You finally write the perfect AI art prompt. You hit “generate” and wait, only to be met with a distorted nightmare—disconnected limbs, warped facial features, and weird textures.
AI models don’t just need good prompts; they also need negative prompts to filter out unwanted elements. If you’ve ever wondered why your results have strange artifacts or unwanted styles, it’s likely because you’re missing this crucial step.
In this guide, you’ll find AI negative prompt examples that help refine the generated content, ensuring your creations turn out crisp, clean, and exactly how you envisioned.
⏰ 60-Second Summary
Here’s why negative prompts are key to improving AI-generated content:
- Negative prompts are essential for precision: They refine AI-generated images and copy by removing distortions, incorrect styles, and irrelevant text for professional results
- Use case-specific negative prompts matter: Whether creating realistic portraits, anime art, realistic photos, an article, or a Python script, tailoring your negative prompts ensures consistency and fewer AI errors
- Balance is key when crafting prompts: Overloading negative prompts can confuse AI, so test iteratively and use weighting techniques for control
- Different AI platforms handle prompts uniquely: For example, Stable Diffusion allows for advanced negative prompt fine-tuning, while MidJourney uses no commands to exclude elements
- AI negative prompting is just one part of the process: Optimizing prompts over time is crucial for efficiency. Tools like ClickUp Brain & Whiteboards help track AI-generated projects
- What Are AI Negative Prompts?
- Why Use Negative Prompts in AI Image Generation?
- Why Use Negative Prompts in AI Text Generation?
- AI Negative Prompt Examples by Use Case
- Best Practices for Crafting Effective Negative Prompts
- How to Use Negative Prompts in AI Platforms
- Limitations of Using AI Tools with Negative Prompts
- ClickUp as the Alternative AI Tool
- Manage AI Content Projects with ClickUp
What Are AI Negative Prompts?
AI negative prompts tell an AI model what to avoid when generating images or text. Just like a regular prompt guides the AI on what to include, a negative prompt refines the output by removing unwanted elements.
A negative prompt is commonly used in text, image, and video generation models to refine results and exclude unwanted elements. This is especially useful when dealing with AI models that generate blurry details, poorly rendered features, strange distortions, superfluous detail, or incorrect styles.
