting a post-project review
A structured closure phase prevents lingering issues, captures lessons learned, and allows teams to transition smoothly to their next priorities.
Change management might involve a formal review process in a software development project. Any feature requests after the development phase will require approval from the product manager and feasibility assessment to understand its impact on the timeline.
Closure criteria could include final user testing, bug fixes, security audits, and a sign-off from key stakeholders before the product officially launches.
Using Project Management Software and Tools
Keeping a project on track requires the right project planning tools to bring it to life.
However, work today is often fragmented — projects, knowledge, and communication are scattered across disconnected tools that slow down progress.
ClickUp solves this problem by bringing everything into one platform, combining project, knowledge, and chat in a single, AI-powered solution that helps teams work faster and smarter.
The ClickUp Project Management Software offers a robust platform to streamline project planning through customizable views and integrated tools. It allows you to define tasks, set priorities, and allocate resources with precision.
Let’s look at how ClickUp supports project planning. 👀
Manage tasks with ease
ClickUp makes task management easy, helping teams stay organized, focused, and on top of deadlines. With everything in one place, tracking progress, prioritizing tasks, and keeping work moving without the usual back-and-forth becomes easy.
Begin by creating and assigning ClickUp Tasks with detailed descriptions and due dates to keep your team aligned on what needs to be done.
For example, a marketing team preparing a product launch can create a task for ‘Social Media Ad Design,’ assign it to the designer, attach brand assets, and add a due date to ensure it is ready before the launch campaign kicks off.
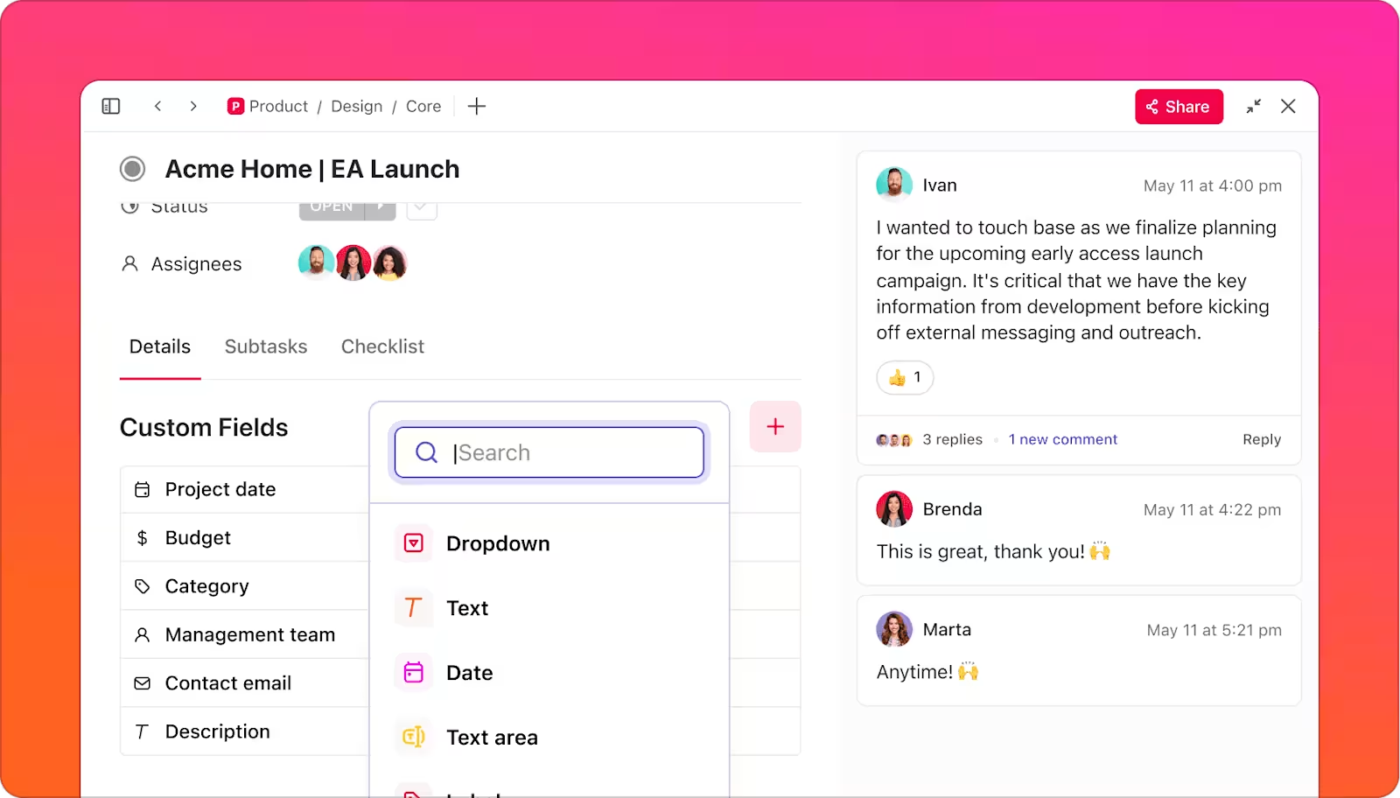
ClickUp Custom Fields let you tailor Tasks with extra details.
