How to Train Gemini on Your Own Data in 2026
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”

According to a recent enterprise study, 73% of organizations report that their AI models fail to understand company-specific terminology and context, leading to outputs that require extensive manual correction. This becomes one of the largest challenges with AI adoption.
Large language models like Google Gemini are already trained on massive public datasets. What most companies really need is not training a new model, but teaching Gemini your business context: your documents, workflows, customers, and internal knowledge.
This guide walks you through the complete process of training Google’s Gemini model on your own data. We’ll cover everything from preparing datasets in the correct JSONL format to running tuning jobs in Google AI Studio.
We’ll also explore whether a converged workspace with built-in AI context might save you weeks of setup time.
Gemini fine-tuning is the process of training Google’s foundation model on your own data.
You want an AI that understands your business, but out-of-the-box models give generic responses that miss the mark. This means you waste time constantly correcting outputs, re-explaining your company’s terminology, and getting frustrated when the AI just doesn’t get it.
This constant back-and-forth slows down your team and undermines the productivity promise of AI.
Fine-tuning Gemini creates a custom Gemini model that learns your specific patterns, tone, and domain knowledge, allowing it to respond more accurately to your unique use cases. This approach works best for consistent, repeatable tasks where the base model repeatedly fails.
Prompt engineering involves giving the model temporary, session-based instructions each time you interact with it. Once the conversation ends, the model forgets your context.
This approach hits a ceiling when your use case requires specialized knowledge that the base model simply doesn’t have. You can only give so many instructions before you need the model to actually learn your patterns.
In contrast, fine-tuning permanently adjusts the model’s behavior by modifying its internal weights based on your training examples, so the changes persist across all future sessions.
Fine-tuning isn’t a quick fix for occasional AI frustrations; it’s a significant investment of time and data. It makes the most sense in specific scenarios where the base model consistently falls short, and you need a permanent solution.
Consider fine-tuning when you need the AI to master:
| Aspect | Prompt engineering | Fine tuning |
| What it is | Crafting better instructions in the prompt to guide model behavior | Training the model further on your own examples |
| What changes | The input you send to the model | The model’s internal weights |
| Speed to implement | Immediate — works instantly | Slow — requires dataset prep and training time |
| Technical complexity | Low — no ML expertise needed | Medium to high — requires ML pipelines |
| Data required | A few good examples inside the prompt | Hundreds to thousands of labeled examples |
| Consistency of output | Medium — varies across prompts | High — behavior is baked into the model |
| Best for | One-off tasks, experiments, fast iteration | Repetitive tasks needing consistent outputs |
Prompt engineering shapes what you say to the model. Fine-tuning shapes how the model thinks.
While this article focuses on Gemini, understanding alternative approaches to AI customization can provide a valuable perspective on different methods for achieving similar goals.
This video demonstrates how to create a custom GPT, another popular approach to tailoring AI for specific use cases:
📖 Also Read: How to Become a Prompt Engineer
Most fine-tuning projects fail before they even start because teams underestimate the data preparation process. Gartner predicts 60% of AI projects will be abandoned due to inadequate AI-ready data.
You can spend weeks gathering and formatting data incorrectly, only to have the training job fail or produce a useless model. This is often the most time-consuming part of the entire process, but getting it right is the single most important factor for success.
The principle of “garbage in, garbage out” applies heavily here. The quality of your custom model will be a direct reflection of the quality of the data you train it on.
Gemini requires your training data to be in a specific format called JSONL, which stands for JSON Lines. In a JSONL file, each line is a complete, self-contained JSON object that represents one training example. This structure makes it easy for the system to process large datasets one line at a time.
Each training example must contain two key fields:
For convenience, Google AI Studio also accepts uploads in CSV format and will convert them into the required JSONL structure for you.
This can make the initial data entry a bit easier if your team is more comfortable working in spreadsheets.
While quality is more important than quantity, you still need a minimum number of examples for the model to recognize and learn patterns. Starting with too few examples will result in a model that can’t generalize or perform reliably.
Here are some general guidelines for dataset size:
Gathering hundreds of high-quality examples is a significant challenge for most teams. Plan for this data collection phase accordingly before you commit to the fine-tuning process.
