
The Lean Startup is a popular book by the American entrepreneur Eric Ries. In this book, he shares some unique insights into the entrepreneurial management approach startups should follow and how it differs from what traditional businesses do.
He applies the Lean methodology pioneered by Toyota to startups in an attempt to improve how startups are managed. It is a project management approach that eliminates waste to make processes more efficient.
The book introduced many innovative ideas and principles that changed the way startup owners approached product development.
In our The Lean Startup summary, we’ll discuss some of the best ideas and learnings shared in the book to help startups achieve sustainable growth. We’ll also give you tips on how to apply these learnings to your startup business.
Let’s get started.
The Lean Startup Book Summary at Glance

Eric Ries, an American entrepreneur, has written this remarkable book by combining the lessons from his own experiences with the Lean methodology.
In the book The Lean Startup, he talks about the importance of iterative testing for product development instead of spending months, or even years, developing a product that no one wants.
He emphasizes the importance of starting with an idea and testing it, learning from it, testing again, and repeating the process multiple times to develop a product that will be most useful and in demand.
Need a more detailed summary? Read on to learn the most essential ideas and principles discussed in the book—The Lean Startup.
Before we get into the detailed summary of The Lean Startup, here’s a quick overview of the book:
Author: Eric Ries
No. of Pages: 336
Goodreads Rating: 4.1/5.0
Year Published: 2011
Publisher: Crown Business
Estimated Reading Time: 5.5-6.5 hours
Listening Length: 8 hours 38 minutes
Key Takeaways from The Lean Startup by Eric Ries
The book The Lean Startup offers ways to manage startups in an agile and flexible manner, leaving behind the traditional management approach. In this section, we’ll summarize some of the most important ones.
1. Create a minimum viable product (MVP)
Many entrepreneurs believe that launching a perfect product is necessary for its success. Eric Ries, in his book The Lean Startup, busts this myth.
He argues that startups do not need to invest tons of money and resources in perfecting a product that consumers may not even need or want. Instead, he suggests creating a minimum viable product and testing it to see how consumers respond.
An MVP is the simplest, most functional version of a product. It performs the basic function with the fewest bells and whistles. For example, you may launch a basic version of an app and gather user feedback to improve it over time.
It doesn’t even have to be a physical product but can be a landing page or a video explaining the product concept. Evaluating audience engagement and feedback on it enables you to develop the actual product, which is in line with what consumers want.
He suggests that startups create an MVP and ask consumers for feedback on it to assess its usefulness and what features people want in it.
2. Use the build-measure-learn loop
Once a startup has created a minimum viable product, Ries recommends testing it and improving upon the basic version.
He suggests various iterations to improve the product in increments instead of doing it in one go. Here’s what the build-measure-learn feedback loop entails:
- Build a minimum viable product
- Measure key metrics to understand its current performance
- Learn insights from these metrics to improve the product
Note that your MVP could simply be an idea or hypothesis. There are two kinds of hypotheses in the lean startup methodology that Ries details in the books:
- Value hypothesis: This centers around the core value proposition of a startup and tests whether it solves a user problem or meets a market need. For instance, let’s say you’re building a mobile app where users can get skincare recommendations. To validate your idea, you’d first test the value hypothesis. This might involve creating a simple landing page asking if people struggle to find skincare products that would suit their needs
- Growth hypothesis: This focuses on how a startup plans to win and retain customers. The tests, in this case, are conducted on the various strategies and acquisition channels a startup plans to use. Continuing the same example, for the growth hypothesis—you’d build a basic app with limited popular brands. Let users input skin concerns and track downloads, engagement time, clicks to product pages, etc.
The idea is to test your product or hypothesis to assess its viability.
Repeat the cycle as long as necessary to develop a fully functional and feature-rich product that your consumers want. With each cycle, make tiny improvements to the product and test it again.
How does it help?
It involves the end customer in the product development process. By taking feedback during each cycle, you improve your product based on what customers want and create a solution to their specific problems.
