Aggregate Planning: Strategies for Effective Resource Management

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Why does any business exist? To meet market demand by producing and selling a product/service in exchange for a price.
If demand exceeds production, you miss revenue opportunity. If production exceeds demand, you will be unable to sell your goods, leading to wastage and losses.
In essence, success lies in a business’s ability to forecast demand accurately and appropriately manage production capacity. Operations strategy and resource management rely on one critical tool to achieve this: Aggregate planning.
Aggregate planning is the process of designing a formula to ensure uninterrupted production at a manufacturing plant in order to meet customer demand for the products.
Operations teams forecast future demand, typically for the next 3-18 months, and then perform aggregate planning to manage the capacity to meet it.
Let’s take the example of a car manufacturer with an aggregate demand forecast of 150,000 units of three types of cars over the next 18 months. The aggregate plan designs the right production planning—including labor, machinery, logistics, and financial resources—to meet that demand.
Typically, aggregate production planning is performed for all activities at a production facility, not just individual runs or products. In the above example, aggregate planning isn’t performed for each type of car individually. It is always performed as an aggregate of all the company’s products and facilities.
While used primarily in manufacturing and supply chain management, aggregate planning can also be applied to service businesses.
For instance, if your sales team is pursuing a software development project that needs 20 developers over the next year, your aggregate plan would outline the acquisition, training, and utilization of these resources.
Aggregation planning is a critical and popular operational tool in the manufacturing and supply chain industry, offering several benefits.
With a good aggregate plan, you can prevent two unwelcome scenarios: Unused capacity and unmet demand. Aggregate planning helps forecast the resources needed accurately, preventing wastage or storage-related expenses. It prevents excess inventory levels that might go unsold or be sold at heavy discounts.
The most significant advantage of aggregate planning is that it makes inventory management efficient on multiple levels.
Employees can better plan and organize their lives with a clear view of what lies ahead. Managers can hire the resources they need and train them adequately. Team members can reskill/upskill for future demand. Various teams/departments can collaborate more effectively.
Most importantly, organizations can avoid firing/layoffs with effective aggregate planning.
Aggregate plans give a big picture of an organization’s production capacity, facilitating several business decisions.
For example, aggregate planning balances market demand with the organization’s ability to supply. With these metrics, you can effortlessly make pricing decisions. If the aggregate plan shows that you’re likely to have more inventory than forecast demand, you can up your promotions to affect the customer side.
Most importantly, aggregate planning clarifies your investment decisions. It helps answer the question, “Do we need to invest in additional equipment or people?”
In line with the demand, aggregate planning shows how to optimize the production plan without additional capital investment.
Aggregate planning helps control variable costs while increasing the efficiency of the assembly line. This contributes directly to the organization’s profitability.
Moreover, it strengthens the organization’s ability to make on-time-in-full (OTIF) delivery—a critical metric in retail supply chains.
Despite its significant benefits, aggregate planning isn’t easy. It brings with it several challenges, which we explore next.
In its simplest form, aggregate planning forecasts future demand and builds capacity to meet it. For an aggregate plan to be effective, it needs accurate data on demand and supply from sales, operations management, procurement, human resources, and finance teams.
For most organizations, collecting this data is the biggest challenge to aggregate planning. But that’s not all.
Demand fluctuations: Demand isn’t easy to predict. Demand fluctuates depending on the economy, market, pricing, competition, and technological advancement, affecting aggregate planning.
Planning horizon: Organizations typically plan for anywhere from three to 18 months. A lot can happen during this time. A global pandemic or a swing election can change a lot quickly.
Supply chain disruptions: A supply chain is a complex web through which the product travels. A war or a natural disaster in any corner of the world can affect even the best-laid plans.
Bottlenecks: Planning tightly might create bottlenecks in the assembly line, causing the very inefficiencies aggregate planning aims to prevent.
Smoothing: Frequently changing production, resources, etc., comes with smoothing costs that often go unconsidered.
While these challenges can derail aggregate planning initiatives, a good project management tool and thoughtful processes can help. Here’s how.
For effective aggregate planning, you need data around demand and capacity, which any resource management tool can help consolidate.
For example, on the demand side, collect data around:
On the capacity side, learn:
When you use a project management software like ClickUp, much of this data might be instantly accessible. Some of ClickUp’s customers use the tool as a customer relationship management (CRM) solution to track sales.