📮 ClickUp Insight: The average professional spends 30+ minutes a day searching for work-related information—that’s over 120 hours a year lost to digging through emails, Slack threads, and scattered files.
An intelligent AI assistant embedded in your workspace can change that. Enter ClickUp Brain. It delivers instant insights and answers by surfacing the right documents, conversations, and task details in seconds—so you can stop searching and start working.
💫 Real Results: Teams like QubicaAMF reclaimed 5+ hours weekly using ClickUp—that’s over 250 hours annually per person—by eliminating outdated knowledge management processes. Imagine what your team could create with an extra week of productivity every quarter!
Inconsistent or contradictory examples will confuse the model, leading to unreliable and unpredictable outputs. To avoid this, your training data needs to be meticulously curated and cleaned. A single bad example can undo the learning from many good ones.
Follow these guidelines to ensure high data quality:
It’s highly recommended to have multiple people review and validate the training examples. A fresh pair of eyes can often catch errors or inconsistencies that you might have missed.
The Gemini fine-tuning process involves several technical steps across Google’s platforms. A single misconfiguration can waste hours of valuable training time and compute resources, forcing you to start over. This practical walkthrough is designed to reduce that trial-and-error, guiding you through the process from start to finish. 🛠️
Before you begin, you’ll need a Google Cloud account with billing enabled and access to Google AI Studio. Set aside at least a few hours for the initial setup and your first training job, plus additional time for testing and iterating on your model.
Google AI Studio is the web-based interface where you’ll manage the entire fine-tuning process. It provides a user-friendly way to upload data, configure training, and test your custom model without writing code.
First, navigate to ai.google.dev and sign in with your Google account.
You’ll need to accept the terms of service and create a new project in the Google Cloud Console if you don’t have one already. Make sure you enable the necessary APIs as prompted by the platform.
Once you’re set up, navigate to the tuning section within Google AI Studio. Here, you’ll start the process of creating your custom model.
Select the option to “Create tuned model” and choose your base model. Gemini 1.5 Flash is a common and cost-effective choice for fine-tuning.
Next, upload the JSONL or CSV file containing your prepared training dataset. The platform will then validate your file to ensure it meets the formatting requirements, flagging any common errors like missing fields or improper structure.
After your data is uploaded and validated, you’ll configure the training parameters. These settings, known as hyperparameters, control how the model learns from your data.
The key options you’ll see are:
For your first attempt, it’s best to start with the default settings recommended by Google AI Studio. The platform simplifies these complex decisions, making it accessible even if you’re not a machine learning expert.
With your settings configured, you can now start the tuning job. Google’s servers will begin processing your data and adjusting the model’s parameters. This training process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size of your dataset and the model you selected.
You can monitor the job’s progress directly within the Google AI Studio dashboard. Since the job runs on Google’s servers, you can safely close your browser and come back later to check the status. If a job fails, it’s almost always due to an issue with the quality or formatting of your training data.
Once the training job is complete, your custom model is ready for testing. ✨
You can access it through the playground interface in Google AI Studio.
Start by sending it test prompts that are similar to your training examples to verify its accuracy. Then, test it on edge cases and new variations it hasn’t seen before to evaluate its ability to generalize.
If the results aren’t satisfactory, you’ll likely need to go back, improve your training data by adding more examples or fixing inconsistencies, and then retrain the model.
Simply following the technical steps doesn’t guarantee a great model. Many teams complete the process only to be disappointed with the results because they miss the optimization strategies that experienced practitioners use. This is what separates a functional model from a high-performing one.
Not surprisingly, Deloitte’s State of Generative AI in the Enterprise report found two-thirds of companies report that 30% or fewer of their gen-AI experiments will be fully scaled within six months.
Adopting these best practices will save you time and lead to a much better outcome.
Managing these iterations, dataset versions, and documentation requires robust project management. Centralizing this work in a platform designed for structured workflows can prevent the process from becoming chaotic.
Teams often invest significant time and resources into fine-tuning, only to hit predictable roadblocks that lead to wasted effort and frustration. Knowing these common pitfalls ahead of time can help you navigate the process more smoothly.
Here are some of the most frequent challenges and how to address them:
These challenges are a key reason why many teams ultimately seek alternatives to the manual fine-tuning process.