A video production team, for instance, can create fields like ‘Video Length’ to track runtime, ‘Script Status’ to mark drafts as pending or approved, and ‘Platform’ to specify if a video is for YouTube, Instagram, or LinkedIn.
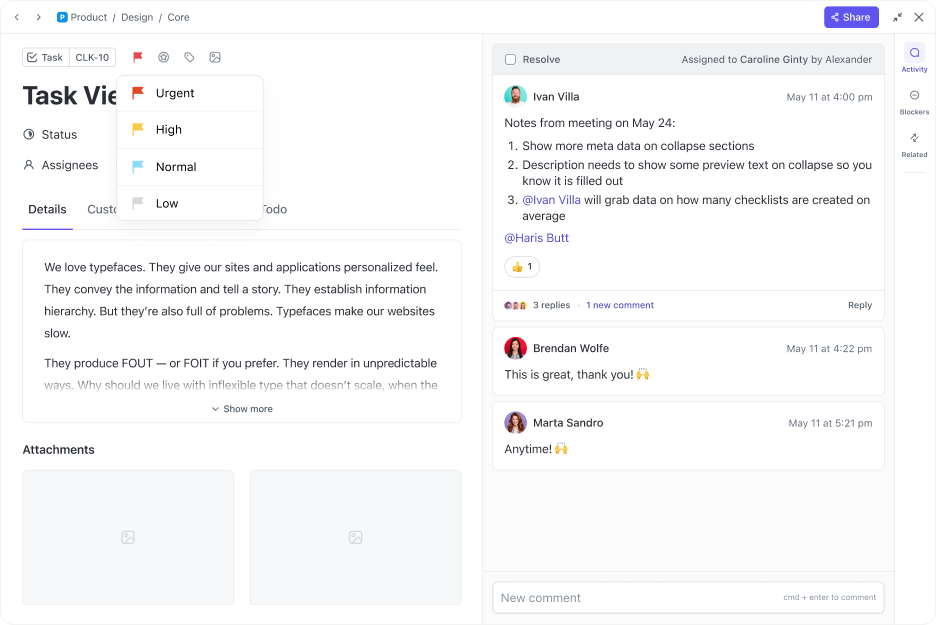
Further, you can use ClickUp Task Priorities to set color-coded priority levels (Urgent, High, Normal, Low). This helps your team focus on what matters most.
ClickUp Custom Task Statuses replace rigid ‘To Do’ and ‘Done’ labels with statuses that match real project stages. A content team managing blog posts, for example, can set statuses like ‘Drafting,’ ‘Editing,’ and ‘Ready to Publish’ to make progress clear.
Optimize your project management plan
Wondering how to bring AI in for a productivity boost?
ClickUp Brain is an AI-powered neural network that integrates with your projects, documents, and team communications into one seamless workspace. It allows teams to manage files, research, and project-related information in one location.
This is particularly beneficial for projects that require frequent reference to technical documents or industry research.