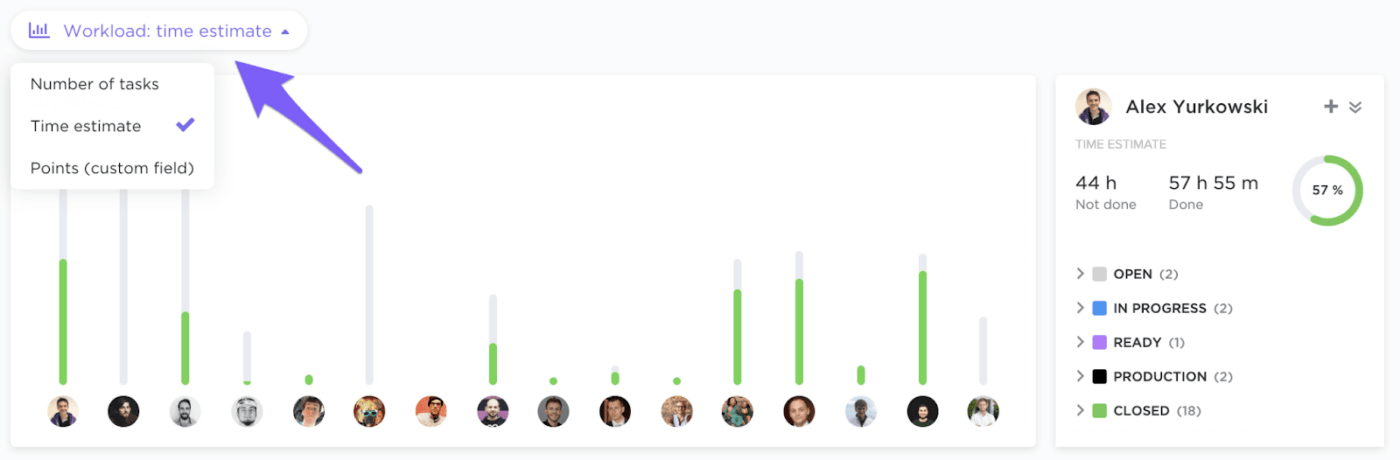
Service organizations use the workload view to manage human resources’ capacity. ClickUp Reports offer deep insights into who is doing what, how long it takes, how the team performs, etc.
Now that you have data from both sides, it’s time to visualize how they map with each other. This step is essential to assign appropriate capacity to various stages in the process.
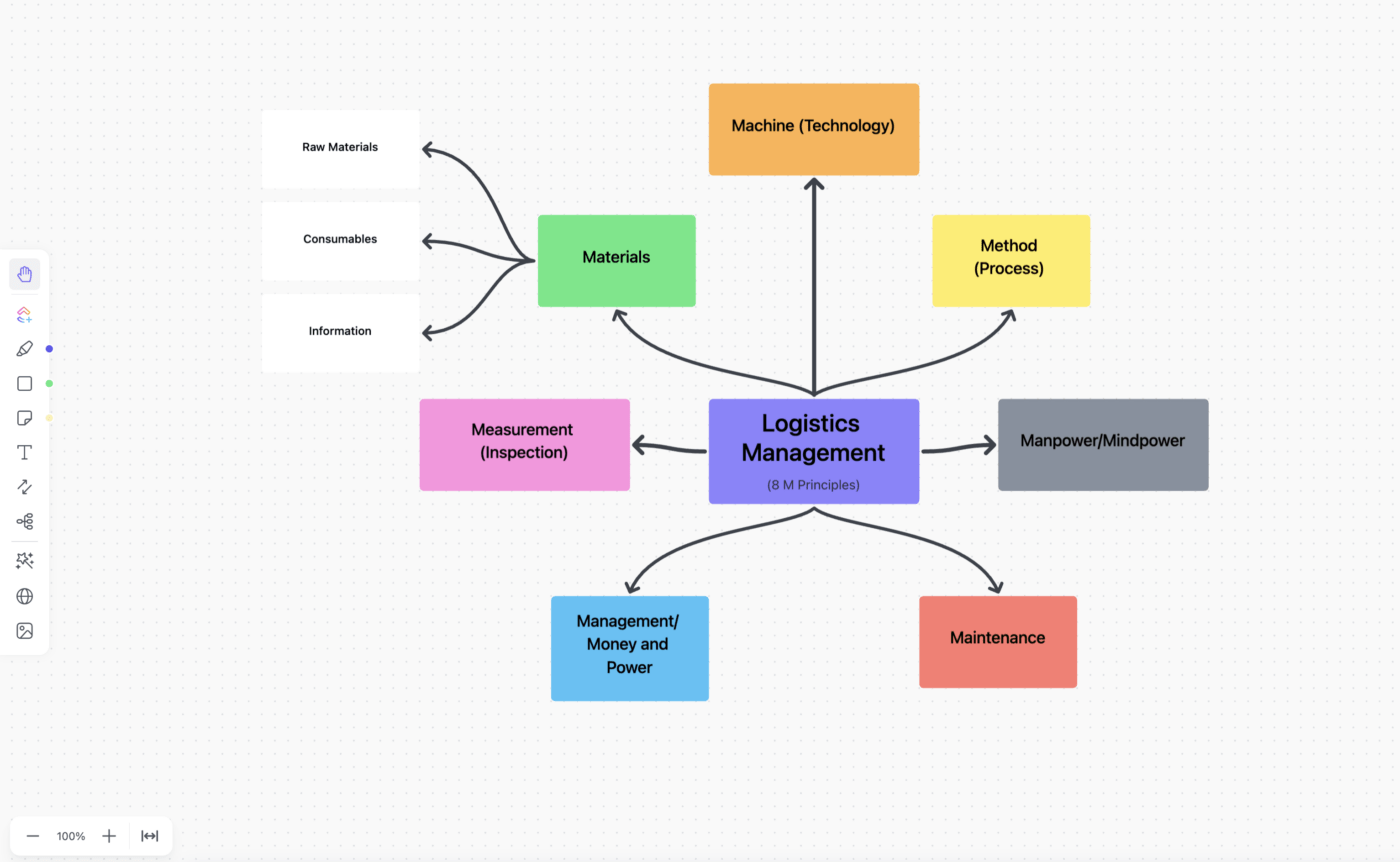
For example, a car manufacturer wouldn’t need seat covers or people to fit them until the end of the process. A sound mind map of the process helps identify this flow.
ClickUp Mind Maps is a great way to draw the demand curve and the corresponding capacity requirements. It serves as a capacity planning tool to align resources with the demand.
If your current processes are too scattered, use these ClickUp project increment (PI) planning templates. They help you streamline project communication, enable better collaboration, and set a shared vision.
Good aggregate planning considers all the costs involved in the entire product lifecycle. This helps with allocating your existing capacity and budgeting for future requirements.

Don’t know where to start? No problem. ClickUp’s estimate templates give you a great starting point. Download any of the templates and customize them for your needs.
Once you have all the information handy, it is time to choose how you will build your aggregate plan. There are three commonly used aggregate planning strategies.
Level strategy: This method aims to keep production and employment stable without sudden investments in manufacturing capacity. While this keeps the workload steady, it runs the risk of always running at maximum capacity or creating unnecessary inventory despite low demand.
Chase strategy: In this method, capacity chases demand. As a result, you might outsource production to another facility, buy/rent equipment, or hire/fire resources. This approach can be disruptive for the teams and runs the risk of quality issues.
Hybrid strategy: This method combines the best of both worlds. It retains a stable capacity with space for additional production available at short notice.
On the other hand, you can also manage the demand side of this equation by:

Based on how you visualize the production workflow, break it down into tasks and subtasks. ClickUp tasks allow you to set deadlines, indicate dependencies, and even add checklists for better quality control.
Use your chosen aggregate planning methodology to allocate resources to each project or production run.