3. Leverage innovation accounting
The Lean Startup dives into the differences between traditional firms and startups and explains why the basics of financial accounting for the former don’t work for the latter.
Traditional accounting measures a company’s performance based on financial metrics like revenue and profit.
However, startups operate in a highly uncertain, dynamic environment and often take years to perform in the way traditional accounting would be considered successful.
Eric Ries offers ‘innovation accounting’ as a solution and asks entrepreneurs to focus on strategic learning goals instead of financial goals. It involves creating hypotheses and testing them with each build-measure-learn cycle, a concept he calls ‘validated learning.’
He asks startup owners to create their own progress goals and metrics. These could be anything that shows a positive response from the target consumers that the company’s product is useful to them.
We’ll elaborate on metrics in the next section, but innovation accounting is all about changing the way performance is measured in successful startups.
Here are the key steps involved in the process:
- Identify metrics that help you effectively assess the viability of a product
- Let your target customers try it and offer their feedback
- Assess the metrics and see if they align with your targets
- Decide if the metrics are positive and the product idea should be developed further or scrapped
4. Understand the three A’s of metrics
In The Lean Startup, the author talks about the misconception of tracking vanity metrics to measure the performance of a startup.
These vanity metrics could be app installs, page views, or anything else that doesn’t effectively show that a product is useful and has a market demand.
For instance, a new app could have thousands of installs, but if most people leave after engaging with it for a few minutes, it doesn’t matter. What matters is how many people engage with the app and use it for a significant period.
He suggests steering clear of vanity metrics and focusing on real metrics that show how good or bad your product is. That’s where the 3 A’s of metrics come in. These are three criteria to test metrics to ensure they’re useful.
These are:
- Actionable: The author emphasizes that the metrics you use to measure a startup’s performance should drive decision-making. You should be able to make informed decisions and change your approach based on the metrics you track
- Accessible: The reports you prepare based on tracked metrics should be easily understood by everyone involved. Your chosen metrics should also be easy to track and measure
- Auditable: Make sure that the data you collect can be easily tested, verified, and traced back to its original source
5. Decide whether to pivot or persevere
As discussed, The Lean Startup explains the importance of having an agile startup where ideas are regularly tested and improved upon.
The insights you get from the build-measure-learn feedback loop should inform your startup’s strategic direction. Specifically, based on your performance metrics, you need to decide whether to continue on the same path or pivot and adopt a different strategy.
This is a crucial decision, as not changing your direction may lead to wasted effort.
In his book, the author explains that it’s as important to understand when to give up as it is to persevere through challenges. If you continue indefinitely on a path that is not delivering results, that’s worse than trying something new and failing again.
So, analyze your performance metrics carefully and change your strategy as often as necessary until you perfect it.
6. Utilize the three engines of growth
The last principle we’ll cover in this summary of The Lean Startup is the concept of three engines of growth. Startups can use these to drive business growth and achieve success.
Here are the three growth engines listed in The Lean Startup:
- Sticky engine of growth: If you acquire more customers than you lose, your startup will grow. The rate of growth would be the difference between the new customer acquisition rate and the customer churn rate
- Viral engine of growth: This is based on the concept of viral growth achieved through word-of-mouth marketing by existing customers. If every new customer brings one or more other customers along with them, then the startup will grow
- Paid engine of growth: This involves using paid marketing to acquire new customers and grow a new business. If a startup spends enough on advertising and can retain the customers acquired by this means, it will grow
There you have it—the most important ideas and takeaways from the book. Of course, The Lean Startup summary is useful only if you apply it practically to your business. We’ll discuss ways of using this approach in your business later in this article. But first, let’s see some famous quotes from the book.
Popular Quotes From The Lean Startup
Apart from the numerous radical concepts introduced in the book The Lean Startup, it’s also known for its life-changing quotes.
Eric Ries presents some of his ideas beautifully in just one or two sentences, and they can change how you think about managing a business.
Here are some of the most famous quotes from the book to inspire you.