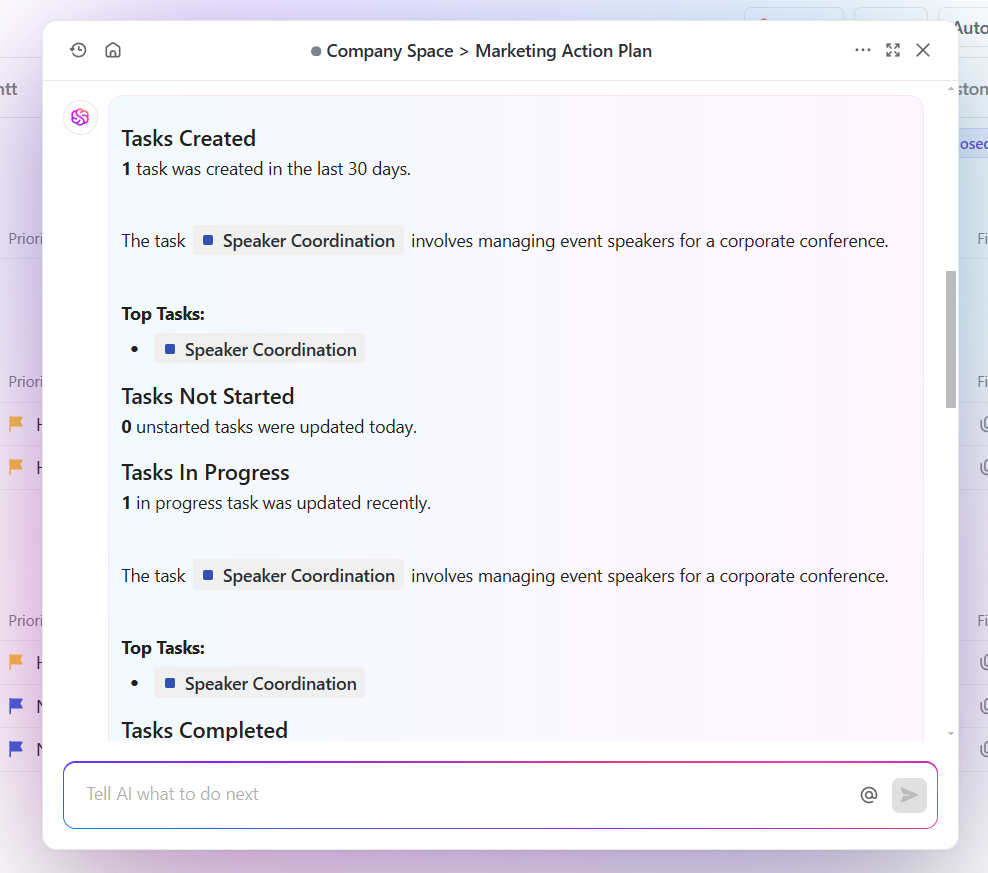
One standout feature is the AI Project Manager, which helps keep your projects on track with intelligent automation and real-time insights. Here’s how it optimizes your plan:
- Project summaries: Automatically generate status updates, action items, and next steps for any project, saving time with accurate reporting
- Personal standups: Instantly see your to-do list and share it with your team or manager, streamlining communication and alignment
- Team updates: Track team progress by selecting team members to see how workloads are distributed and how the project is advancing towards its goals
