

The best-performing teams need top-notch software to hit the mark.
According to the Cisco 2023 Global Networking Trends study, 66% of organizations host over 40% of their workloads across multiple clouds. Most organizations use more than ten SaaS applications, including team collaboration, CRM, task management, video conferencing, and automation, to name a few.
Managing and securing these applications becomes extremely crucial, yet they present several challenges, including implementation hurdles, shadow IT, data migration issues, and unforeseen costs.
So, how do you overcome these challenges and effectively manage a huge stack of applications? The answer lies in SaaS operations management.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What SaaS operations management is
- How to approach SaaS operations in various departments
- What challenges you could face and how to overcome them, and
- How to conduct successful SaaS operations management
Let’s dive in. 👇
- What are SaaS Operations?
- Why SaaS Operations Are Much More Effective Than Traditional Operations
- The SaaS Operational Framework
- SaaS Operations Challenges
- Best Practices for Optimizing SaaS Operations
- Implementing SaaS in the Real World
- How Do Optimized SaaS Operations Benefit You?
- SaaS Operations Tools and Resources
- What Does The Future Hold for SaaS?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are SaaS Operations?
SaaS operations or SaaSOps refers to a set of operational processes that include an organization’s governance, management, purchasing, and usage optimization of SaaS tools.
They cover the entire lifecycle of SaaS application activity, from discovery and procurement to onboarding and offboarding and everything in between.
With the proper management, you can implement a solid SaaS operations management strategy that boosts productivity, improves data security and compliance, optimizes costs, and supports your organization’s growth.
Why SaaS Operations Are Much More Effective Than Traditional Operations
There is no real competition between SaaS and traditional operations, which involves installing the software directly into your business’s hardware.
However, you must understand the difference between the two to get a comprehensive view of SaaSOps management and how it is better for your business.
Let’s understand this with a table. 👇
| Feature | SaaS | Traditional Software |
| Accessibility & Convenience | Mostly cloud-based, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection; no installations or manual updates are required | Requires purchasing licenses, installing software on local machines, and regular manual updates |
| Cost-Effective Solutions | The subscription-based model includes all costs in a single fee; budget-friendly | Upfront costs for licenses, hardware, and infrastructure; ongoing expenses for maintenance, updates, and support |
| Scalability & Flexibility | Effortless scalability; add or remove users easily; various plans & features tailored to specific needs | Limited scalability and customization, costly and time-consuming to expand or customize |
| Automatic Updates & Maintenance | The service provider handles updates and maintenance, freeing up time and resources | Users are responsible for updating and maintaining the application; time-consuming and irritating |
| Collaboration & Integration | Designed for smooth integration with other applications, enabling streamlined workflows and real-time collaboration | Often requires additional development work and resources for integration with other applications |
| Enhanced Security & Data Protection | SaaS providers handle encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, ensuring top-notch security | Individual organizations responsible for implementing security measures may not match the level of security provided by SaaS providers |
| Disaster Recovery & Redundancy | Hosted in secure data centers with multiple redundancies and backup systems, ensuring data integrity and availability | May lack the same redundancy and disaster recovery options; vulnerable to data loss and downtime |
| Rapid Deployment | Enables fast deployment. Users can log in and start using the software immediately | Involves lengthy installation and setup process, leading to downtime |
| Global Access & Remote Work | It can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, which is ideal for remote work | Tied to specific machines or places, hindering flexibility in remote work |
| Regular Feature Updates | Frequent feature updates and enhancements to ensure the software remains relevant and competitive | Infrequent updates so users may miss out on valuable features and improvements |
Constantly building, testing, and delivering improvements to software code and user environments through continuous development (CD) has become essential in meeting customer demands.
Traditional on-premise systems can’t keep up with constantly shifting demands. That’s why SaaS operations are crucial for achieving your business goals.
The SaaS Operational Framework
The SaaS Operational Framework is a structure that will help you maximize the value of your SaaS operations.