Example:
If you’re generating a realistic portrait but keep getting blurry backgrounds and overly sharp facial features, your prompt might be:
👉 Regular prompt: “A hyper-realistic portrait of a woman with soft lighting”
👉 Negative prompt: “Blurry background, harsh lighting, distorted face, extra limbs, unnatural colors”
By adding negative prompts, the AI focuses on improving the quality of the desired elements while eliminating common flaws. This simple tweak can drastically enhance precision and help generate realistic photos and text.
Negative prompts are primarily used with generative AI models, especially those related to text-to-image or text-to-text generation.
When using a model that supports negative prompting (especially in image generation), the AI adjusts the latent space representation to minimize the presence of the specified unwanted elements.
Why Use Negative Prompts in AI Image Generation?
Negative prompts prevent unwanted elements in AI-generated images, making them more polished and accurate. Removing distortions and irrelevant details can save time and improve quality. Here’s why they’re essential:
1. Avoid distorted or unnatural features
AI models sometimes generate disconnected limbs, poorly drawn faces, or mismatched body parts—especially in portraits or character art. Negative prompts help counter these issues.
Example:
Prompt: “A detailed fantasy warrior in armor, cinematic lighting”
Here’s what ChatGPT made with the above prompt:
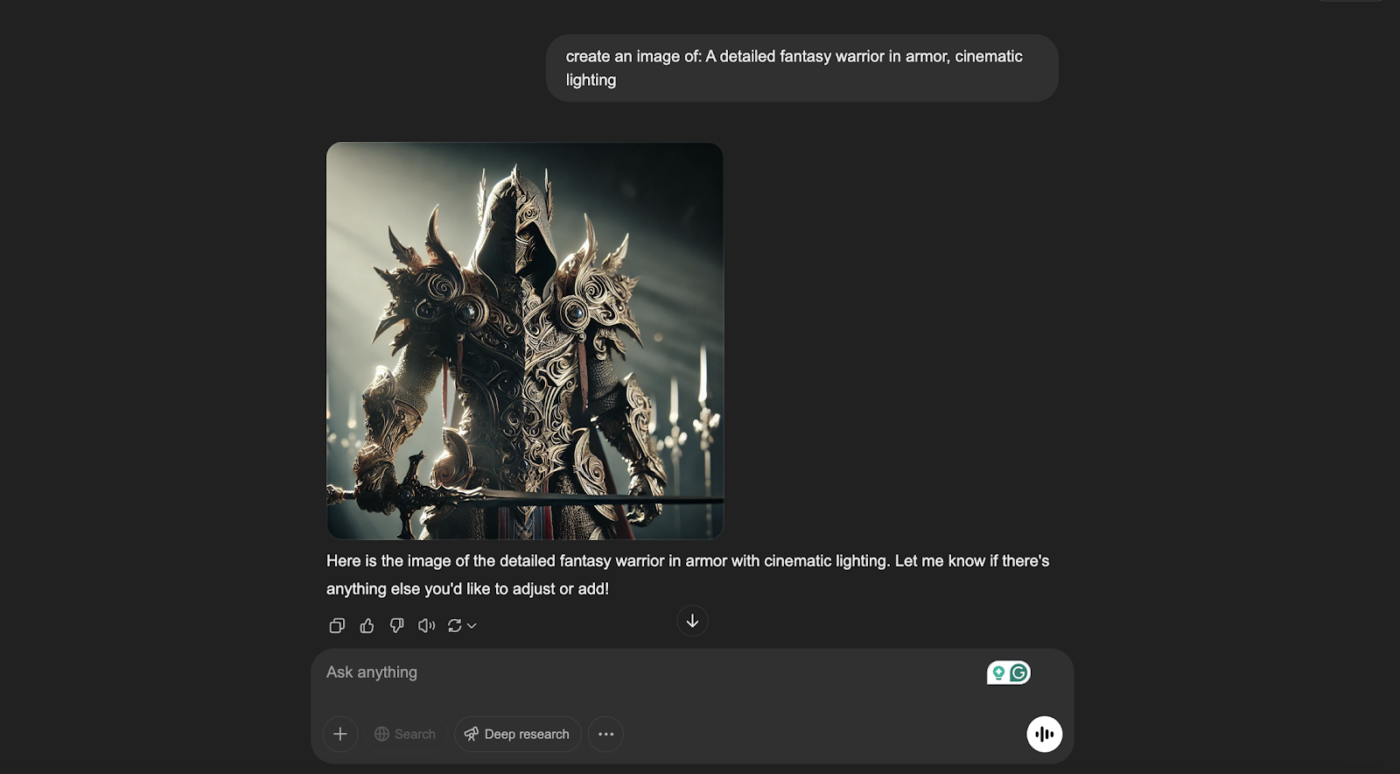
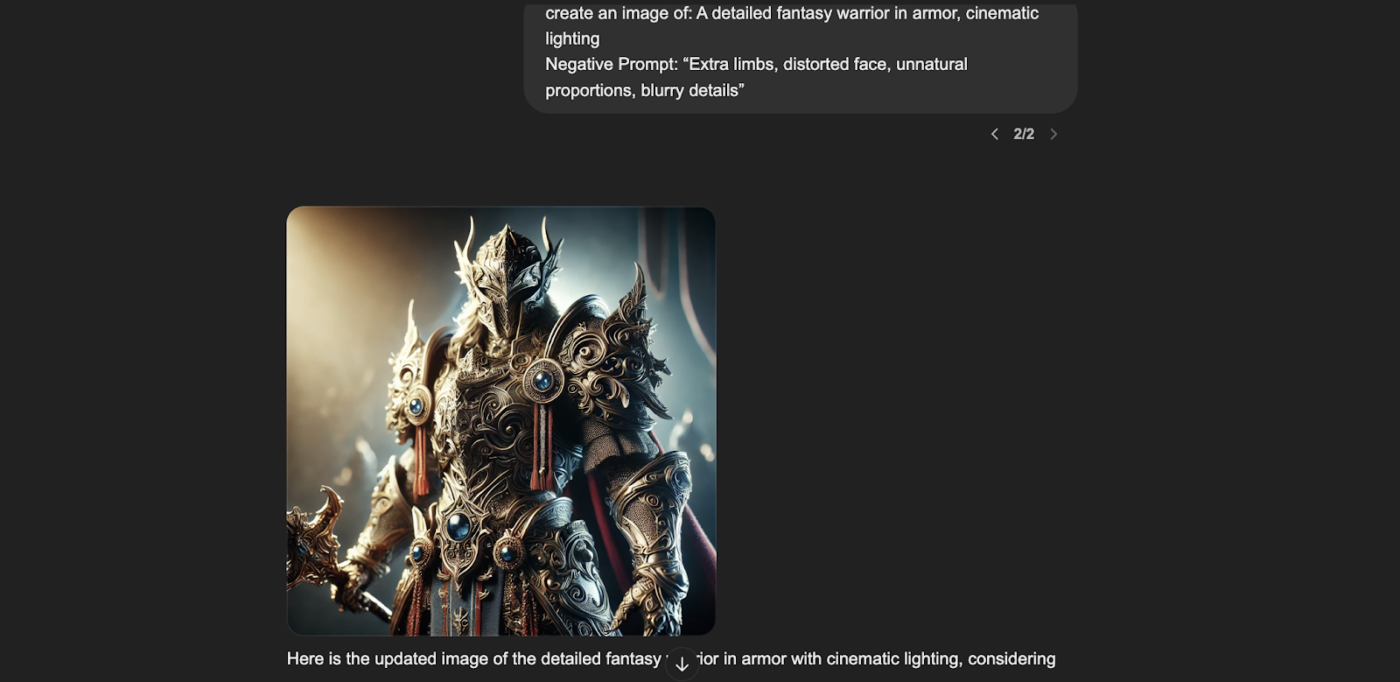
However, the same prompt with an additional negative prompt like “Extra limbs, distorted face, unnatural proportions, blurry details” gives out the result:
The first image had creative variations, such as exaggerated features or less focus on standard human proportions. These can sometimes manifest as slightly unnatural elements in depicting the warrior’s appearance or posture.
The second image, created with the negative prompt, specifically avoids these features. It maintains standard human proportions, ensuring the face and limbs appear natural and realistic.
The details are kept sharp and clear, without any blurring that detracts from the intricacy of the armor or the overall clarity of the scene.
2. Refine art styles and consistency
AI can mix styles unintentionally—blending realism with anime or adding painterly textures when you want a clean digital look. Negative prompts force consistency.
Example:
Prompt: “A clean vector-style illustration of a cat.”