Ries explains that what matters most is what customers want, and the best way to understand that is to ask them instead of guessing or assuming. However, you won’t get the right answer even by asking them outright because customers will not always be able to express what they want correctly. You need to infer this based on what they tell you.
Here, the writer emphasizes the importance of gaining a competitive advantage by experimenting and learning faster than competitors.
With this quote, the writer has defined a startup. He distinguishes startups from other businesses by emphasizing that these businesses operate in a dynamic and uncertain environment to come up with a new product or service. In that sense, even a new division in an established company could be a startup if it operates like one.
This quote explains how important it is to question the validity of an idea by assessing whether there’s a real need for it. What matters is whether customers want a product or service, not its feasibility.
This quote emphasizes the importance of keeping things simple. This is especially useful when developing a business concept or product idea. The simpler, the better.
What Readers Say
Apply The Lean Startup (Principles, Ideas, Learnings) with ClickUp
Learning about an innovative concept is undoubtedly fun, but practically applying it is not as easy. This book summary will be incomplete if we don’t give you some tips on how to apply The Lean Startup concept to launch and grow your own startup business.
Using agile project management software like ClickUp can help you apply this book’s key takeaways. Let’s find out how.
1. Collaborate with your team to form hypotheses and goals
The first step in applying what you have learned from The Lean Startup is to develop ideas and hypotheses that you can test. It could be an idea for a product, software solution, or app.
ClickUp is a versatile project management and team collaboration solution with features that support brainstorming and ideation.
Brainstorm with your team using ClickUp Whiteboards. This feature allows real-time visual team collaboration to bounce ideas around and generate creative solutions from anywhere.
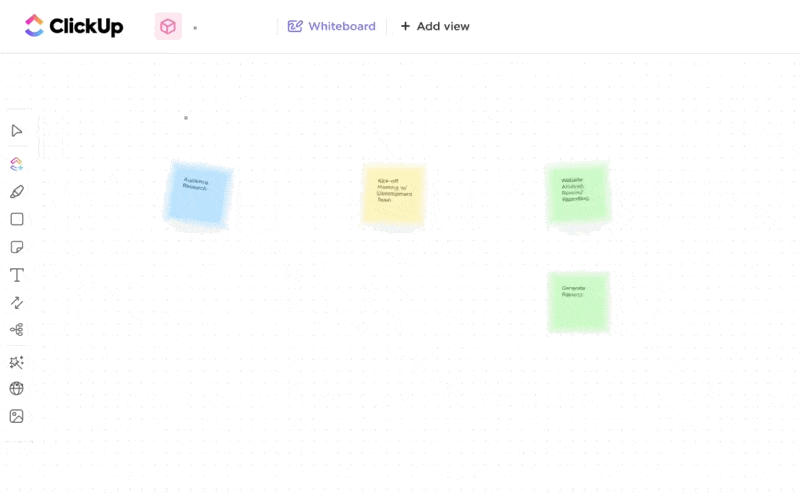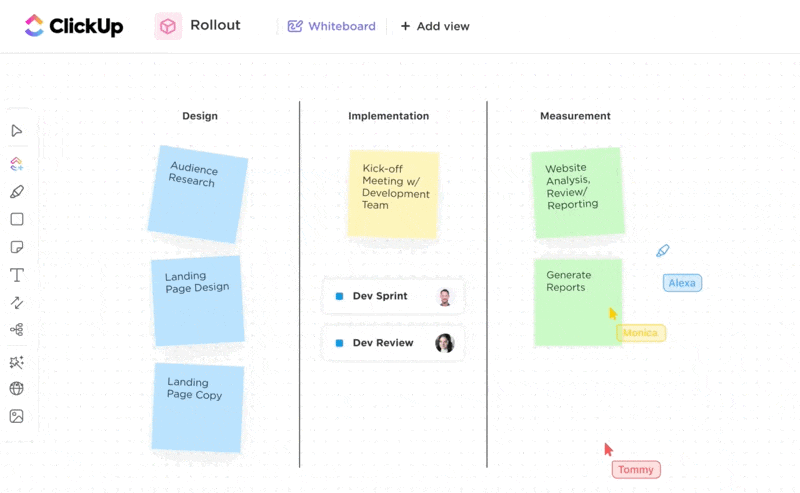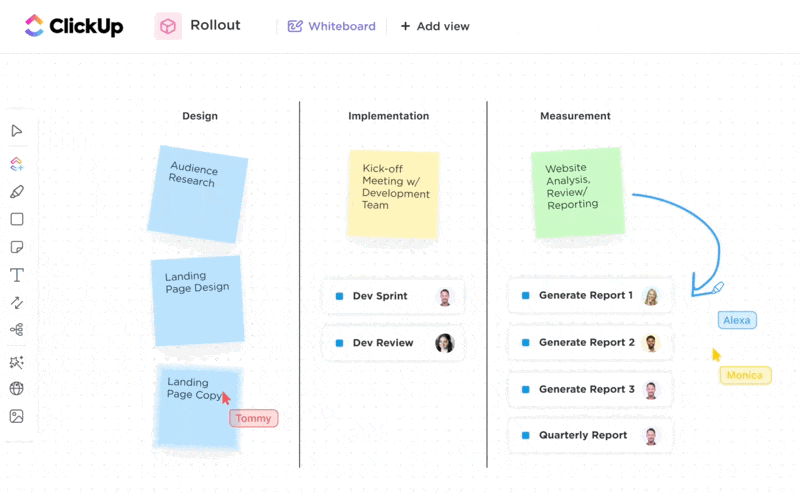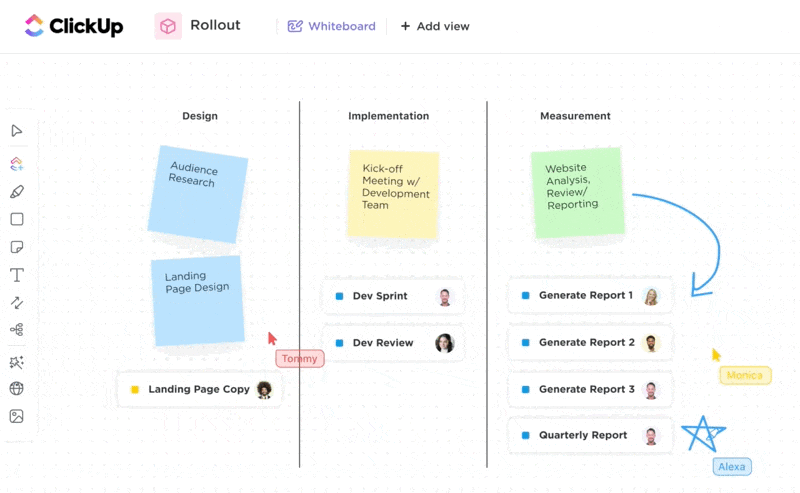
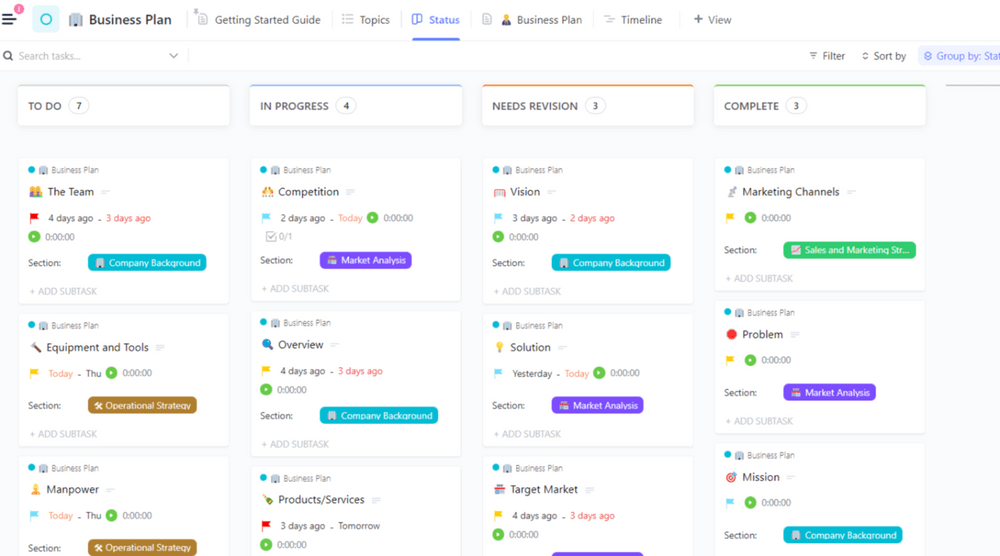
Once you’ve come up with an idea, it’s time to make a solid business plan. Use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to avoid starting from scratch and save time.