The framework can be broken down into two main parts:
- SaaS operations components (what’s involved in doing it) and
- SaaS lifecycle (how it all plays out over time)
SaaS operations components
When managing SaaS operations, there are a few key components to keep in mind.
They are:
1. SaaS objectives:
The objectives include clear goals and outcomes for your SaaS implementation and operations of multiple sub-components like:
- Application visibility and spend management: This involves a comprehensive view of your applications, including their usage, spending, contracts, and ROI. With this visibility, you can monitor both approved and unapproved apps along with their departmental expenses
- Infrastructure management: This covers everything from setting up servers to making sure they are properly patched and updated. Dedicated SaaS tools streamline these tasks, allowing for faster setups and regular updates
- Application management: This includes determining which apps are essential for your business operations and which ones can be discontinued based on how they are used and user behavior
- User management: This entails keeping track of your users, assisting them with their business tasks, and monitoring user trends
- Security and compliance: This involves implementing strong measures for data security and compliance, such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC). These measures help manage employee access to applications and protect your data
- Onboarding and offboarding: This is about managing the adoption or phasing out of various software services.
2. Stakeholders involved:
This component covers your key stakeholders and their roles in your SaaS operations.
Effective SaaSOps management depends on effective collaboration and training among IT, business units, and SaaS vendors.
3. SaaSOps processes:
This involves standardizing your SaaS workflows for deployment and usage.
It also covers change management procedures, which are needed when developers release new updates or when you make changes to your SaaS applications.
4. Constant measurement:
This section outlines your KPIs based on your SaaS goals and the SaaS operations management tool you use to track them.
Important metrics include software usage, adoption, and ROI, but you should choose the ones that best fit your business needs.
5. Accountability:
This component focuses on shared responsibility for SaaS applications and processes.
It includes assigning clear maintenance, security, and compliance roles and ensuring individuals and teams are accountable for achieving objectives and KPIs, as tracked through your monitoring systems. This is all part of ensuring accountability.
✏️ Note: These are only some of the major components of SaaSOps, and there are many more out there, depending on the scale and type of industry in which you work.
SaaS Operations Lifecycle
The SaaS Operations Lifecycle begins with implementation planning and ends with successful offboarding.
We can summarize the lifecycle of your SaaS operations as a series of sequential activities:
- Choose potential SaaS applications that align with your business objectives and goals
- Implement the most suitable applications and involve all relevant stakeholders
- Manage employee access to these applications and ensure accountability for each process and operation
- Monitor KPIs like the usage rate, user trends, and and application performance
- Address any issues that may arise during the process
- Create, provision, and de-provision accounts
- Manage your costs using the accumulated data
SaaS Operations Challenges
Managing SaaS operations is like walking a tightrope—you must find your balance.
Carefully choose the right SaaS operations management platform, invest in team training, and cancel any subscriptions that don’t meet your needs.
Let’s look at some common SaaS operations challenges so you can be prepared to tackle them if they arise.
Challenge 1: Compliance with data protection laws
Following various industry regulations and compliance standards, such as SOC 2, GDPR, CPAA, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, complicates SaaS operations. It requires continuous monitoring and updates to your SaaS software, especially in sectors like healthcare or finance.
Not complying can lead to heavy fines and legal issues and damage your brand reputation.
Back in 2017, Zenefits, a SaaS company that had soared to a valuation of $2 billion, failed dramatically because it couldn’t keep up with compliance and regulatory standards. Another example is Anthem Inc.’s $16 Million HIPAA settlement a few years ago, caused by a data breach due to cyber attacks.
Challenge 2: Inefficient onboarding and offboarding processes
SaaS empowers your employees, but its potential remains untapped if they’re unaware of the available software and its usage. Hence, clear communication during software onboarding is vital.
Create a SaaS onboarding checklist that includes:
- informing your employees about the available SaaS tools in the stack
- explaining how each tool applies to their specific role
- providing documentation and support
- offering hands-on experience and
- regularly checking in and providing support
Establishing an app catalog simplifies access for both new and existing employees. It centralizes information on standard software and purchasing procedures.
Offboarding is as crucial as onboarding but is often overlooked despite its risks.