📮ClickUp Insight: 88% of our survey respondents use AI for their personal tasks, yet over 50% shy away from using it at work. The three main barriers? Lack of seamless integration, knowledge gaps, or security concerns.
But what if AI is built into your workspace and is already secure? ClickUp Brain, ClickUp’s built-in AI assistant, makes this a reality. It understands prompts in plain language, solving all three AI adoption concerns while connecting your chat, tasks, docs, and knowledge across the workspace. Find answers and insights with a single click!
Fine-tuning Gemini is powerful—but it’s also a workaround.
Throughout this article, we’ve seen that fine-tuning is ultimately about one thing: teaching AI to understand your business context. The problem is that fine-tuning does this indirectly. You prepare datasets, engineer examples, retrain models, and maintain pipelines, all so the AI can approximate how your team works.
That makes sense for specialized use cases. But for most teams, the real goal isn’t Gemini personalization for its own sake. The goal is simpler:
You want AI that understands your work.
This is where ClickUp takes a fundamentally different—and smarter—approach.
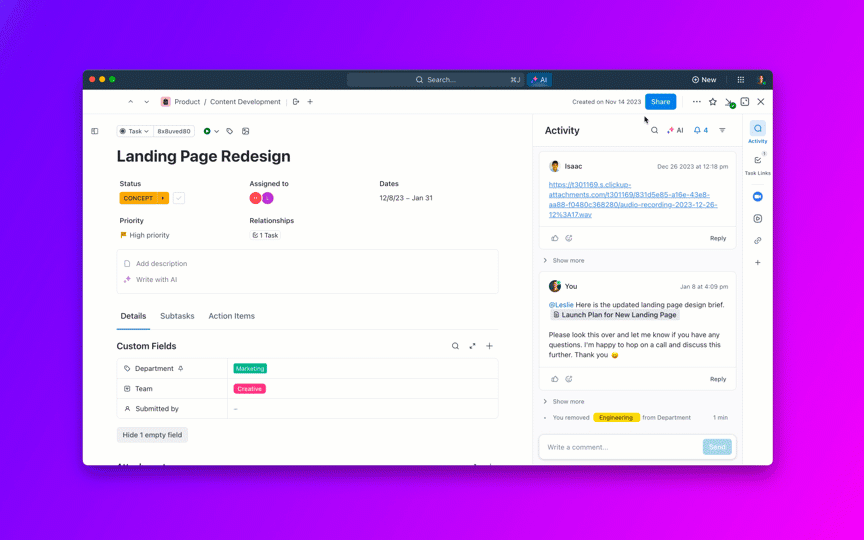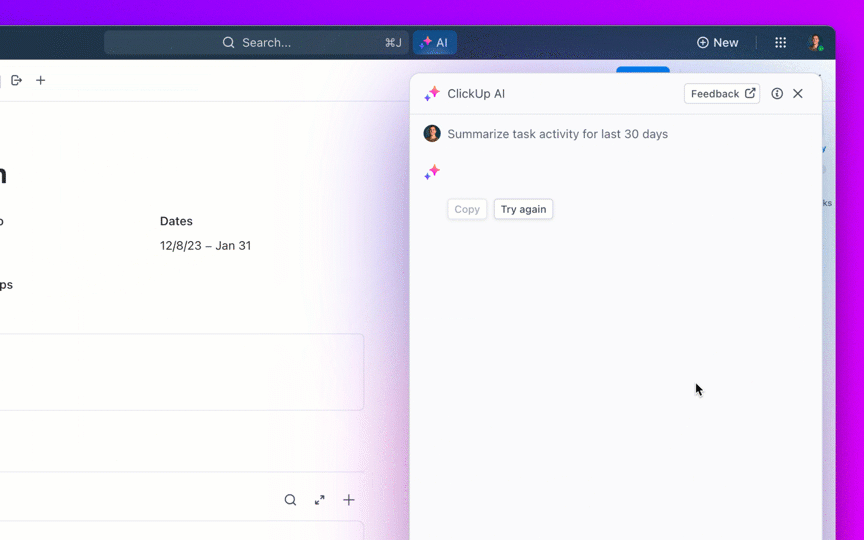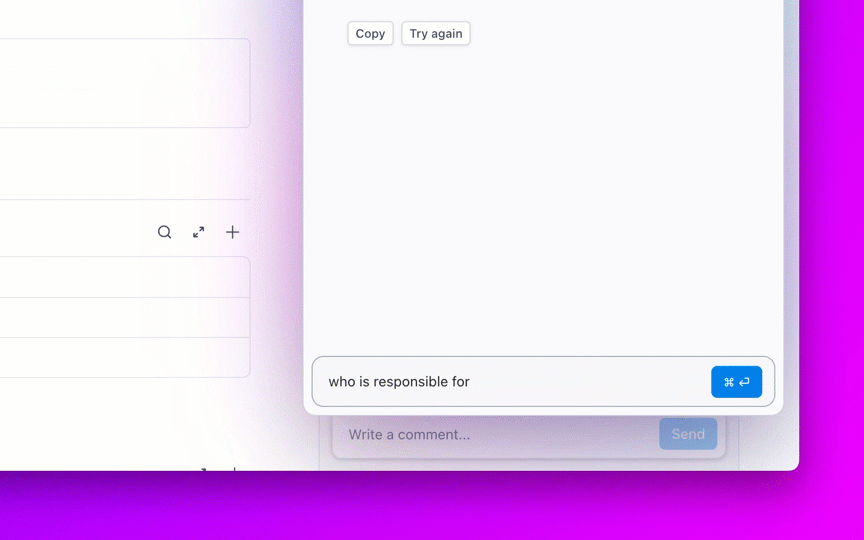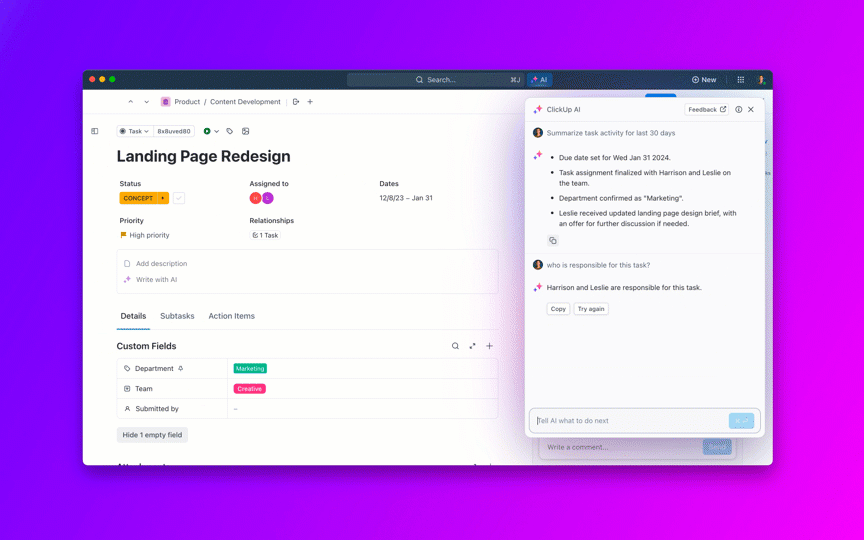
ClickUp’s Converged AI Workspace gives your team an AI that understands your work context instantly—no heavy lifting required. Instead of training AI to learn your context later, you work with ClickUp Brain, the integrated AI assistant, where your context already lives.
Your tasks, docs, comments, project history, and decisions are natively connected. There’s no need to train the AI on your data because it already lives where your work happens, tapping into your existing knowledge management ecosystem.
| Aspect | Gemini Fine-Tuning | ClickUp Brain |
|---|---|---|
| Setup time | Days to weeks of data preparation | Immediate—works with existing workspace data |
| Context source | Manually curated training examples | Automatic access to all connected work |
| Maintenance | Retrain when your needs change | Continuously updated as your workspace evolves |
| Technical skill required | Moderate to high | None |
Because ClickUp is your system of work, ClickUp Brain operates inside your connected data graph. There’s no AI sprawl across disconnected tools, no brittle training pipelines, and no risk of the model falling out of sync with how your team actually works.