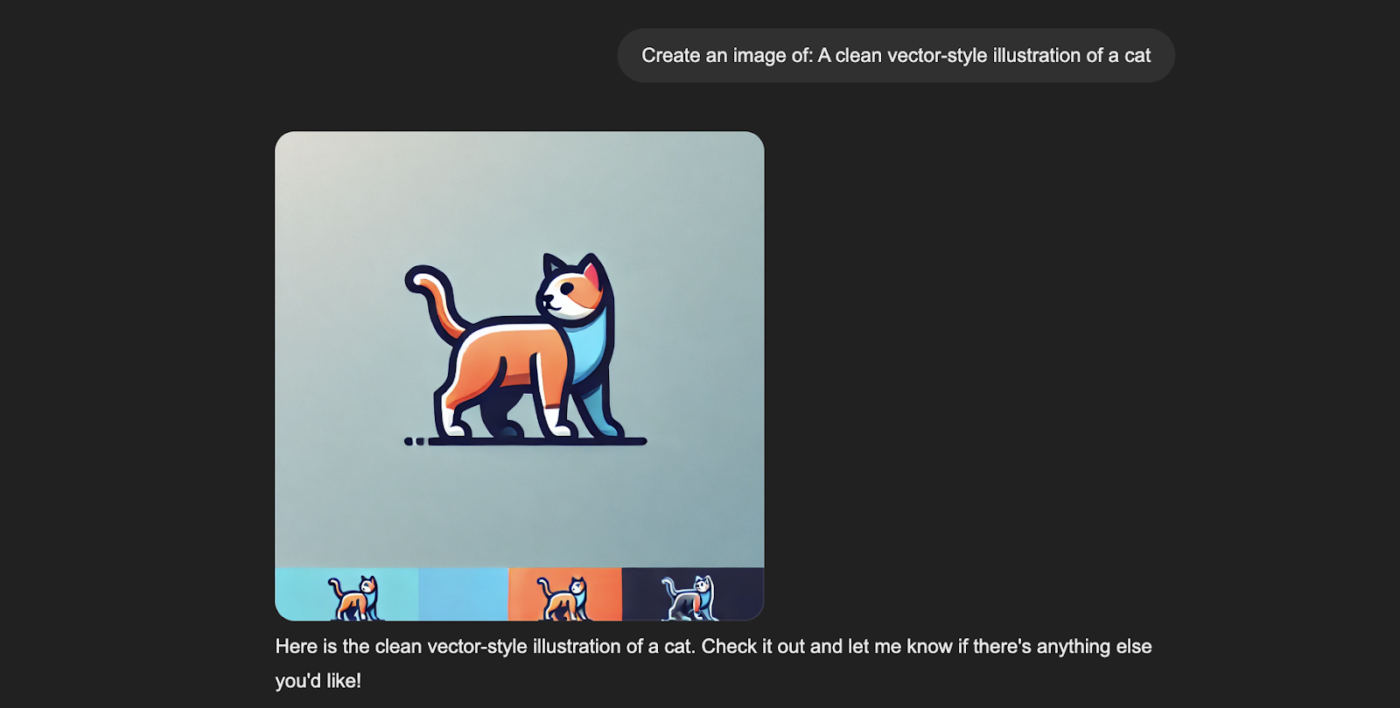
The same prompt, when given alongside a negative prompt, like: “Watercolor, oil painting, 3D render, noise, rough texture.” The output changes to:
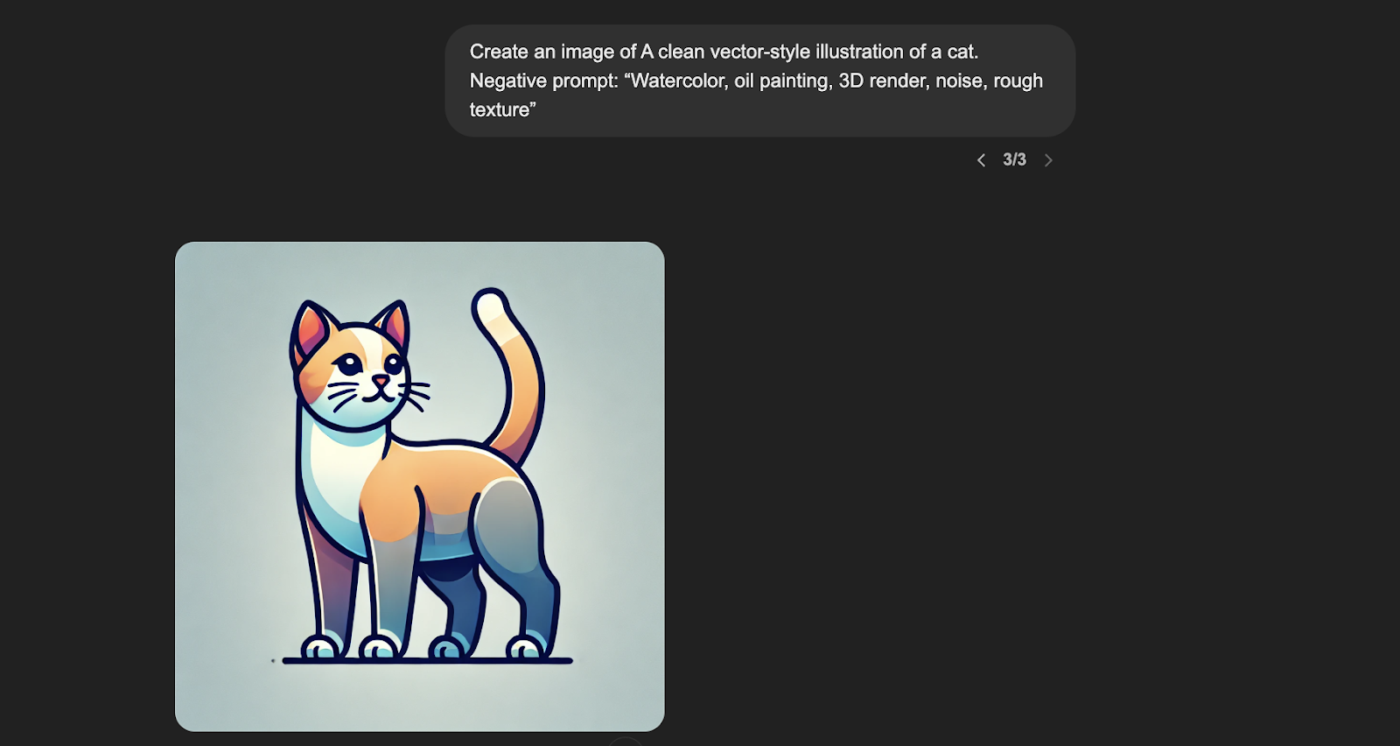
While clean and modern, the first vector illustration was created without constraints. This can lead to unintended variations in texture or style resembling non-vector art forms.