You should manage data securely during offboarding, ensure proper transfer or removal, and terminate software licenses in compliance with legal standards.
Poor offboarding practices can result in compliance violations. For example, allowing ex-employees to retain access to sensitive data can breach regulations like HIPAA or GDPR, leading to severe fines and legal action.
Challenge 3: Shadow IT
Shadow IT refers to employees using unauthorized SaaS applications without IT approval. This can lead to security risks, compliance issues, and data fragmentation, hampering productivity.
To combat shadow IT, your organization must:
- Use effective SaaS discovery to gain visibility and insight into your entire SaaS portfolio
- Focus on building relationships with your unauthorized SaaS buyers and understanding their needs
- Define a SaaS governance strategy to prevent future instances of shadow IT. This strategy should control what enters your tech stack, define IT management levels, and distribute SaaS management responsibilities
Challenge 4: Hidden costs & overspending
According to a 2024 report, organizations allocate approximately $45 million annually to SaaS expenditures. However, a substantial portion of this budget (roughly $18 million) is squandered on unused licenses.
Without effective cost monitoring and optimization strategies, you risk overspending on SaaS subscriptions, licenses, and services, draining your financial resources and impeding strategic initiatives.
One effective solution is rationalizing applications and removing unnecessary ones from your stack.
Another approach is rightsizing, i.e., purchasing only the amount and duration of the licenses you need and no more than that. Both require insights into how, where, and why SaaS is utilized in your stack.
Challenge 5: Managing the SaaS budget to identify potential savings
Uncontrolled SaaS subscriptions and unexpected expenses can strain your financial resources and throw off your budget plans.
To avoid overspending, focus on managing costs effectively. This way, you can predict expenses, allocate resources wisely, and maximize your return on investment.
Best Practices for Optimizing SaaS Operations
Here are some best practices to use while optimizing your SaaS operations: 👇
1. Centralize database management
Whenever you consult with anyone about SaaSOps, their first advice would be to centralize your SaaS applications into a single database.
This centralized system gives you optimal visibility across your organization’s SaaS stack, providing a complete view of user identity and access across applications and resources.
2. Analyze your SaaS usage data
Analyze your usage data thoroughly by reviewing each application to determine if all employees with licenses truly require them.
You can find this information in the admin panel of many applications or consolidated within a SaaS management platform. Additionally, identify employees who could benefit from reduced or free licenses instead of premium ones.
3. Opt for provision access in SaaS operations
Provisioning in SaaS involves granting access and resources to new users, managing user accounts, and assigning access levels and permissions.
This step equips you with the necessary tools and access rights to fulfill your role efficiently.
4. Implement single sign-on (SSO)
Single sign-on (SSO) in enterprise settings allows you to use one set of credentials to log in once and access all permitted corporate SaaS apps, websites, and data.
SSO addresses key business challenges by providing:
- Enhanced security and compliance
- Improved usability and satisfaction
- Reduced IT costs
Implementing SaaS in the Real World
Let us take you through a step-by-step guide on how you can effectively implement SaaS in your business.
Step 1: Plan your project
In this pre-implementation phase, decide on the key control factors of your project management. This includes:
- Crafting your ideal SaaS team
- Defining the scope of the project by drawing out a time map and setting milestones
- Establishing clear communication channels among the involved stakeholders
- Preparing a data migration strategy to minimize downtime and mitigate data loss
Step 2: Customize your configuration
Customize the SaaS software to meet your specific needs. Ensure clear communication between your organization and the third-party SaaS provider to define your requirements precisely.
Step 3: Migrate your data
This is the most critical step of your SaaS implementation journey. It involves transferring data while minimizing the risk of data loss, which could cause severe financial setbacks.
To minimize risk, you must cleanse, format, and prepare your data for its new destination and stay vigilant against potential security threats. Also, have a backup ready in case of any glitches in the process.
Step 4: Integrate existing software
Integrate existing applications and other useful software into the new SaaS system to ensure a smooth workflow.
