How to Use DBRX for AI Model Training in 2026
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

AI training projects rarely fail at the model level. They struggle when experiments, documentation, and stakeholder updates are scattered across too many tools.
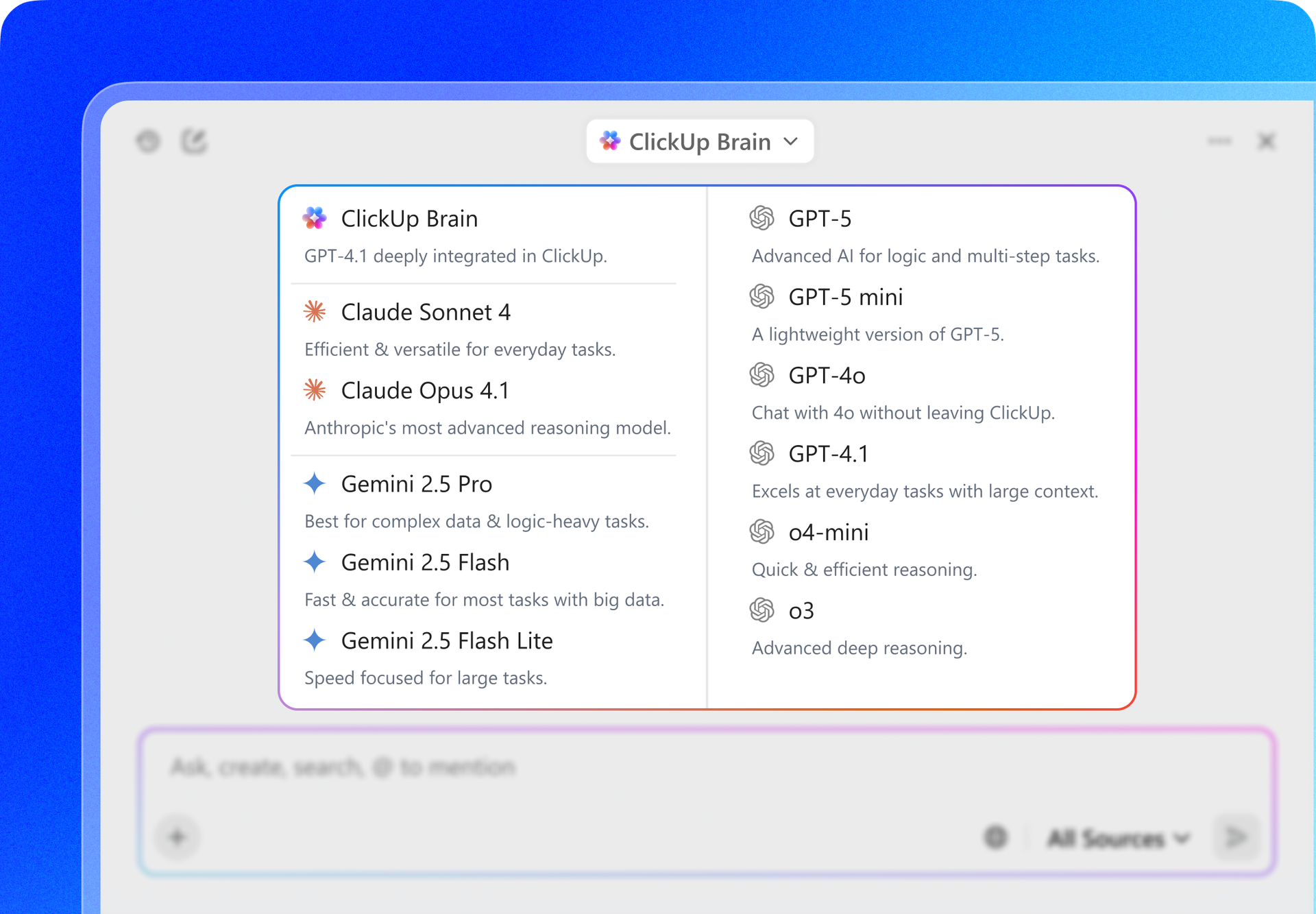
This guide walks you through training models with Databricks DBRX—an LLM that’s up to twice as compute-efficient as other leading models—while keeping the work around it organized in ClickUp.
