Does GitHub Support MCP (Model Context Protocol)?
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Summary: Want safer AI workflows? Learn how to use GitHub MCP support with scoped permissions. Start small and expand based on team needs.
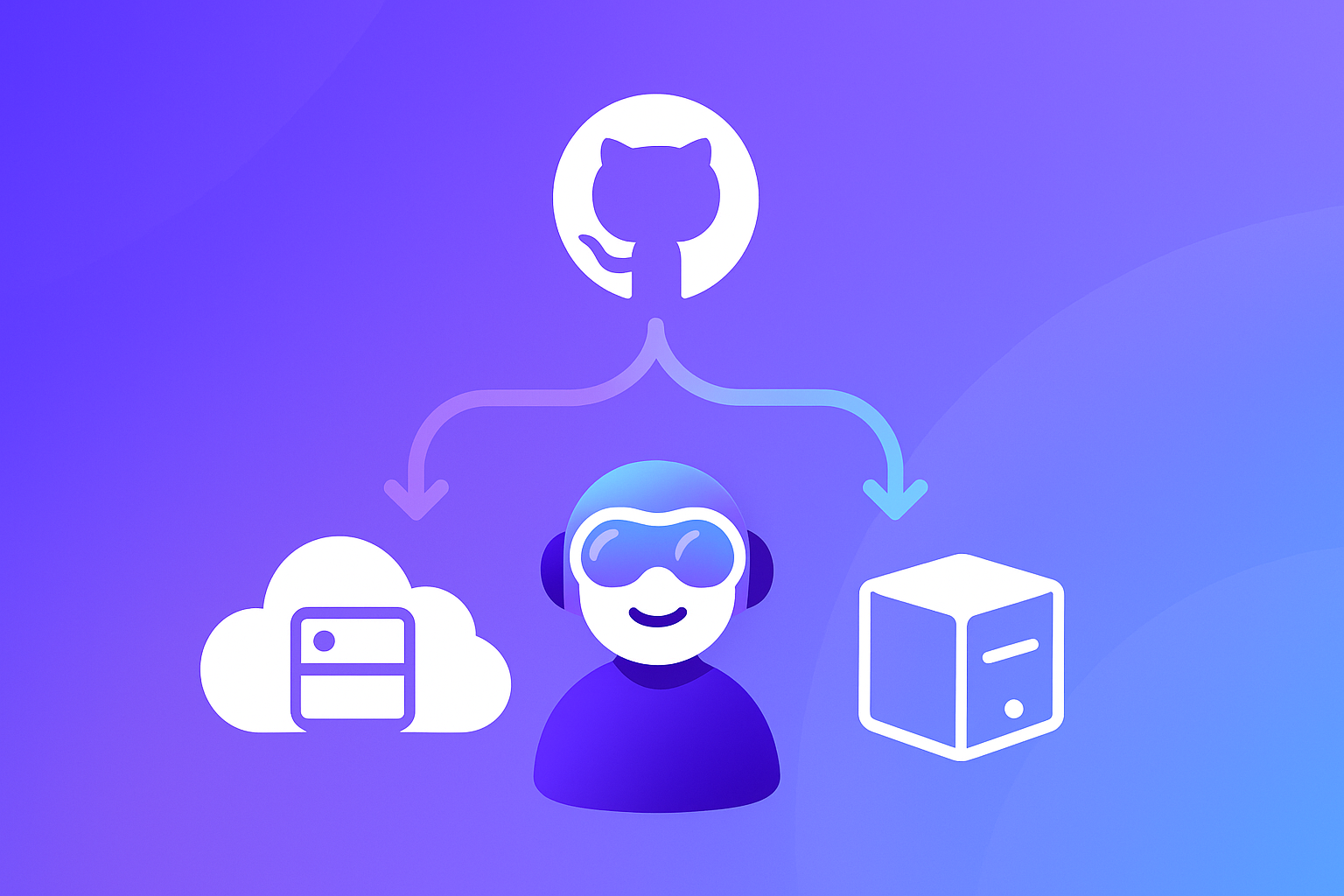
Yes. Support is delivered through Copilot, primarily in Copilot Chat, which can connect to protocol‑compatible servers – including a first‑party server for repositories, issues, and pull requests – and a registry that manages what’s available.
The registry is in public preview, and organization‑level allow/deny policies are available on Copilot Business and Enterprise.
Think of servers as a toolbox the assistant can reach into when it needs data or to perform a task. The platform sits between your requests and the tools or sources you approve, then blends model reasoning with what those systems return.
First, you connect things. An admin or power user selects one or two servers that map to a real task, registers them via the registry or IDE settings, and leaves others off to keep behavior predictable.
Second, you set boundaries. On supported plans, policies can allow or block specific servers so the assistant only touches systems you’re comfortable with, using existing developer identities.
Third, you use it day to day. In VS Code or another supported IDE, a developer asks Copilot for help; when needed, it calls an approved server behind the scenes, pulls live context, and responds accordingly.
This capability suits teams already using Copilot who want the assistant to work with internal systems, not just public code or generic patterns.
It’s particularly useful for platform and DevOps groups exposing APIs, logs, or databases, and for security teams that want centralized allow/block control.
Individuals and small teams can benefit, but the strongest fit is mid‑sized and larger orgs with multiple internal tools.
It’s probably not a fit if you’re not using Copilot, your policies block assistant access to internal systems, or your environment is so restricted that IDEs can’t reach servers reliably.
Here’s a quick, balanced look at strengths and trade‑offs. Real value depends on which systems you expose, the plan you have, and the client environment your teams use.
Given that, a few constraints often matter in practice.
If you already have Copilot in a supported IDE, you can try these integrations without changing your workflow.
Start narrow, confirm governance, and measure a single outcome like reduced context switching or faster query writing.
Next, stand up a minimal server that exposes a single read‑only capability tied to a non‑critical project. Use least‑privilege credentials, enable audit logging, cap rate limits, and time‑box the pilot so you can evaluate behavior without risk.
Define simple success criteria before you start (for example, fewer context switches, faster query writing, or fewer copy‑paste errors).
If those targets are met, expand to one additional capability or a second server and document who can enable or approve changes. If not, adjust scope, tighten permissions, and rerun the trial.
Keep experiments small and reversible. Start read‑only, review access and logs with your security team, and only then broaden access and capabilities.
© 2026 ClickUp