On the other hand, the second illustration was deliberately crafted to exclude certain characteristics, such as watercolor effects, oil painting textures, 3D render appearances, noise, and rough textures.
This resulted in a more refined and strictly vector-style graphic, ensuring the design remained crisp, clear, and solidly colored.
3. Eliminating unwanted colors and lighting issues
Sometimes, AI over-saturates colors or introduces harsh lighting effects that disrupt the intended mood. Negative prompts help control this.
Example:
Prompt: “A moody cyberpunk street with neon lights.”

The same prompt with a negative prompt addition: “Washed-out tones, oversaturation, excessive glow, foggy” gives:

Typically, unrestricted cyberpunk visuals might lean heavily on atmospheric effects like fog and glow to convey moodiness and an otherworldly feel. This results in a blurred or less detailed appearance, with vibrant colors bleeding into each other, creating a more abstract visual.
In contrast, the image with a negative prompt offers a distinctly crisper and more defined portrayal of a cyberpunk street scene than one might expect from an image generated without these restrictions.
💡 Pro Tip: A well-structured prompt ensures better AI results. Instead of writing vague inputs, use clear, detailed phrasing to avoid randomness. See real-world prompt engineering examples here.
Why Use Negative Prompts in AI Text Generation?
Negative prompts (or guiding constraints) in text generation help fine-tune responses, ensuring they meet specific requirements while avoiding unwanted content. They are especially useful for refining outputs in tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Codex.
Here’s an in-depth look at why negative prompts are valuable in AI text generation:
1. Improving relevance and accuracy
AI-generated responses sometimes include off-topic details, redundant information, or assumptions that reduce accuracy. Using negative prompts helps filter out irrelevant content, making the response more focused and precise.
Example:
- Effect: Ensures the summary remains historical without speculative future content
- Prompt: “Summarize the history of artificial intelligence”
- Negative Prompt: “Do not include futuristic predictions or personal opinions”
2. Controlling writing style and tone
AI might generate responses that are too formal, informal, overly detailed, or technical for your needs. Negative prompts can guide the tone, readability, and depth of the content.
Example:
- Effect: Ensures the explanation is simple and beginner-friendly
- Prompt: “Explain blockchain technology for beginners”
- Negative Prompt: “Avoid technical jargon and complex mathematical explanations”

3. Avoiding redundant or repetitive content and encouraging creativity
AI sometimes repeats the same points using different phrasing, making responses unnecessarily long. It can sometimes produce generic or overused phrases instead of unique, engaging content.
Negative prompts help maintain concise and engaging writing and push the AI toward originality.
Example:
- Effect: Forces the AI to list unique benefits rather than rewording the same points and avoid predictable phrases
- Prompt: “Describe the benefits of exercise”
- Negative Prompt: “Do not repeat the same benefit in different words, and avoid clichés like ‘Never give up'”
4. Filtering out bias and subjectivity
AI models are trained on vast datasets, which can sometimes introduce biases or subjective opinions into responses. Negative prompts help keep responses neutral and fact-based.
Example:
- Effect: Ensures the response is objective and data-driven rather than speculative
- Prompt: “Discuss the impact of AI on jobs”
- Negative Prompt: “Do not express personal opinions or make unsupported claims”
5. Excluding unwanted topics or sensitive information
Sometimes, AI-generated content includes controversial topics, sensitive details, or unwanted themes that are irrelevant to the request. Negative prompts can explicitly filter out such content.
Example:
- Effect: Keeps the focus on productivity techniques without discussing health-related factors
- Prompt: “Write a blog about time management strategies”
- Negative Prompt: “Do not mention diet or exercise”
AI Negative Prompt Examples by Use Case
Negative prompts help fine-tune AI-generated content by eliminating distortions, unwanted elements, bias, and inconsistencies. Whether you’re working on realistic portraits, anime art, landscapes, product photography, ad copy, or a blog, the right negative prompts make all the difference.
Below are practical negative prompt examples tailored to different creative needs.
1. Realistic human portraits
AI struggles with anatomy, facial symmetry, and natural-looking features. These negative prompts help maintain realism.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Extra limbs, extra fingers, extra arms, poorly drawn face, asymmetrical features, bad anatomy, distorted eyes, blurry details, plastic texture, uncanny valley, over-sharpened, exaggerated muscles, grainy skin.”
💡 Pro Tip: If AI keeps generating creepy hands, add “bad hands, extra fingers, too many fingers, fused fingers, unnatural grip” to your negative prompt.
2. Anime and cartoon characters
AI can mix styles or generate strange anatomical errors when making anime art. Use these to keep your characters clean and sharp:
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Realistic details, over-detailed textures, 3D elements, hyper-realism, blurred lines, jagged edges, bad proportions, extra eyes, poorly drawn hands, wrong anime proportions, noise, washed-out colors, realism filter”
🧠 Fun Fact: Some AI models accidentally add noses to anime characters because they struggle with 2D stylization!