Step 5: Test the system
Do not ignore the testing phase. Thoroughly test the software’s functionality to ensure it performs well under heavy loads and stressful conditions.
Step 6: Train your team
Educate your team members on how to use the new software. Implementation will be unsuccessful if your team can’t use the software effectively.
Also read: Best SaaS Conferences to Attend for Business Success
Step 7: Deploy the software
Carefully roll out the software across the organization. You can also do this in batches to limit friction. Be proactive and vigilant regarding any issues that may arise in the system during this phase and try to tackle them immediately.
During deployment, provide role-based access control to help maintain a secure work environment.
Step 8: Implement role-based access control
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage user permissions within a system based on predefined roles. As a SaaSOps administrator, you assign specific roles to users, thus limiting their access to only the data and features necessary for their specific jobs.
This drastically improves data security by mitigating unauthorized access and data breach risks. You can manage these permissions through a central system and change them on the go, as needed.
Step 9: Monitor and optimize
The post-implementation phase is just as important, if not more. You need to check the system’s performance and make necessary adjustments regularly. Gathering user feedback and monitoring KPIs like adoption rate, CSAT, NPS, churn rate, etc., are essential aspects of this step.
How Do Optimized SaaS Operations Benefit You?
Optimized SaaS operations are like a well-oiled machine. They ensure the smooth functioning of your business activities on multiple levels.
Here are some of the benefits:
- Increased work efficiency: A well-optimized SaaS stack streamlines workflows and helps your teams swiftly adapt to the processes, ultimately improving their productivity
- Lower customer acquisition cost: It reduces customer acquisition costs significantly by building a streamlined marketing funnel, implementing marketing automation, and minimizing human involvement in the process
- Better customer experience: By providing an experience that is free of too many hurdles, you will be able to increase customer satisfaction rates and retain more customers
- Increased app visibility: It serves as a foundation for streamlining your application portfolio, adjusting licensing based on user needs, and ensuring that your teams only use safe and approved apps
- Reduced wasted spending and operation costs: It translates to reduced unnecessary SaaS spending by identifying and removing underused licenses
- Improved data security: It enhances data protection by increasing visibility into what apps your teams are using
Also Read: The best CRM SaaS software for teams
SaaS Operations Tools and Resources
We talked a lot about how you can optimize your SaaS operations to ensure better results. But as you saw, the simple steps can quickly become overwhelming. This is where we have a cheat for you.
SaaS operations tools and resources can ease the pain of optimization. They introduce useful elements like AI, automation, unified interfaces, and more.
Now, you might wonder, “What SaaS operations tools should I use?” That’s the easy part. We recommend ClickUp, the one-stop shop for all your SaaSOps needs.
ClickUp helps teams simplify SaaS onboarding and creates a workspace for streamlined operations. You can set up a ClickUp Hierarchy with tasks and subtasks, each with their own descriptions, statuses, and comment,s to get a granular view of your operations. It can help you carefully organize work by departments, teams, projects, campaigns, etc., with the ability to zoom out and see work across these different areas.
ClickUp’s multiple customizable views give you a bird’s eye view of all your SaaS operations. You can view tasks as a list, board, calendar, timeline, workload, etc.
For instance, the Workload view lets you visualize your team’s capacity and manage resources. The Board view—a go-to view for agile teams—lets you visualize tasks by status. You can drag and drop your tasks to easily move them through your workflow.

Moreover, you get access to multiple pre-built ClickUp templates with customizable fields so you can mold them according to your business needs.