You can use this template to determine the ideal customer segments and target market for a business. Create a plan for expansion and success with this ready-to-use template.
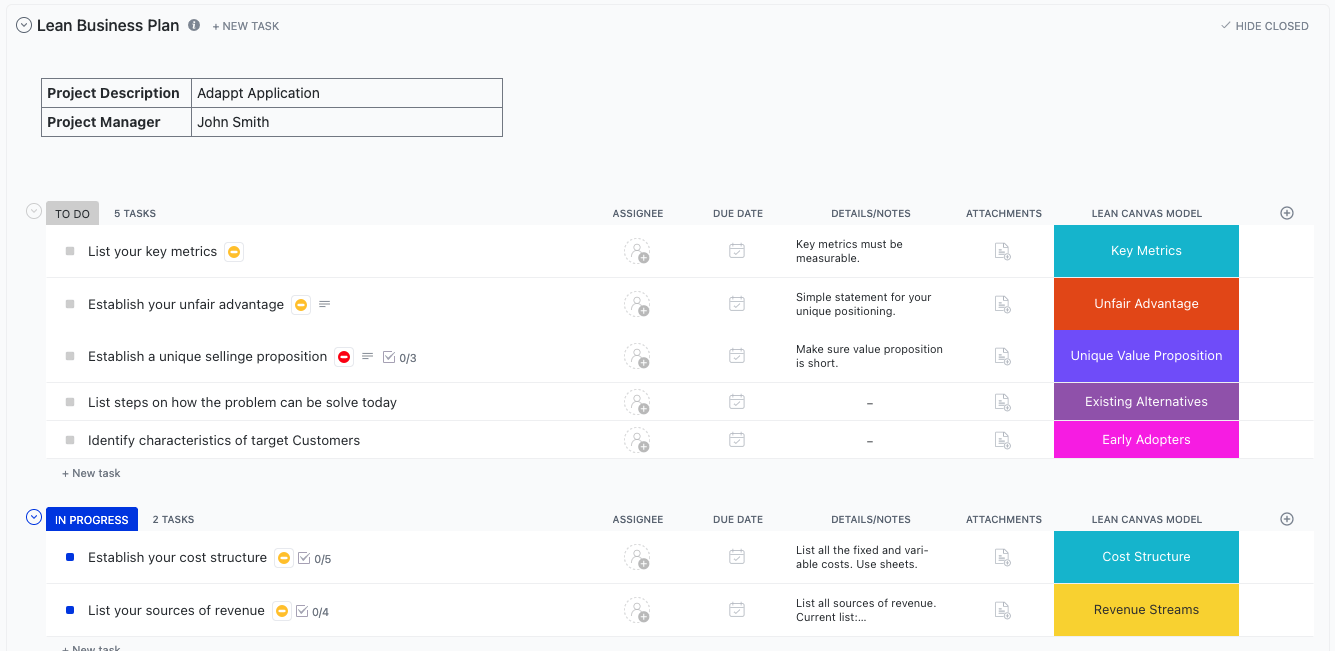
Another useful template is the ClickUp Lean Business Plan Template, which uses the ClickUp List View to organize tasks by status.