3. Product photography and e-commerce images
For product-focused images, AI often adds unwanted reflections, cluttered or boring backgrounds, or inconsistent lighting. The following negative prompts can overcome this:
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Text, watermark, logo, extra objects, shadows, clutter, boring background, incorrect reflections, uneven lighting, low quality, worst quality lens distortion, poor resolution, overexposed, blurry, ugly fingers, normal quality, low resolution”
💡 Pro Tip: AI-generated graphics need refinement. Negative prompts help remove unwanted elements, ensuring cleaner compositions. Learn how AI can enhance graphic design here.
4. Landscapes and cityscapes
In environmental images, AI can sometimes generate floating objects, unrealistic lighting, or unwanted crowds.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Unnatural shadows, over-saturation, floating objects, distorted buildings, missing textures, unrealistic reflections, low contrast, incorrect lighting, glitch artifacts, washed-out sky, overexposed highlights, duplicate elements”
5. Cyberpunk and futuristic sci-fi art
AI might overdo neon lighting, unnatural color schemes, or distorted elements in sci-fi compositions.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Overexposure, unrealistic glow, excessive neon, wrong perspective, lens flares, blurry edges, poor contrast, extra lights, glitch artifacts, pixelated, distorted geometry, duplicate buildings.”
🧠 Fun Fact: AI models sometimes lack data for certain output images, and in that case, they often ‘hallucinate’ answers as they misinterpret data or fabricate answers!
6. Fantasy art and mythical creatures
Fantasy-themed generations sometimes add inconsistent details, extra limbs, or incorrect anatomy to mythical creatures.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Extra wings, disproportionate body parts, random glowing elements, plastic texture, over-saturated colors, deformed legs, asymmetry, misplaced shadows, wrong perspective, poorly blended details”
🎯 Bonus Tip: Avoid AI realism for a painted fantasy look by adding “photorealistic, 3D render, hyper-detailed, lifelike” to the negative prompt.
7. Vintage and retro art styles
AI sometimes adds modern textures or incorrect color palettes when attempting vintage styles.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“HD, high-definition, sharp edges, digital artifacts, modern style, over-saturation, new-age details, incorrect era, futuristic elements, plastic texture”
8. Horror and dark-themed art
AI horror images can sometimes generate unintended comedy or over-the-top gore. Negative prompts help refine the eerie effect.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Cartoonish, goofy, exaggerated horror, excessive blood, over-detailed, unnatural color grading, unrealistic expressions, poorly drawn face, poor contrast, washed-out tones, blank background, blurry body.”
➡️ Read More: Dall-E Alternatives to Create AI Images!
9. Architectural renders and interiors
AI often adds incorrect lighting, extra furniture, or distorted structures in architectural images.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Uneven lighting, warped walls, unrealistic reflections, floating objects, poor perspective, extra furniture, cluttered background, distorted proportions, incorrect shadows, missing details, fisheye distortion, gross proportions”
10. Food photography and culinary art
AI food images sometimes look too artificial, overly glossy, or strangely textured.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Plastic texture, unrealistic shine, incorrect food proportions, extra objects, clutter, text, watermark, logo, wrong ingredients, floating elements, overly saturated, blurry edges, cartoonish, 3D-rendered”
11. Ad copywriting
AI can generate overly generic, exaggerated, or overly salesy language that may reduce credibility. These negative prompts help create persuasive yet realistic ads.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Clickbait, exaggerated claims, overly promotional, repetitive phrases, unnatural enthusiasm, generic buzzwords, vague benefits, robotic tone, forced urgency, overuse of exclamation marks, irrelevant details.”
12. Customer outreach email creation
AI-generated emails may sound too robotic, impersonal, or overly formal, making them less effective for engagement. These negative prompts help keep emails natural and relatable.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Generic greeting, excessive formality, robotic language, unnatural phrasing, overly apologetic tone, vague subject line, impersonal approach, excessive flattery, overly long paragraphs, irrelevant information, clickbait-style CTA.”
13. Business reports
AI-generated business reports can sometimes include filler content, vague conclusions, or an overly casual tone. These negative prompts help maintain a professional and data-driven approach.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Unsubstantiated claims, casual language, excessive adjectives, redundant information, vague conclusions, unnecessary storytelling, excessive wordiness, unsupported opinions, overly general statistics, marketing-style language.”
14. Story writing
AI may introduce clichés, repetitive plot points, or overly simplistic character development. These negative prompts help encourage originality and depth in storytelling.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Cliché plot twists, predictable storyline, one-dimensional characters, excessive exposition, unrealistic dialogue, info-dumping, repetitive phrases, overused tropes, forced happy endings, lack of emotional depth.”
15. Code snippets
AI may generate inefficient, outdated, or unnecessarily complex code. These negative prompts help ensure clean, modern, and readable code.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Deprecated functions, inefficient loops, overly complex logic, unnecessary comments, poor indentation, excessive nesting, insecure practices, outdated libraries, redundant code, lack of error handling.”
16. News summaries
AI may introduce bias, unnecessary opinions, or excessive detail in news summaries. These negative prompts help keep summaries factual, concise, and neutral.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Speculation, personal opinions, exaggerated language, biased phrasing, excessive background details, emotionally charged words, misleading headlines, unnecessary repetition, filler content, casual tone.”
17. Social media captions
AI-generated captions can be too generic, overly promotional, or lack engagement. These negative prompts help create concise, relatable, and engaging content.