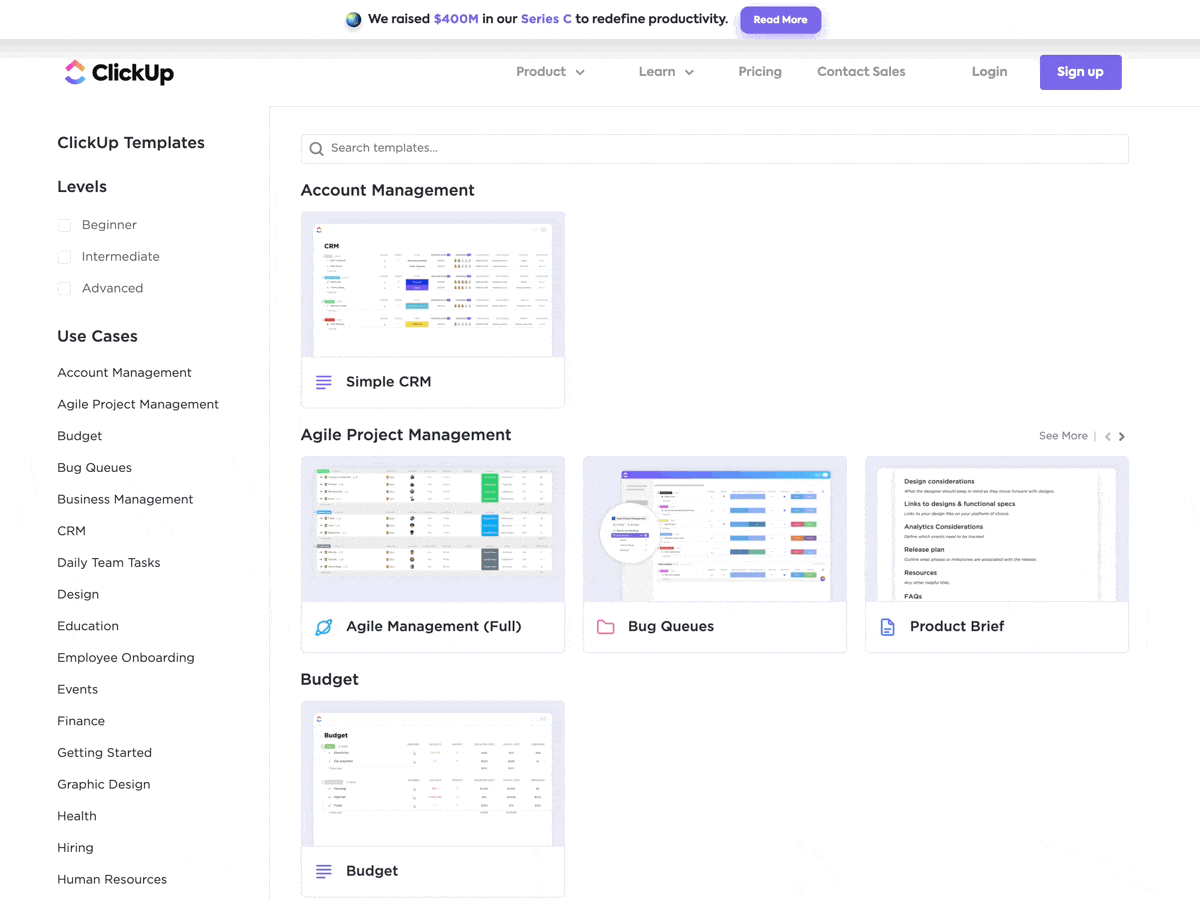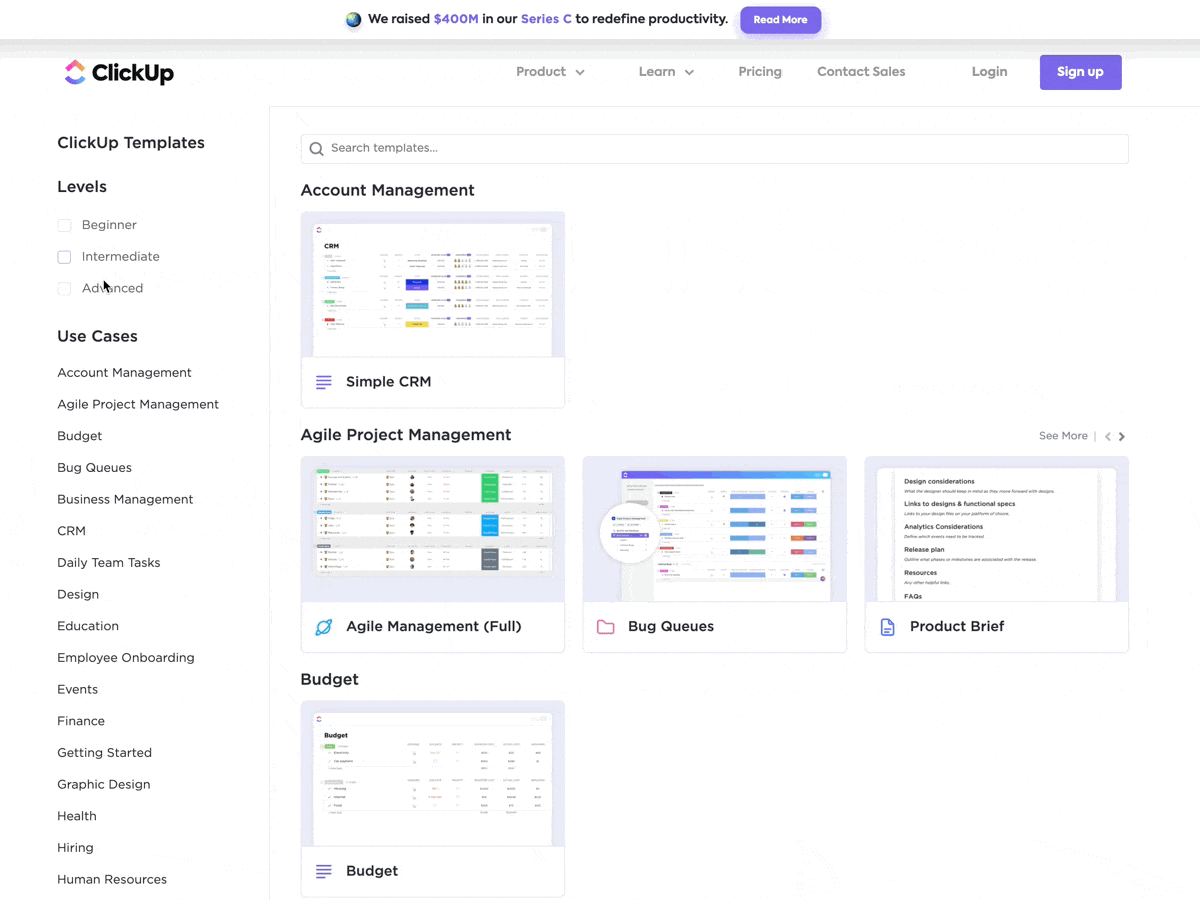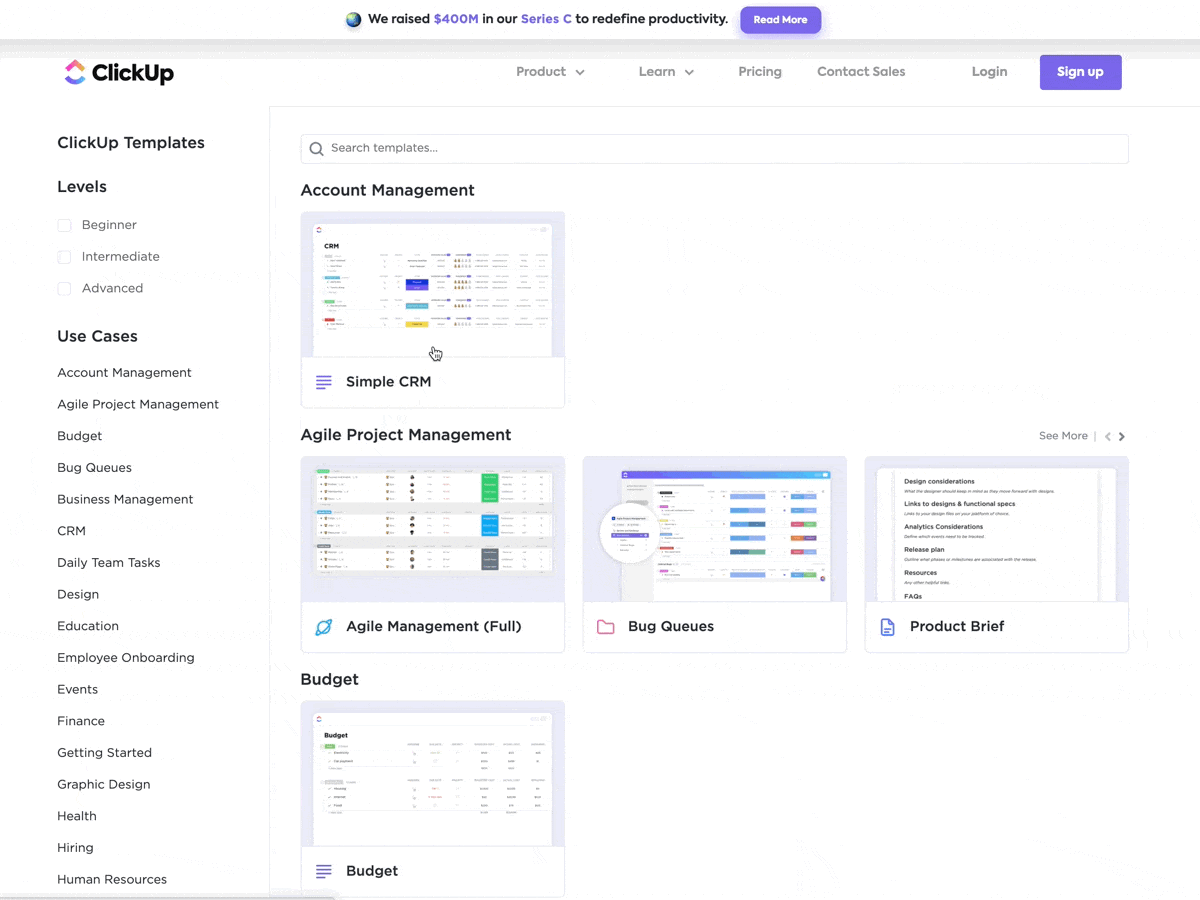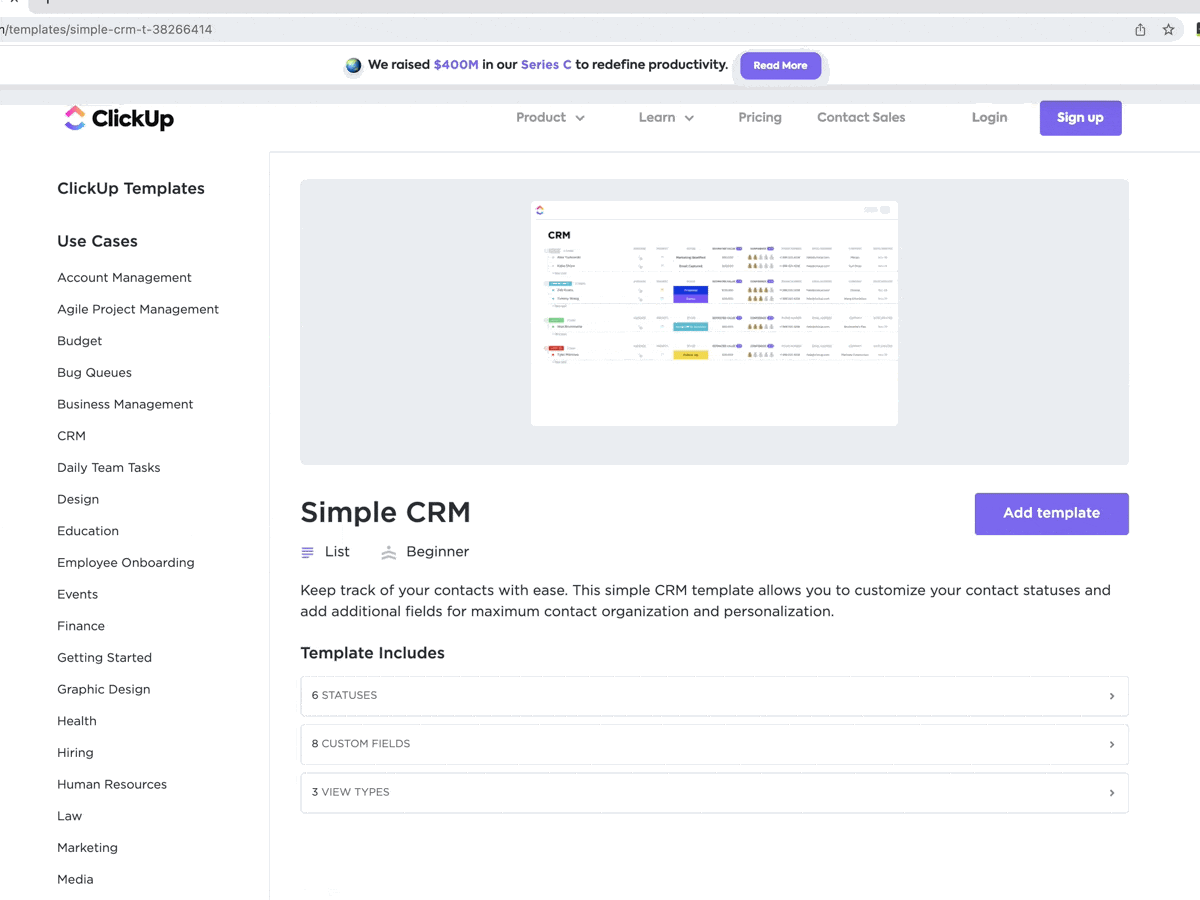
ClickUp’s Project Management platform is an all-in-one solution that brings your teams closer together with connected workflows, docs, real-time dashboards, and more.
The real-time ClickUp Dashboards give you a high-level look at your team’s operations. They can work as your headquarters to track your project.

ClickUp’s workflow automation allows you to capture and consolidate data through customizable forms. They standardize and unify the process of requesting, accessing, and maintaining data from your employees. You can use conditional logic to collect relevant details for everything from bug reports and new ideas to software access requests.