From setup and fine-tuning to documentation and cross-team updates, you’ll see how a single, converged workspace helps eliminate context sprawl and keeps your team focused on building, not searching. 🛠
DBRX is a powerful, open-source large language model (LLM) designed specifically for enterprise AI model training and inference. Because it’s open source under the Databricks Open Model License,, your team has full access to the model’s weights and architecture, allowing you to inspect, modify, and deploy it on your own terms.
It comes in two variants: DBRX Base for deep pre-training and DBRX Instruct for out-of-the-box instruction-following tasks.
DBRX solves tasks using a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. Unlike traditional large language models that use all of their billions of parameters for every single calculation, DBRX only activates a fraction of its total parameters (the most relevant experts) for any given task.
Think of it as a team of specialized experts; instead of everyone working on every problem, the system intelligently routes each task to the most qualified matching parameters.
Not only does this cut down on response time, but it also delivers top-tier performance and outputs while significantly reducing computational costs.
Here’s a quick look at its key specifications:
The performance of an LLM is only as good as the data it’s trained on. DBRX was pre-trained on a massive 12-trillion-token dataset carefully curated by the Databricks team using their advanced data processing tools. It’s exactly why it performed strongly on industry benchmarks.
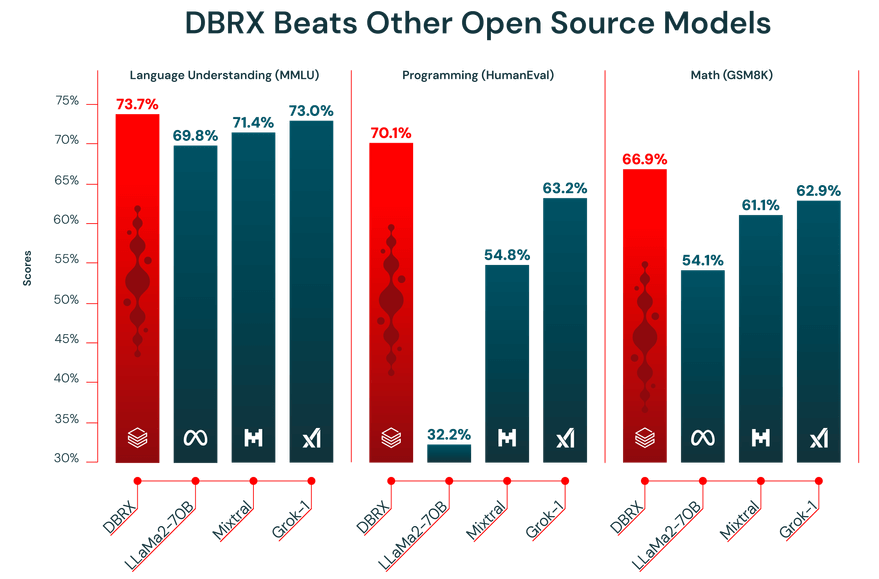
Additionally, DBRX features a 32,000-token context window. This is the amount of text the model can consider at one time. A large context window is super helpful for complex tasks like summarizing long reports, digging through lengthy legal documents, or building advanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, as it allows the model to maintain context without truncating or forgetting information.
🎥 Watch this video to see how streamlined project coordination can transform your AI training workflow and eliminate the friction of switching between disconnected tools.👇🏽
DBRX offers two primary access routes, both of which provide full access to the model weights under permissive commercial terms. You can use Hugging Face for maximum flexibility or access it directly through Databricks for a more integrated experience.
For teams that value flexibility and are already comfortable with the Hugging Face ecosystem, accessing DBRX through the Hub is the ideal path. It allows you to integrate the model into your existing transformers-based workflows.
Here’s how to get started:
transformers library along with necessary dependencies like accelerateAutoModelForCausalLM class in your Python script to load the DBRX model📖 Read More: How to Configure LLM Temperature
If your team already uses Databricks for data engineering or machine learning, accessing DBRX through the platform is the easiest way. It cuts out setup friction and gives you all the tools you need for MLOps right where you’re already working.
Follow these steps within your Databricks workspace to get started:
This approach gives you seamless access to tools such as MLflow for experiment tracking and the Unity Catalog for model governance.
📮 ClickUp Insight: The average professional spends 30+ minutes a day searching for work-related information—that’s over 120 hours a year lost to digging through emails, Slack threads, and scattered files.