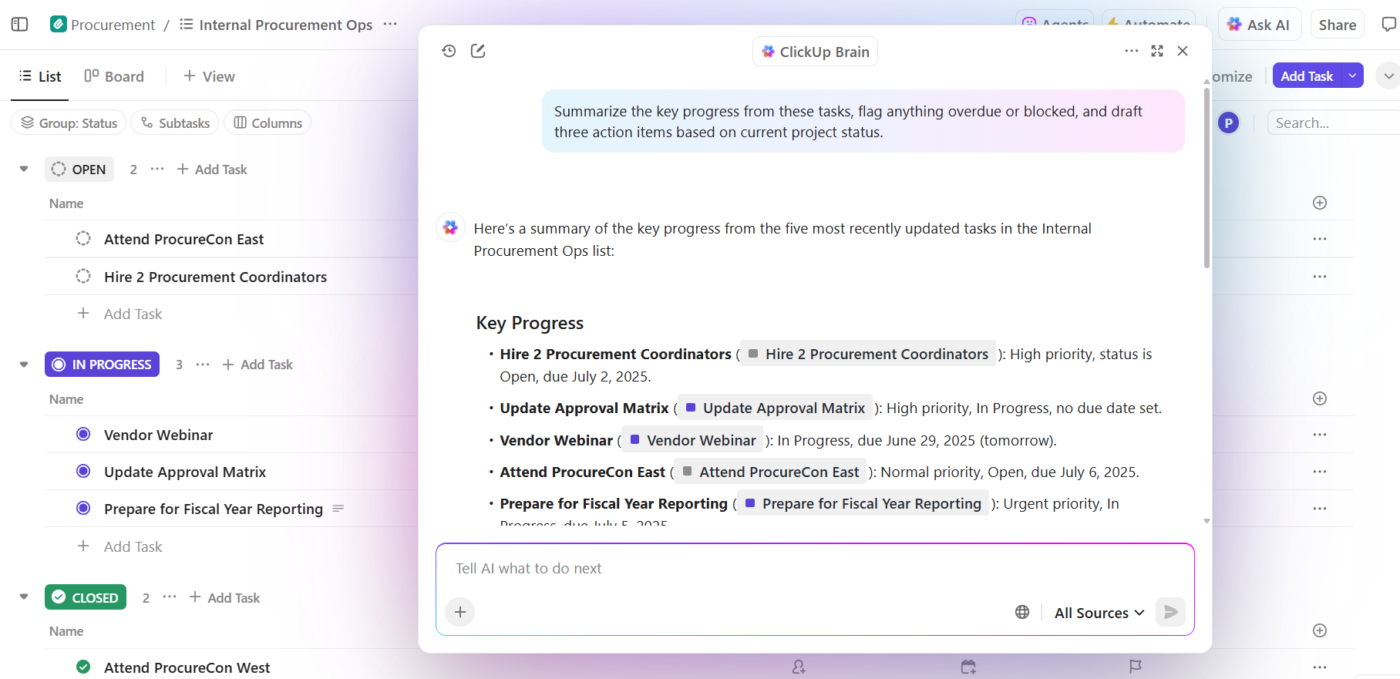
This is what that looks like in practice:
💡Pro Tip: Harness the true power of AI in your workspace with ClickUp Super Agents.
Super Agents are ClickUp’s AI-powered teammates—configured as AI “users” that work alongside your team inside the workspace. They are ambient and contextual, and can be assigned to tasks, mentioned in comments, triggered through events or schedules, or directed via chat—just like a human teammate.