- Automation builder: Create custom project management automations by adding instructions in plain language to speed up repetitive workflows
Visualize workflows and track performance
Want to see your tasks come to life? ClickUp Gantt Chart View helps visualize task sequences, dependencies, and deadlines. You can gain insight into your project’s progress and foresee any possible delays.
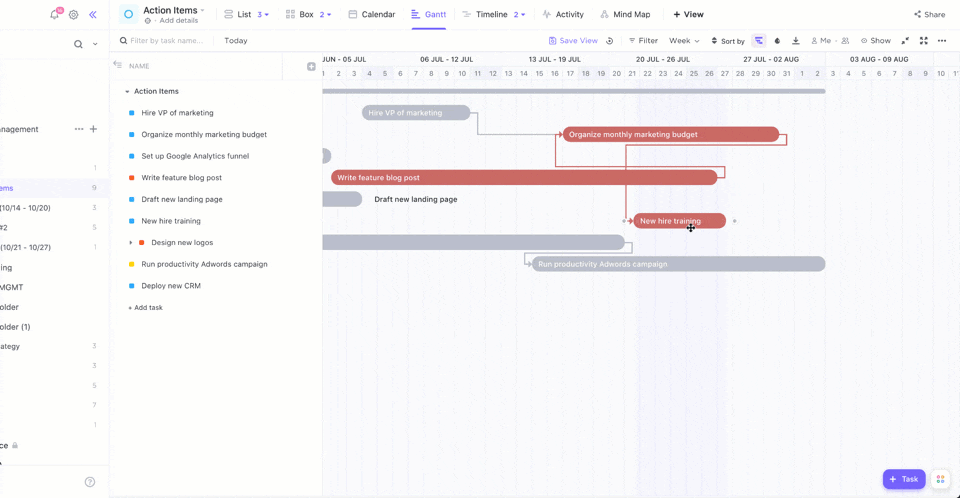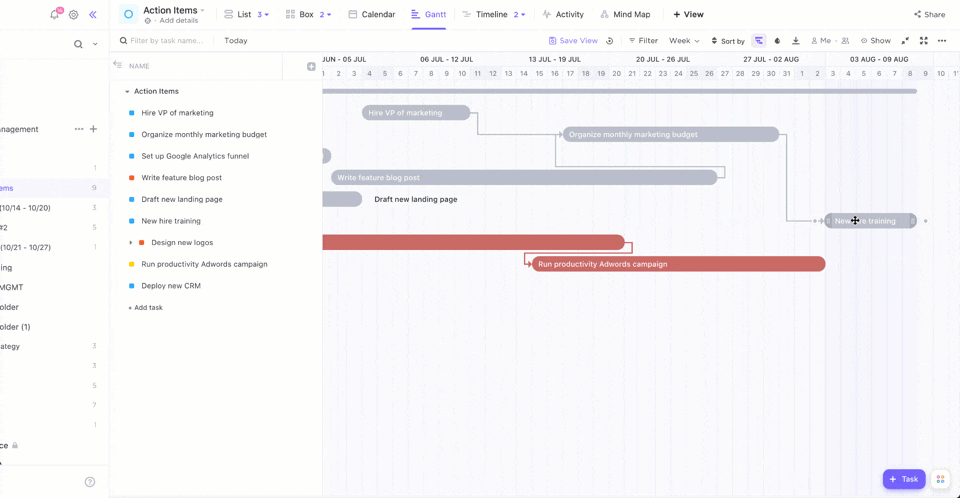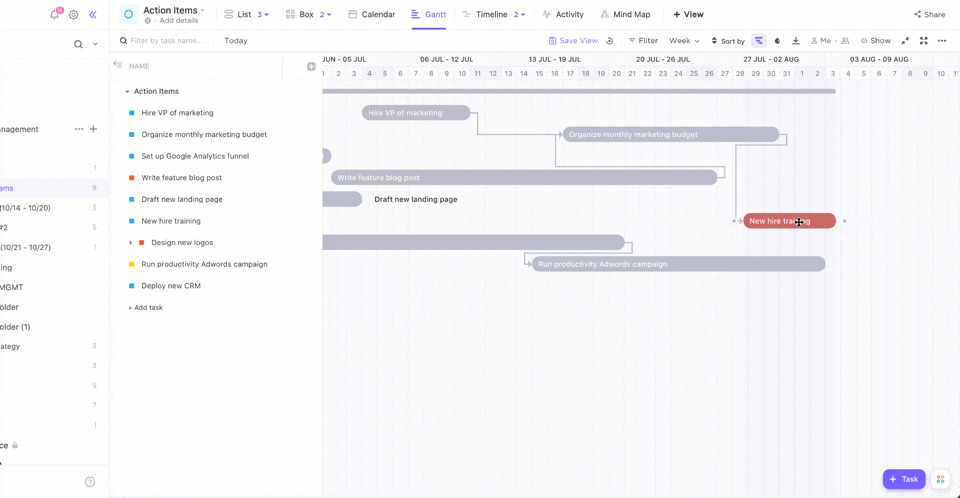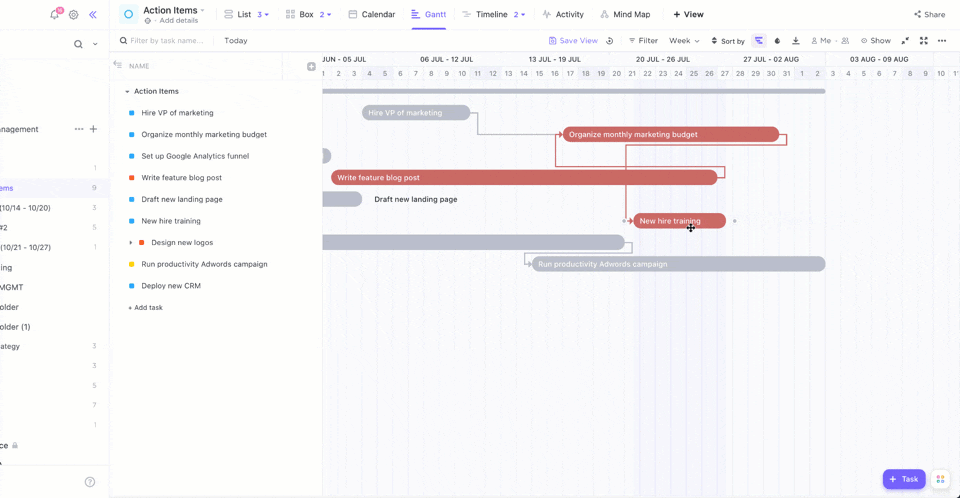
The Critical Path highlights tasks that affect your deadlines, while Slack Time shows tasks with more flexible timelines. This brings us to the next step: Visualizing actual progress!