An intelligent AI assistant embedded in your workspace can change that. Enter ClickUp Brain.
It delivers instant insights and answers by surfacing the right documents, conversations, and task details in seconds—so you can stop searching and start working.
An off-the-shelf model, no matter how powerful, will never understand the unique nuances of your business. Because DBRX is open source, you can fine-tune it to create a custom model that speaks your company’s language or performs a specific task you would like it to handle.
Here are three common ways you can do this:
For teams just starting out or working on common tasks, public datasets from Hugging Face Hub are a great resource. They are pre-formatted and easy to load, meaning you don’t have to spend hours preparing your data.
The process is pretty straightforward:
datasets libraryYou’ll usually get the best results by fine-tuning with your own proprietary data. This allows you to teach the model your company’s specific terminology, style, and domain knowledge. Just keep in mind that it only pays off if your data is clean and well-prepared, and has sufficient volume.
Follow these steps to prepare your internal data:
If your dataset ends up being too large to fit into your machine’s memory, no worries, you can use Databricks’ Streaming Dataset library. It allows you to stream data directly from cloud storage while the model is training, rather than loading it all into memory at once.
Here’s how you can do it:
💡Pro tip: Instead of building a DBRX training plan from scratch, start with ClickUp’s AI and Machine Learning Projects Roadmap Template and tweak it to your team’s needs. It provides a clear structure for planning datasets, training phases, evaluation, and deployment, so you can focus on organizing your work rather than structuring a workflow.
It’s one thing to have a powerful model, but it’s another to know exactly where it shines.
When you don’t have a clear picture of a model’s strengths, it’s easy to spend time and resources trying to make it work where it simply doesn’t fit. This leads to subpar results and frustration.
DBRX’s unique architecture and training data make it exceptionally well-suited for several key enterprise use cases. Knowing these strengths helps you align the model with your business objectives and maximize your return on investment.
DBRX Instruct is finely tuned for following instructions and generating high-quality text. This makes it a powerful tool for automating a wide range of content-related tasks. Its large context window is a significant advantage, enabling it to handle long documents without losing the thread.
You can use it for:
A significant portion of DBRX’s training data included code, making it a capable LLM support for developers. It can help accelerate development cycles by automating repetitive coding tasks and assisting with complex problem-solving.
Here are a few ways your engineering team can leverage it:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique that grounds a model’s responses in your company’s private data. However, RAG systems often struggle with models that have small context windows, forcing aggressive data chunking that can lose important context. DBRX’s 32K context window makes it an excellent foundation for robust RAG applications.
This lets you build powerful internal tools, such as:
A successful AI model training project is about more than just code and compute. It’s a collaborative effort involving ML engineers, data scientists, product managers, and stakeholders.
When this collaboration is scattered across Jupyter notebooks, Slack channels, and separate project management tools, you create context sprawl, a situation where critical project info is scattered across too many tools.
ClickUp solves that. Instead of juggling multiple tools, you get one Converged AI Workspace where project management, documentation, and communication live together—so your experiments stay connected from planning to execution to evaluation.
When running multiple experiments, the hardest part is not training the model; it’s keeping track of what changed during the process. Which dataset version was used, what learning rate performed best, or which run shipped?
ClickUp makes this process super easy for you. You can track each training run separately in ClickUp Tasks, and within tasks, you can use Custom Fields to log:
That way, every documented experiment is searchable, easy to compare with others, and reproducible.
You don’t have to jump between Jupyter notebooks, README files, or Slack threads to understand the context of an experiment’s task.
With ClickUp Docs, you can keep your model architecture, data prep scripts, or evaluation metrics organized and accessible by documenting them in a searchable doc that links directly to the experiment tasks they came from.
💡Pro Tip: Maintain a living project brief in ClickUp Docs that details every decision, from architecture to deployment, so new team members can always get up to speed with project details without digging through old threads
ClickUp Dashboards show experiment progress and team workload in real time. I
nstead of manually compiling updates or sending emails, dashboards update automatically based on the data in your tasks. so stakeholders can check in anytime, see where things stand, and never need to interrupt you with “what’s the status?” questions.