If you’re looking for more powerful automation, you should definitely check out ClickUp Brain. It’s the world’s first neural network that connects your tasks, docs, people, and all of your company’s knowledge with AI. With it, you can set up automatic progress updates, generate standups, summarize meeting notes, and quickly analyze data to create talking points for reports.

What Does The Future Hold for SaaS?
Over 70% of organizations worldwide use some mix of SaaS tools. Couple that with the fact that remote work is gaining in popularity, with 12.7% of full-time employees working remotely and 28.2% following a hybrid work model, the SaaS industry is seeing massive growth
So, maintaining a robust SaaS stack becomes vital. As your organization scales up, this framework becomes even more crucial for you as operation managers and business leaders. It keeps your operations running smoothly and ensures your team stays productive, no matter where they work. The right SaaS operations management software can be a game-changer here.
Related: Essential SaaS marketing strategies for a scaling company
Optimize Your SaaS Operations with ClickUp
While businesses often emphasize using SaaS, they sometimes overlook the pitfalls of not optimizing their SaaS operations. You don’t want to fall into that trap.
Adopt the suggested strategies and, most importantly, use a SaaS operations and project management tool that can significantly reduce the workload of your SaaS operations teams.
Choose ClickUp as your go-to central SaaS management platform, and sign up today. Experience our powerful capabilities at no cost. Join over 2 million teams worldwide who enhance their productivity daily with ClickUp.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the meaning of SaaS operations?
SaaS operations, or SaaSOps, refer to the comprehensive set of rules governing the governance, management, purchasing, and usage optimization of SaaS products.
2. What does SaaS stand for?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service, a cloud-based software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a third-party provider and made available to users over the Internet.
3. What is a SaaS operating model?
A SaaS operating model encompasses the lifecycle of SaaS applications, from discovery and procurement to onboarding and offboarding, including management and optimization throughout the process. It involves application visibility, infrastructure management, user management, security, compliance, automation, and more.