ClickUp Dashboards aggregate data from various projects, offering real-time insights into performance metrics. They enable you to track time spent on tasks, simplify billing, and prioritize client work with a centralized dashboard to improve transparency and efficiency.
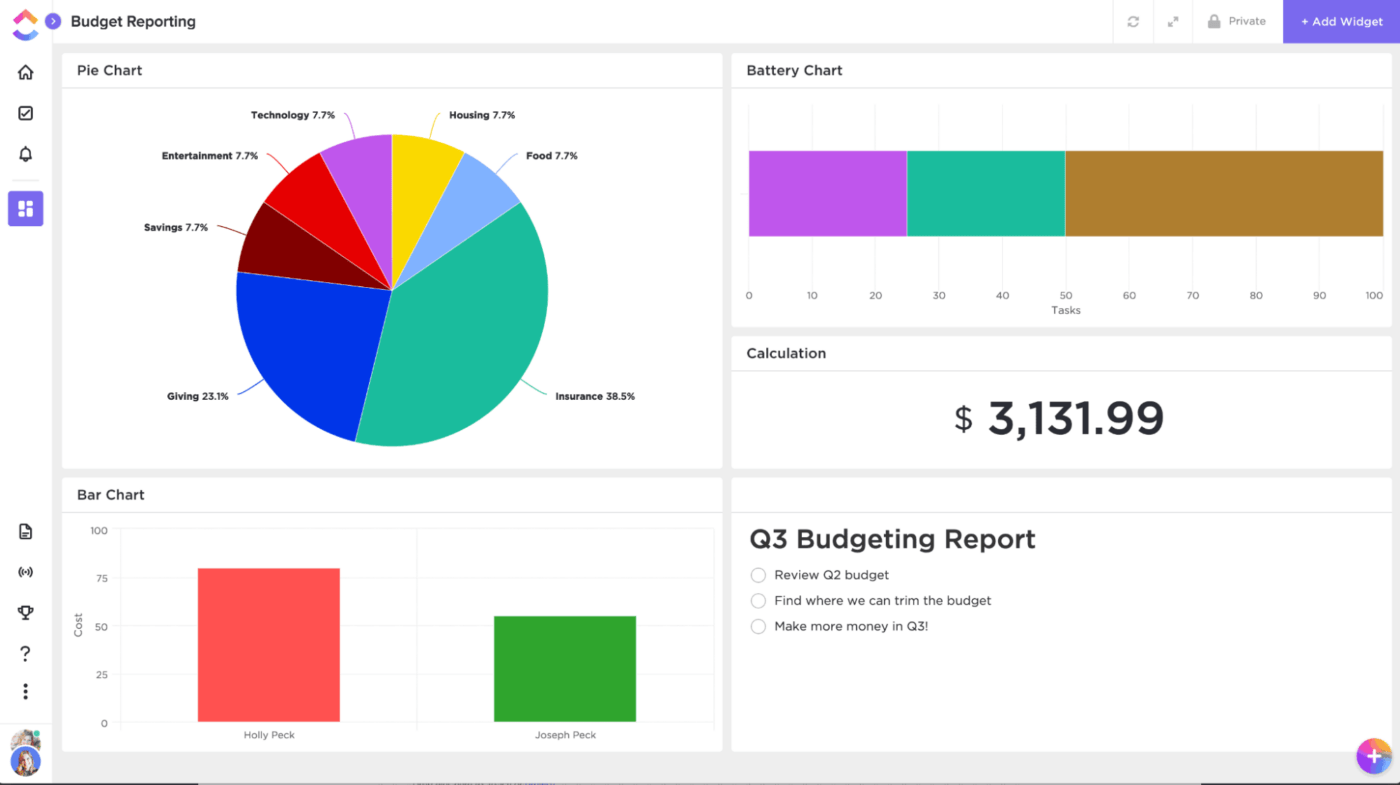
A sales team could use a Dashboard to monitor lead conversion rates and campaign performance, while a customer support team might track ticket resolution times and workload distribution.