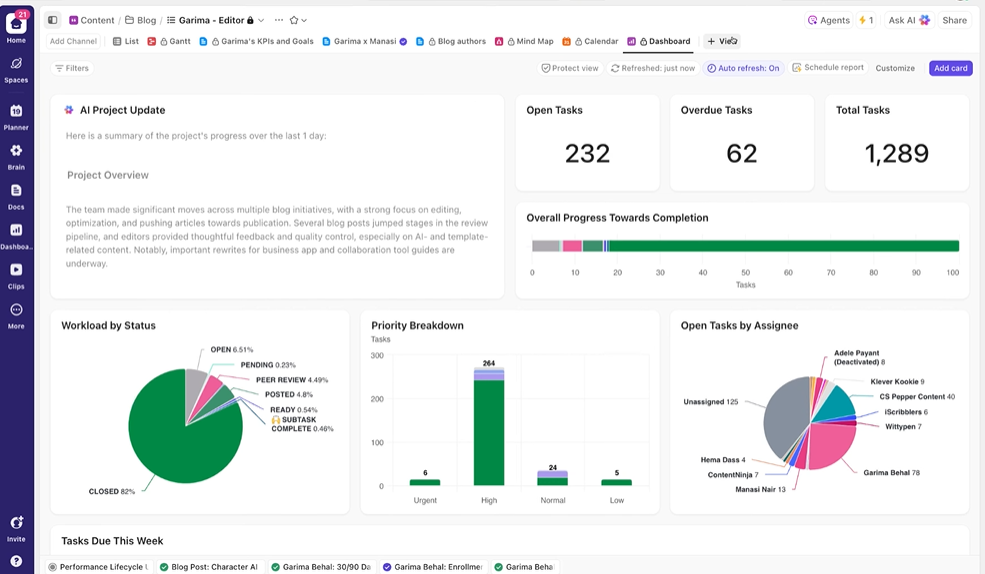
This way, you focus on running experiments rather than constantly having to report on them manually.
You don’t have to manually dig through weeks of training data to get a summary of experiments so far. Just mention @Brain on any task comment, and ClickUp Brain will give you the help you need with full context to your past and ongoing projects.
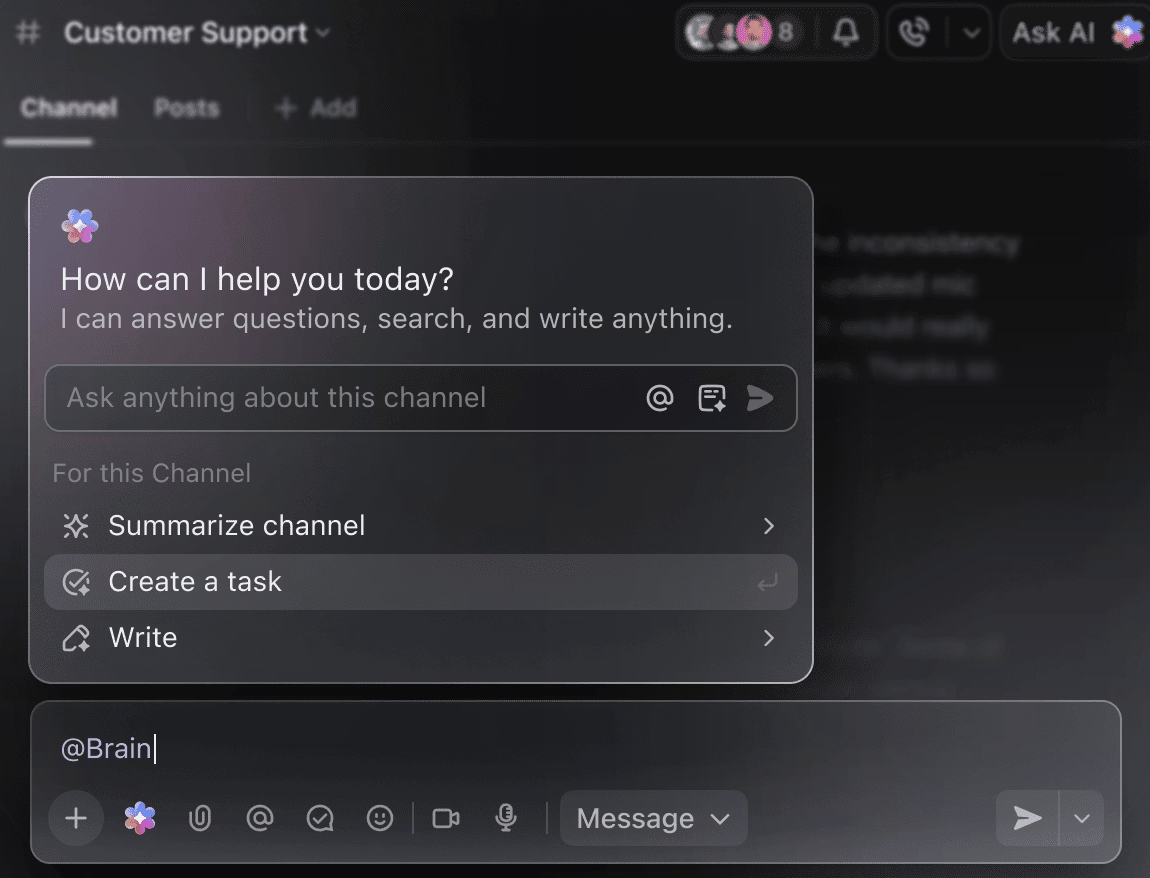
You can ask Brain to ‘Summarize last week’s experiments in 5 bullet points’ or ‘Draft a doc with the latest hyperparameter results,’ and instantly get a polished output.