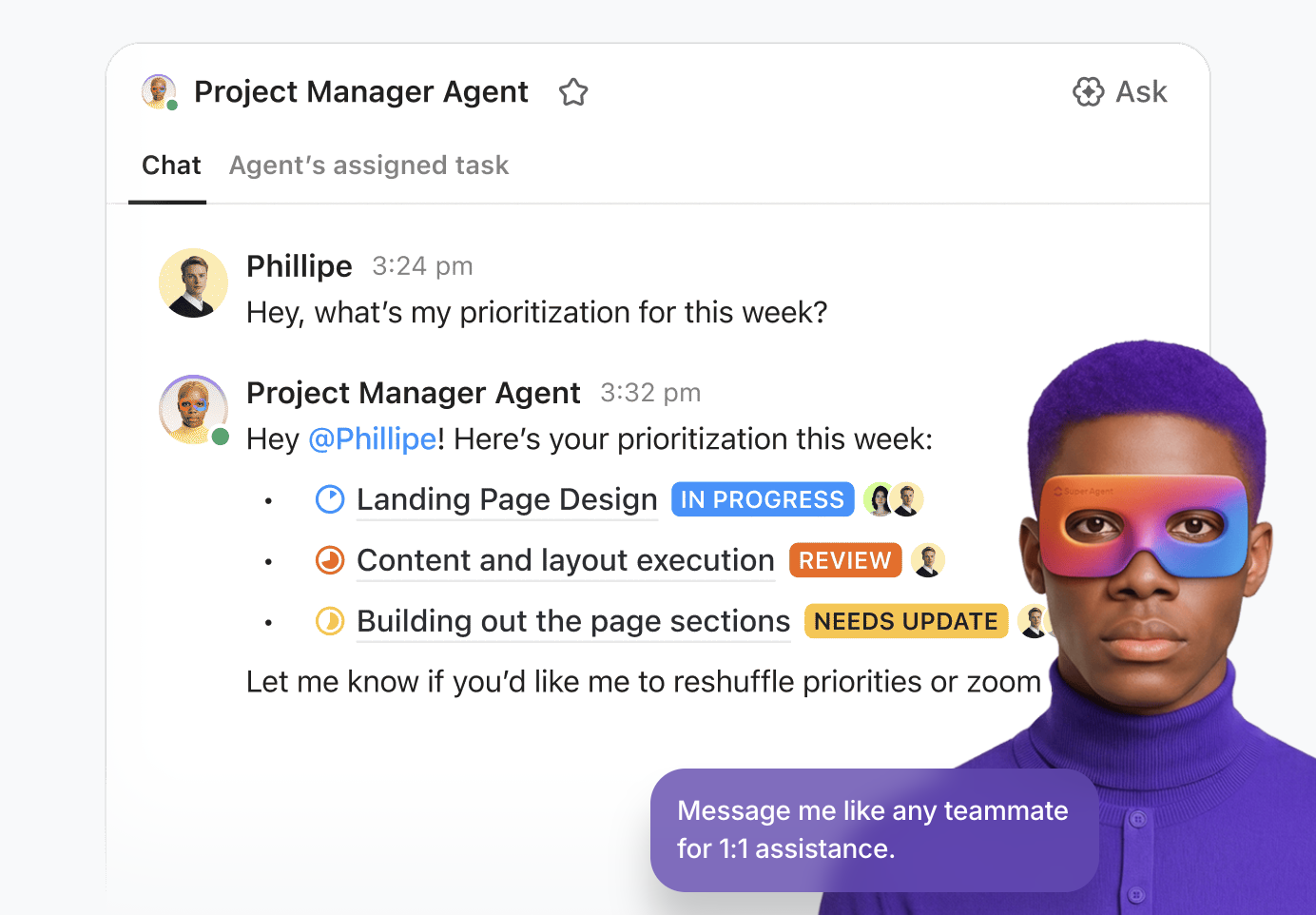
You can build and deploy them using the no-code visual builder that lets you:
Learn more about Super Agents in the video below.
Fine-tuning teaches an AI your patterns through static examples, but using converged software in a workspace like ClickUp eliminates context sprawl by giving your AI live, automatic context.
This is the core of a successful AI transformation: teams that centralize their work in a connected platform spend less time training AI and more time benefiting from it. As your workspace evolves, your AI evolves automatically—no retraining cycles required.
Ready to skip the training and start with AI that already knows your work? Get started for free with ClickUp and experience the benefits of a converged workspace.
Your fine-tuned model learns from your training examples, but Google’s base Gemini model does not retain or learn from your conversational data by default. Your custom model is separate from the foundation model that serves other users.
While the training job itself may only take a few hours, the larger time investment is in preparing the high-quality training data. This data preparation phase can often take days or even weeks to complete properly.
Yes, you can fine-tune a model without writing code by using Google AI Studio. It provides a visual interface that handles most of the technical complexity, though you will still need to understand the data formatting requirements.
Custom instructions are temporary, session-based prompts that guide the model’s behavior for a single conversation. Fine-tuning, however, permanently adjusts the model’s internal parameters based on your training examples, creating lasting changes to its behavior.
© 2026 ClickUp