Enhance cross-functional collaboration
ClickUp Chat brings project planning and team conversations together, eliminating the hassle of switching between apps to track updates, share ideas, or assign tasks.
See something important in chat? Turn it into a task on the spot, assign a FollowUp, or let AI handle the details. Since every chat connects to your Lists, Folders, and Spaces, checking progress or updating a task happens right where the conversation does.
It is also built to keep distractions in check. Customize notifications to focus on conversations that matter, and let AI-powered Catch Me Up summarize what you missed instead of scrolling through endless messages.
When a quick message is not enough, start an audio or video SyncUp right from Chat.
Monitor team productivity
ClickUp Time Tracking helps teams monitor productivity and ensure accountability. Team members can log hours spent on tasks, making it easier to identify time sinks and improve workflow efficiency.

For instance, a consulting firm might track billable hours per client project, while an IT department could monitor time spent on system maintenance tasks.
Automate workflows and processes
ClickUp Automation reduces manual workload and minimizes the risk of human error. Set up triggers for recurring tasks, status updates, and notifications, so workflows move forward without constant check-ins.
Need to keep things on track? Automate task assignments, add watchers to key action items, and update statuses as progress is made.
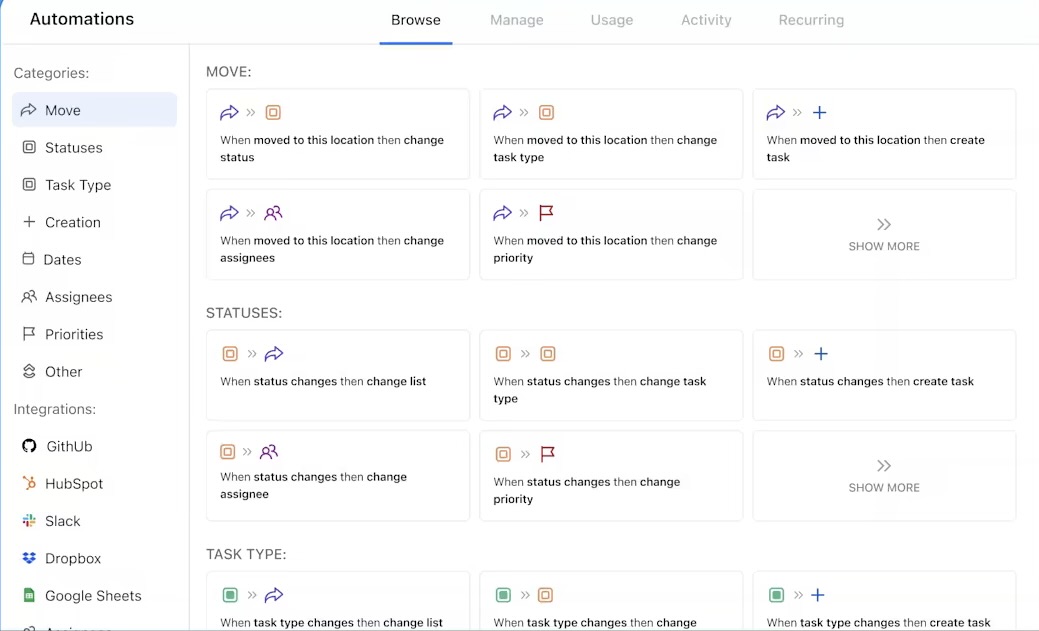
Say a marketing team is prepping a product launch. The moment an ‘Ad Creative’ task is added, ClickUp can instantly assign it to a designer, add a marketing lead as a watcher, and update the status to ‘In Progress.’ Once the final design is uploaded, the status moves to ‘Ready for Review.’
Sample Project Management Plan Outline
A project plan document keeps everything in check, but where do you start? A solid outline makes it easier to map out tasks, timelines, and responsibilities without overcomplicating things.
Here’s a sample structure to guide you. 👇
Project Management Plan
Project name: GreenTech Solar Expansion Project
Prepared by: Project Manager, GreenTech Solutions
Date: March 1, 2025
1. Project overview
Objective: Expand GreenTech Solutions’ solar energy production by installing 500 new solar panels across three locations. The project aims to increase renewable energy output by 20% within six months.