❌ Negative prompt examples:
“Clickbait, excessive emojis, all caps, forced enthusiasm, generic phrases, robotic tone, too formal, vague messaging, excessively long captions, unnecessary hashtags.”
➡️ Read More: Best Stable Diffusion Alternatives for Art Generation
Best Practices for Crafting Effective Negative Prompts
Negative prompts help refine AI-generated images and text, but crafting them requires strategy. Instead of just dumping a list of generic terms, fine-tuning your approach can help you get precise, high-quality results.
Here are some out-of-the-box best practices to improve your basic negative prompts.
1. Avoid overloading your negative prompt with too many terms
Throwing every unwanted element into the negative prompt is tempting, but too many restrictions can confuse the AI.
This can flatten details or make results unpredictable. Instead, start with key terms that target specific issues—like “extra limbs” or “blurred details.” If the problem persists, refine it by gradually adding more terms.
💡 Pro Tip: Save and categorize successful prompts to improve efficiency. ClickUp helps track and refine them for future use. Find ready-made AI prompt templates here.
2. Use weight adjustments for more precise control
Many AI tools for image generation allow weighting terms to control their influence. By adjusting importance using syntax like (word:1.5) or [word], you can prioritize major flaws without completely removing minor elements.
✅ Example: If AI keeps generating harsh shadows, try “harsh shadows: (1.5), blurry background: (0.8)” to downplay blur while strongly reducing shadows.
🎯 Why it works: It fine-tunes the AI’s interpretation rather than completely blocking an element, which can sometimes create unexpected results.
3. Negative prompts work best when paired with precise main prompts
A strong main prompt is just as important as a negative prompt. If your positive prompt is vague, the AI has more room for randomness, making your negative prompt less effective. Be as detailed as possible in the main prompt before adjusting negative terms.
🔹 Bad example: “A beautiful woman in a city” + “bad anatomy, blurry”
🔹 Better: “A highly detailed, symmetrical portrait of a woman, soft lighting, natural pose” + “bad anatomy, too many fingers, asymmetry, oversaturation, jpeg artifacts.”
🚀 Pro Tip: A focused main prompt reduces trial and error when refining images.
4. Test one change at a time instead of guessing blindly
Don’t immediately spam negative prompts if an AI-generated image or text isn’t turning out right. Instead, change one thing at a time to see what’s affecting the result.
⚒️ How to troubleshoot:
- Run your prompt without any negative terms and note errors
- Add one negative term targeting the biggest issue
- Generate again and compare changes
- Repeat by adding or adjusting terms gradually
📌 Why it works: This approach isolates what works and what doesn’t, making refinement faster and more intentional.
5. Don’t just remove elements—use negative prompts to guide style
Negative prompts aren’t just for fixing mistakes—they can refine artistic style and mood. If you want an artsy look, you can negatively prompt realism. If you prefer smooth digital art, remove rough textures and noisy details.
Similarly, when generating text, if you require copy that reads light and cheery, try negatively prompting formal language.
🎨 Example:
✅ For a clean anime aesthetic: Negative Prompt: “realism, photorealistic, 3D-rendered, oil painting, harsh textures”
✅ For a vintage film look: Negative Prompt: “digital, sharp focus, oversaturated, modern style”
⚡ Bonus Tip: Think about what you don’t want stylistically, not just technical flaws. Negative prompts are just as useful for curating aesthetics as filtering errors.
How to Use Negative Prompts in AI Platforms
Negative prompts help refine AI-generated content by removing unwanted elements. Different AI tools for images, like Stable Diffusion and Midjourney, allow users to add negative prompts to control the final output. Similarly, text generator AI tools such as ChatGPT and Claude also recognize negative prompts.
Below are step-by-step guides for using negative prompts effectively on major generative AI platforms.
Using Stable Diffusion negative prompts
Stable Diffusion gives users precise output control, allowing for detailed negative prompting.
⚒️ Steps to use negative prompts in Stable Diffusion:
Step 1: Open Stable Diffusion UI
Use platforms like Automatic1111, InvokeAI, or ComfyUI to access Stable Diffusion. Let’s use HuggingFace to access Stable Diffusion’s 3.5 model to understand how to give prompts.