🧠 The ClickUp Advantage: ClickUp’s Super Agents take this much further—they can automate entire workflows based on triggers you define, not just answer your questions. With super agents, you can automatically create a new DBRX training task whenever a dataset is uploaded, notify your team, and link relevant Docs when the training run finishes or hits a checkpoint, and generate a weekly progress summary and push it to stakeholders without you touching a thing.
Embarking on a DBRX training project is exciting, but a few common pitfalls can derail your progress. Avoiding these mistakes will save you time, money, and a lot of frustration.
Deciding on an AI training platform involves a fundamental trade-off: control vs. convenience. Proprietary, API-only models are easy to use but lock you into a vendor’s ecosystem.
Open weights models like DBRX offer complete control but require more technical expertise and infrastructure. This choice can leave you feeling stuck, unsure which path actually supports your long-term goals—a challenge many teams face during AI adoption.
This table breaks down the key differences to help you make an informed decision.
| Criteria | DBRX | GPT-5 / GPT-5.2 | LLaMA 3.1 / 4 | Claude 4.5 |
| Weights | Open (Custom) | Proprietary | Open (Custom) | Proprietary |
| Fine-tuning | Full Control | API-based | Full Control | API-based |
| Self-hosting | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| License | DB Open Model | OpenAI Terms | Llama Community | Anthropic Terms |
| Context | 32K | 128K – 1M | 128K | 200K – 1M |
DBRX is the right choice when you need full control over the model, must self-host for security or compliance, or want the flexibility of a permissive commercial license. If you don’t have dedicated GPU infrastructure—or you value speed to market more than deep customization—API-based alternatives may be a better fit.
DBRX gives you an enterprise-ready foundation for building custom AI applications, with the transparency and control you don’t get from proprietary models. Its efficient MoE architecture keeps inference costs down, and its open design makes fine-tuning easy. But strong tech is only half the equation.
True success comes from aligning your technical work with your team’s collaborative workflow. AI model training is a team sport, and keeping experiments, documentation, and stakeholder communication in sync is crucial. When you bring everything into a single converged workspace and cut down on context sprawl, you can ship better models, faster.
Get started for free with ClickUp to coordinate your AI training projects in one workspace. ✨
You can monitor training using standard ML tools like TensorBoard, Weights & Biases, or MLflow. If you’re training within the Databricks ecosystem, MLflow is natively integrated for seamless experiment tracking.
Yes, DBRX can be integrated into standard MLOps pipelines. By containerizing the model, you can deploy it using orchestration platforms like Kubeflow or custom CI/CD workflows.
DBRX Base is the foundational pre-trained model intended for teams that want to perform domain-specific continued pre-training or deep architectural fine-tuning. DBRX Instruct is a fine-tuned version optimized for following instructions, making it a better starting point for most application development.
The main difference is control. DBRX gives you full access to the model weights for deep customization and self-hosting, whereas GPT-4 is an API-only service.
The DBRX model weights are available for free under the Databricks Open Model License. However, you are responsible for the costs of the compute infrastructure required to run or fine-tune the model.
© 2026 ClickUp