Scope:
- Site preparation and infrastructure setup
- Procurement and installation of solar panels
- Integration with the existing power grid
- Performance testing and quality assurance
- Final review and handover
Stakeholders:
- Project sponsor: GreenTech Executive Team
- Project manager: John Doe
- Engineering team: Solar panel installation specialists
- Finance team: Budget tracking and approvals
- Local authorities: Permits and compliance oversight
2. Task and timeline management
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
- Planning (March 1-15): Site selection, permit approvals
- Procurement (March 16-April 5): Ordering panels, hiring contractors
- Installation (April 6-May 30): Panel setup, system integration
- Testing and quality control (June 1-15): Performance verification
- Handover and reporting (June 16-30): Final approvals, project closure
Schedule Management:
- Gantt Chart used: Tracks dependencies and deadlines
- Milestones:
- March 15 – Permits approved
- April 5 – Procurement complete
- May 30 – Installation complete
3. Performance indicators to track progress
- Schedule variance (SV): Measures if installation is on track per milestone dates
- Cost performance index (CPI): Ensures budget adherence by tracking planned vs. actual expenses
- Task completion rate: Tracks installation progress against the total goal (500 panels)
- Risk assessment: Identifies delays in permits, weather impacts, or supply chain issues
4. Communication and reporting
Stakeholder updates:
- Weekly progress reports via ClickUp Dashboards
- Monthly meetings with GreenTech executives
Collaboration tools:
- ClickUp Tasks for assignments and tracking
- ClickUp Chat for real-time updates
- Automated email updates for status changes
Issue tracking:
- All project risks and blockers logged in ClickUp Risk Register
- Escalation process in place for critical delays
🧠 Fun Fact: The term ‘silver bullet’ in project management has its roots in folklore. It originally referred to the only thing that could kill a werewolf. In project terms, it’s the mythical ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution that rarely exists.
Best Practices and Tips for Successful Project Planning
A project plan is only useful if it actually helps your team work smarter, not just look good on paper. The real challenge isn’t making a plan; it’s making one that people actually follow.
Here’s how to create a plan that’s realistic, actionable, and built for success. ✍️
Plan backwards, not forwards
Rather than asking ‘What do we do first?’ start with the end goal in mind.
Work backwards from the deadline to map out the essential steps, focusing on the key deliverables that define success. This approach helps eliminate unnecessary tasks, keeps the timeline realistic, and ensures that every step leads directly to the final outcome.
If launching a new product, pinpoint the release date first, then map out essential steps like testing, manufacturing, and marketing campaigns. This ensures everything is aligned and realistic.
Assume things will go wrong
No matter how carefully you plan, unexpected problems will arise.
Deadlines might shift, priorities may change, or key resources could become unavailable. A strong plan doesn’t just map out the best-case scenario — it prepares for setbacks and builds in room to adjust.
For example, if a critical software integration depends on an external vendor, plan for delays by identifying an alternative solution or a manual workaround. This prevents a single delay from stalling the entire project.
📖 Also Read: Real Project Management Examples for Your Team
Close the loop with retrospectives
A project isn’t truly done until you’ve had a good look back. Retrospectives help uncover what worked well, what caused delays, and what needs improvement. The focus isn’t on assigning blame but on making the next project smoother and more efficient.
Teams that consistently review and refine their approach avoid repeating mistakes and find better ways to collaborate.
After a product launch, if approval delays slowed progress, update workflows with clearer checkpoints. If miscommunication caused issues, introduce regular cross-team check-ins.
Small adjustments like these prevent repeat mistakes and improve future projects.
Master Projects with the Right Plan with ClickUp
A project management plan is your team’s playbook — it keeps tasks organized, deadlines in check, and everyone moving in the right direction. But let’s be real: a plan sitting in a doc doesn’t mean much if no one actually follows it.
Keeping track of updates, progress, and next steps shouldn’t feel like a chore.
ClickUp takes the chaos out of project management.
With everything in one place, teams can track tasks, deadlines, and milestones without switching between tools. Customizable Views make it easy to see progress from every angle, Dashboards provide real-time insights, and Automation eliminates repetitive work.
ClickUp Brain adds an extra layer of intelligence, generating instant project summaries, optimizing resources, and keeping teams on the same page without the extra effort.
Why waste time on manual updates and scattered information? Sign up to ClickUp today and see the difference!