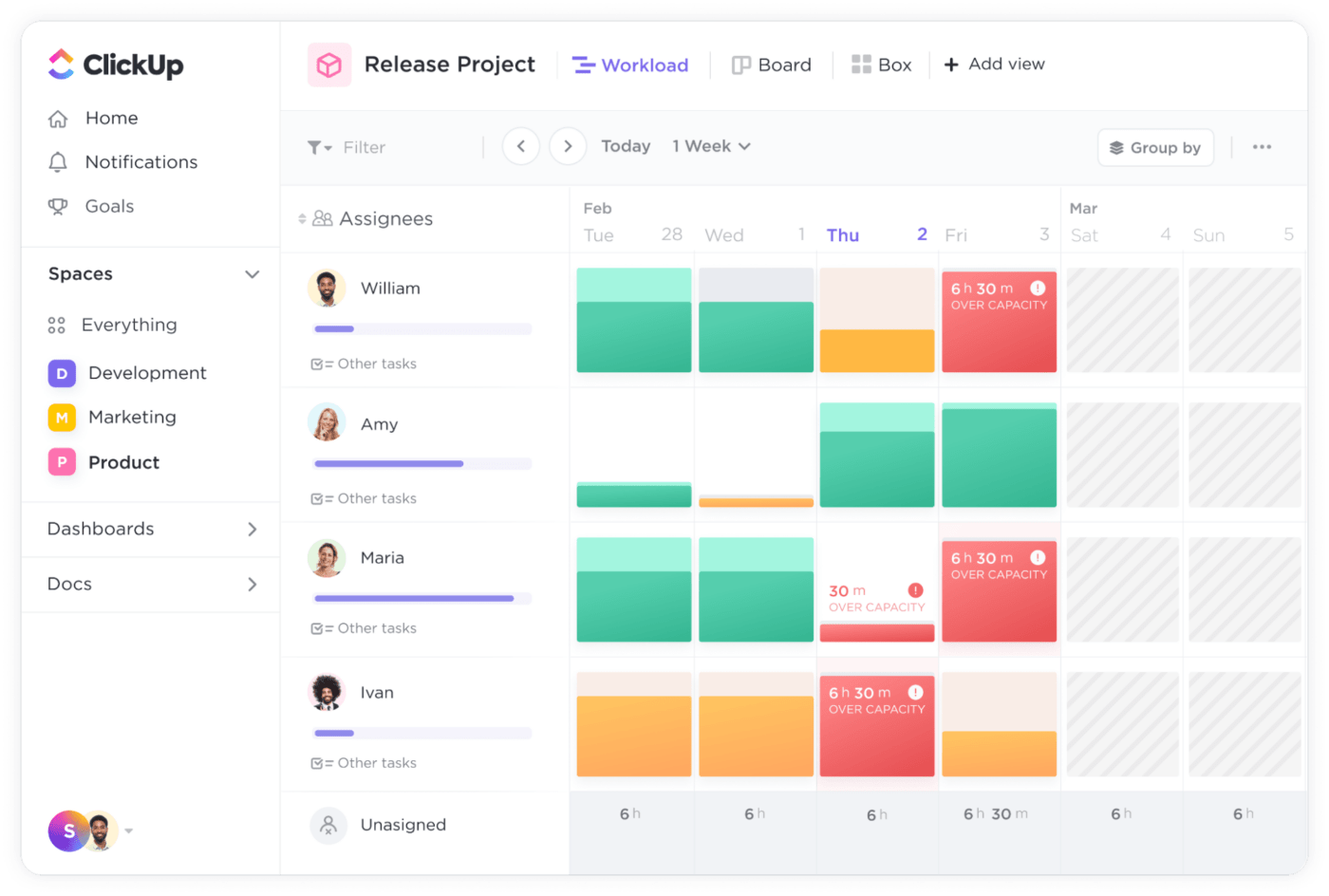
ClickUp’s resource management software is an excellent solution for resource scheduling. Use the Workload view for capacity planning. Use the Calendar view to visualize significant milestones. Create visual roadmaps with the timeline view and collaborate on priorities.
However meticulous your plan is, threats and risks will always arise from external factors. A good aggregate plan includes project forecasting to identify risks and design ways to mitigate them.
An effective way to overcome the challenges of aggregate planning is to be agile. ClickUp’s features enable effective resource management throughout the project’s lifecycle.
It gives the visibility to adjust resource allocation throughout the project in case of unexpected delays or disruption.
Whether you’re a product or a service business, profitability depends on meeting demand, maximizing resource utilization, and minimizing wastage. Aggregate planning is a tried and tested tool that helps organizations optimize their operations consistently.
For aggregate planning to be effective, it needs several business tools to collect data, manage tasks, assign resources, track time, manage sales/purchases, collaborate among team members, document processes, etc.
Organizations often use a different tool for each of these activities, wasting precious time and resources in consolidating information. What they lose in this process is context.
ClickUp’s all-in-one project management software is designed to be your single most powerful tool to perform all these activities and more. It combines all your business intelligence in one place, powering your plans to success. Try ClickUp for free today!
© 2026 ClickUp