Step 2: Enter your main prompt
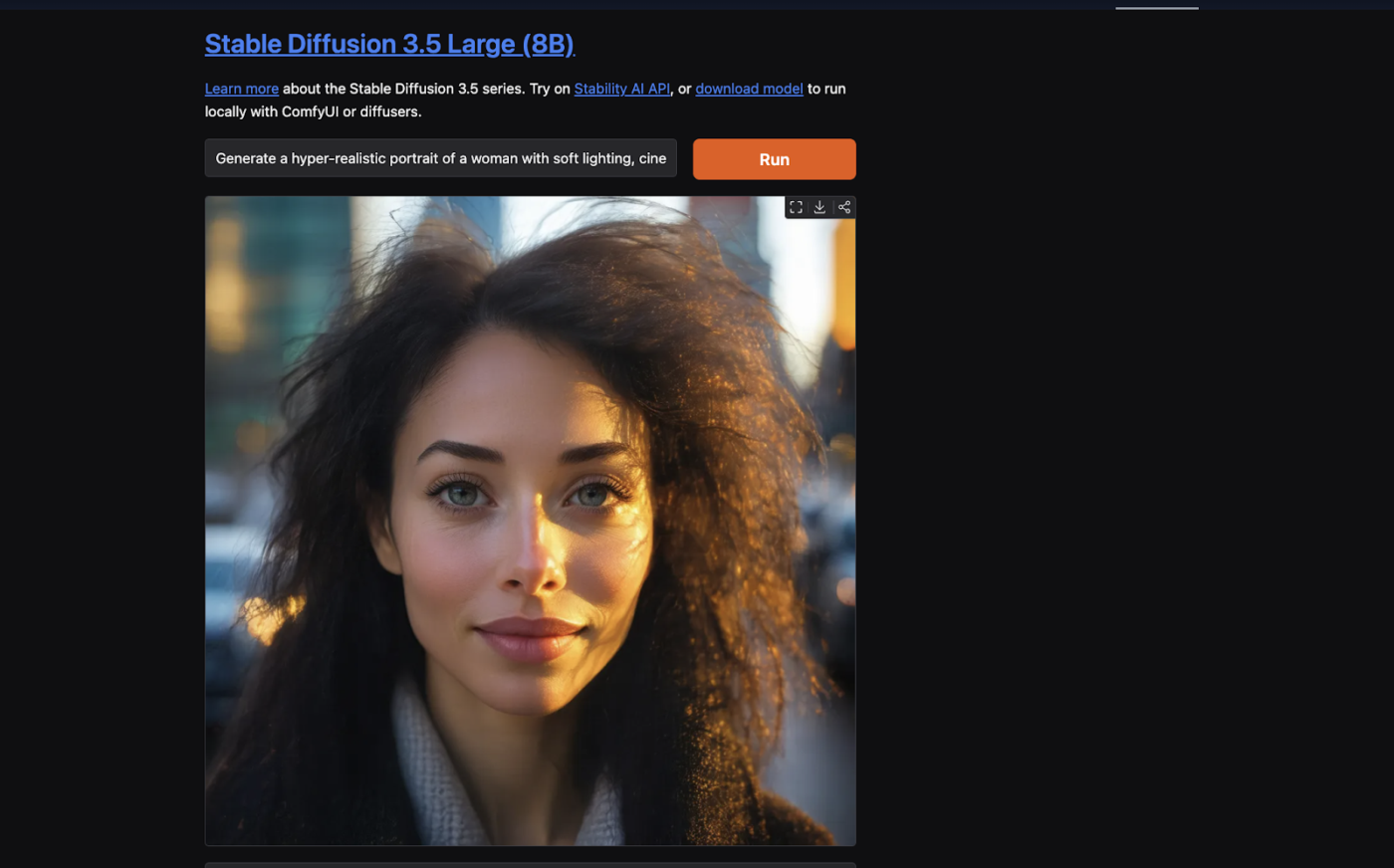
Be as detailed as possible to ensure AI understands the style and subject. Here’s an example of a prompt you can give:
“Generate a hyper-realistic portrait of a woman with soft lighting, cinematic depth of field, detailed skin texture, and natural hair flow. The background should be a blurred cityscape with warm golden tones at sunset.”
Step 3: Add a negative prompt
Look for the “Negative Prompt” input box and type elements to remove (e.g., “blurry, extra fingers, deformed face, text, watermark.”
Here’s the Negative Prompt you can give:
“Blurry, extra fingers, missing arms, missing legs, poorly drawn hands, missing fingers, unnatural lighting, plastic-like texture, grainy, over-sharpened, watermark, text, logo, extra limbs.”
Step 4: Adjust sampling method & settings
Different samplers (Euler, DDIM, etc.) process negative prompts differently, so test variations.
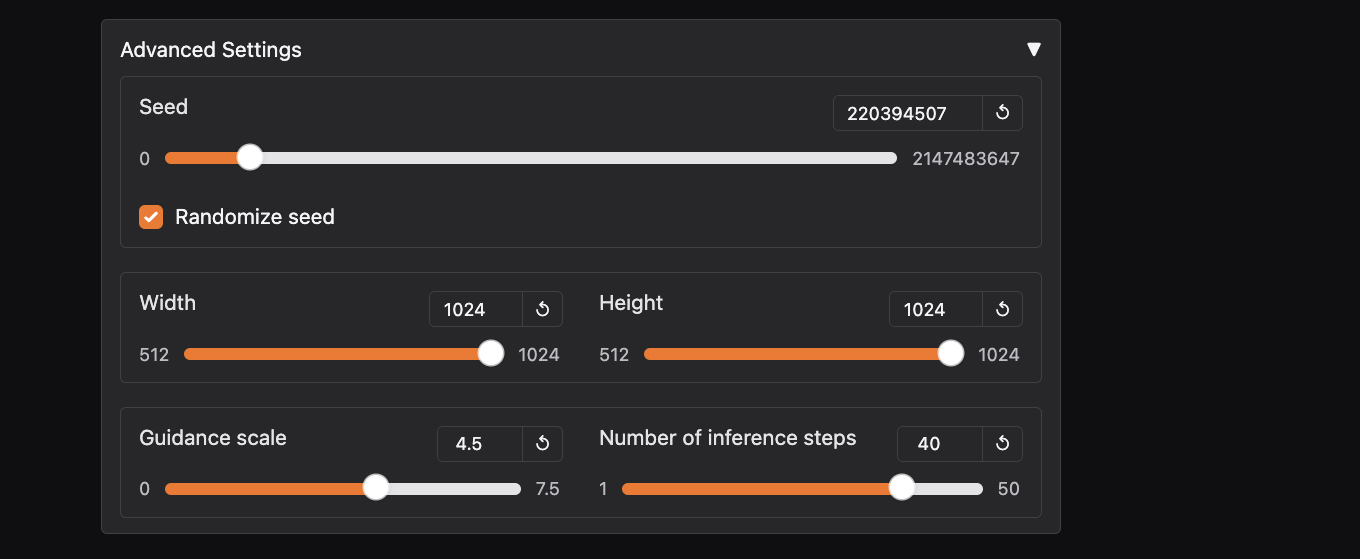
Step 5: Use CFG Scale & Steps
A higher CFG Scale (7–12) ensures the AI follows prompts strictly, while more steps refine details.