This template is an easy-to-read presentation that is succinct and well-organized. With this fully customizable template, you can ensure that you don’t miss anything important.
ClickUp offers various value proposition templates and business proposal templates to help you fine-tune your business idea and refine it before the product launch. These will help you structure your ideas and present them in a way that is easy for all stakeholders to understand. Once your product idea is developed, move to the testing stage.
2. Test your minimum viable product and hypotheses
Once you’ve created a minimum viable product, you must test it on your target customers and get their feedback.
As we learned earlier, this MVP could even be a video explaining your product concept or a landing page to explain your idea and get early adopters to sign up for the app or product launch. It doesn’t need to be a physical product; at this stage, you just need something to test whether there’s an actual demand for your product and whether your business plan will be successful.
You can use ClickUp Forms to collect customer feedback and survey responses. Since they have conditional logic built in, you can personalize the questions. ClickUp also offers various survey templates to get you started, from product development to customer feedback.
Leverage the ClickUp Product Feedback Survey Template to collect user feedback on your MVP or product concept. This will be useful for each iteration of the build-measure-learn cycle as you continue developing and testing your product.
This template helps you:
- Understand customer needs and identify areas of improvement
- Collect meaningful data quickly and accurately
- Analyze user responses and use the results to improve your product or service
Follow the author’s advice and don’t track vanity metrics, such as page views (without understanding engagement) or website traffic (without knowing conversion rates). Instead, focus on metrics that tell you how successful your product or idea is and translate into business success.
3. Decide whether to pivot or persevere
After a few iterations and feedback loops, you’d have enough data to know whether your product resonates with target customers.
This is when you must analyze all the feedback you’ve collected and the performance metrics to decide whether to continue with your current strategy or change direction.
Startups need to make quick business decisions, which requires your core team to come together and discuss the scenarios.
ClickUp Meetings is the perfect tool for conducting organized meetings with your team. It allows you to check availability and schedule team meetings as often as needed.
The best part is that you don’t have to maintain meeting records or minutes manually. Take advantage of ClickUp Brain and let AI take meeting minutes while you focus on making strategic decisions about your startup’s future.
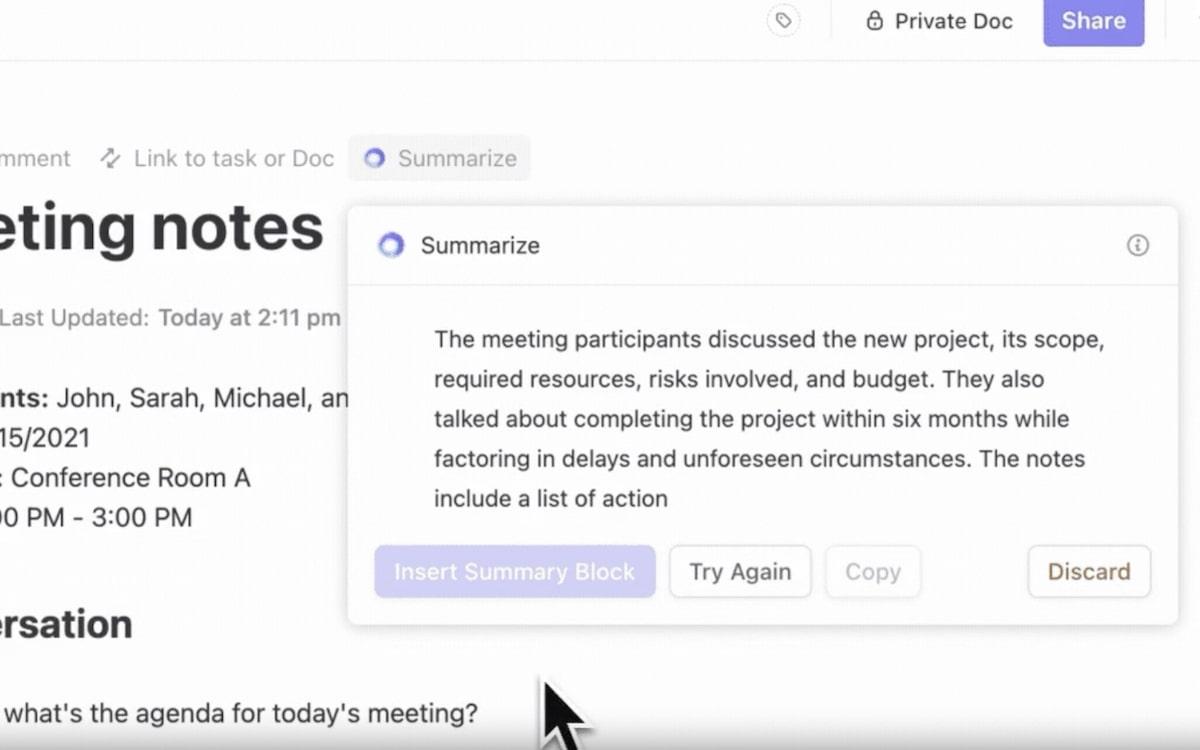
Not sure if you’re making the right decision? There’s a template to help with that.
The ClickUp Decision-Making Framework Template helps make decision-making quick and easy. It helps you:
- Create decision plans
- Assess the impact of your decisions
- Track the progress of your decisions
- Analyze all pertinent information required to make a decision
If you decide to pivot and change your strategy, use one of the good process mapping tools to design a new plan.
4. Create an environment of agility and continuous learning
Lastly, apply the lean methodology in everything you do and make it a core value within your startup.
ClickUp for Startups is an all-in-one platform that enables you to apply the learning from The Lean Startup in real life. It’s one of the few project management solutions for startups that enable agility and flexibility.
With its numerous project views, ClickUp lets you plan your product development project and track its progress visually.
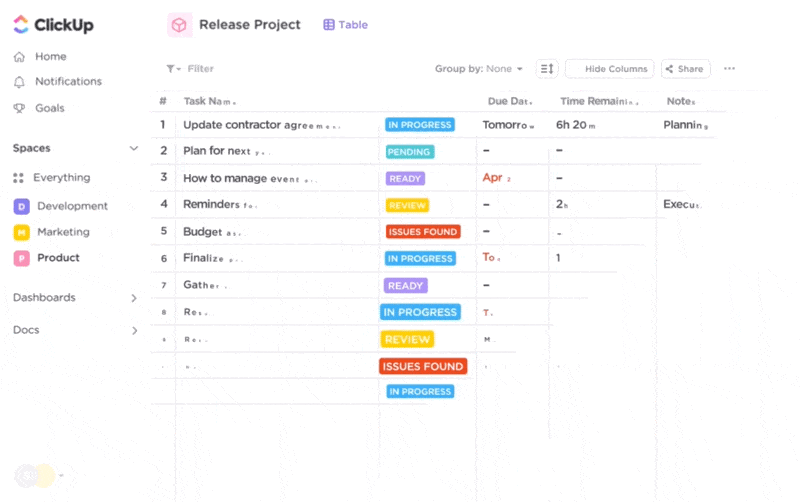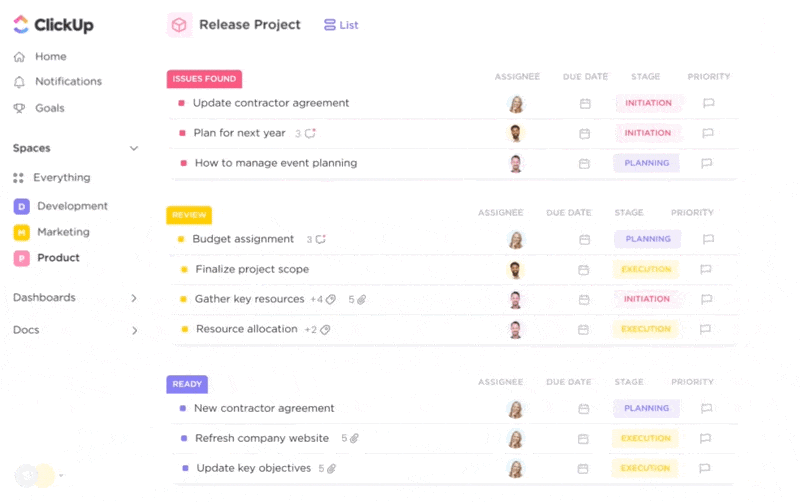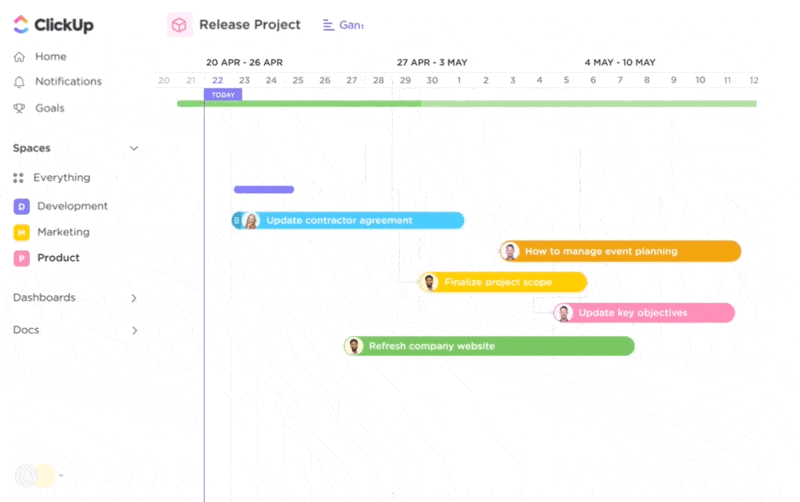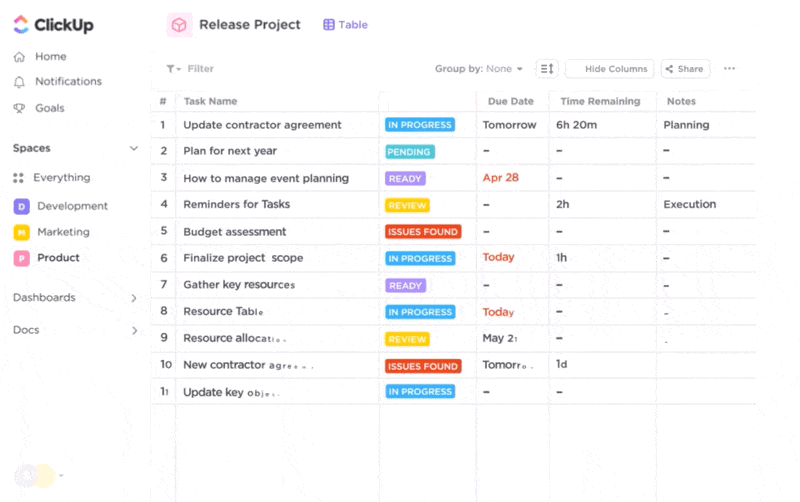
With the ever-evolving ClickUp Brain, you get some of the best AI tools for startups that help you with various aspects of your business. Whether you want to automate specific tasks or use AI to provide quick answers that aid decision-making, ClickUp Brain has everything you need.
Overall, having the right tools at your disposal makes creating an agile work environment easier. With a robust tool like ClickUp, you can modify your strategy and change course as many times as necessary until you develop the best product for your business.
Apply The Lean Startup Learnings with ClickUp
If you’re a startup owner, the principles laid out in the book ‘The Lean Startup’ can change your life and how you run your business.
With this summary of The Lean Startup, we’ve tried to share with you all the key ideas discussed in the book. By applying ideas like validated learning and innovation accounting, you can build a lean business model and achieve sustainable business growth.
Using robust project management software like ClickUp can further help you put the ideas into practice and gain an essential competitive advantage.
Check out its features by signing up for free. Sign up on ClickUp today!




Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.