Step 6: Generate & refine
Run the prompt, check for unwanted elements, and tweak the negative prompt as needed. Here’s what the final output looks like:
💡 Pro Tip: If artifacts or unwanted details persist, experiment with negative embeddings (like EasyNegative) to fine-tune results.
Using negative prompts in Midjourney
Midjourney has a simpler approach but still allows negative prompts for better control.
⚒️ Steps to use negative prompts in Midjourney:
- Type your main prompt: Start in Discord by using /imagine followed by your descriptive prompt
- Add a negative prompt: Use –no followed by the terms you want to remove (e.g., “–no text, watermark, extra limbs, blurry, dark shadows”)
- Adjust aspect ratio & quality: Use –ar for aspect ratio and –q for image quality to fine-tune results
- Experiment with versions & styles: Midjourney’s different versions (V5, V6, etc.) handle prompts differently, so switch versions if needed
- Upscale & refine: If unwanted elements still appear, rerun with updated negative prompts or use Variations to tweak the composition
💡 Pro Tip: MidJourney reacts differently to prompts than Stable Diffusion. If results feel off, tweak both positive and negative prompts for balance. Explore top MidJourney prompt examples here.
Using negative prompts in DALL·E
When using DALL·E, you can refine your outputs by adjusting how you structure your prompts.
⚒️ Steps to use negative prompts in DALL·E:
- Rewrite your prompt to exclude undesired elements: Instead of “A futuristic city with people,” try “A futuristic city, empty streets, no people, clean architecture”
- Specify desired attributes explicitly: If DALL·E tends to generate something unwanted (e.g., blurry images), emphasize words like “sharp, high detail, professional lighting”
- Use contrastive descriptions: Instead of saying, “No dark colors,” say, “Bright and vibrant colors dominate the scene”
- Refine and iterate: If undesired elements still appear, tweak your prompt wording and regenerate the image for better results
Using negative prompts in ChatGPT
You can guide ChatGPT responses by instructing it on what to avoid in your prompt.
⚒️ Steps to use negative prompts in ChatGPT:
- State what you don’t want: Instead of “Write a summary of climate change,” say “Write a summary of climate change without political opinions or speculation”
- Control tone and style: If you want a neutral explanation, say, “Explain this in simple terms, avoiding complex jargon”
- Use explicit exclusions: If ChatGPT provides too much detail, request “Keep it under 100 words, avoid unnecessary background information”
- Refine with follow-ups: If ChatGPT includes something unwanted, you can say, “Rewrite this, but remove any personal opinions or dramatic language”
Using negative prompts in Claude AI
Claude AI, like ChatGPT, responds well to structured instructions that tell it what to avoid in its responses.
⚒️ Steps to use negative prompts in Claude AI:
- Be direct in your prompt: Instead of “Explain blockchain,” say, “Explain blockchain in simple terms, avoiding deep technical details”
- Specify undesired elements: If you want a focused response, say, “Summarize this article but exclude opinions and repetitive details”
- Limit response length: Ask for “a concise summary under 200 words, avoiding unnecessary background context”
- Iterate based on results: If Claude includes something you don’t want, refine with a follow-up like “That’s too technical—rewrite it in layman’s terms”
➡️ Also Read: Best Prompt Engineering Tools for Generative AI
Limitations of Using AI Tools with Negative Prompts
Negative prompts help refine AI-generated content, but they aren’t perfect. AI models still misinterpret inputs, struggle with certain details, and may ignore prompts altogether. Here are some key limitations of usual AI art and text generators to keep in mind:
- AI may still generate unwanted elements: Some terms get ignored, especially in complex prompts
- Overuse of negative prompts can make images flat: Removing too many details can strip depth and realism
- Different AI models interpret prompts differently: What works in Stable Diffusion may not work in Midjourney, so you may want to test different AI negative prompt examples with various models
- Negative prompts can reduce creativity: Too many restrictions may limit unique and artistic outputs
- Limited effectiveness for highly specific details: AI might still generate artifacts or inconsistencies
- Performance varies by model version: Some AI updates may handle negative prompts better than others
ClickUp as the Alternative AI Tool
AI-generated art tools like Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL·E and text-generating AI tools like Claude AI and Chat GPT focus on generating images and text but lack organization, collaboration, and workflow management.
ClickUp stands out in this area.
ClickUp Brain and ClickUp Whiteboards provide an AI-powered workspace that helps artists and prompt engineers streamline their creative process, refine prompts, and collaborate efficiently.
ClickUp fills the gap by:
- Improving prompt refinement: AI-assisted writing helps fine-tune negative prompts for better AI results
- Organizing assets and versions: Keep track of successful, failed, and experimental AI generations in a structured way
- Boosting team collaboration: Ideal for freelancers and creative teams working on multiple AI projects simultaneously
ClickUp Brain: AI-powered project and content management
ClickUp Brain is an AI assistant integrated within ClickUp, designed to enhance project management, brainstorming, and content creation. For AI creators, this tool simplifies storing, refining, and optimizing prompts to improve the efficiency of the generative process.
With ClickUp Brain, you can:
- Organize AI prompts: Instead of losing track of effective prompts, ClickUp Brain helps store, categorize, and retrieve them for future use
- Generate structured negative prompts: AI can suggest optimized negative prompt phrases to eliminate unwanted elements in generated images and text
- Summarize and refine ideas: Creators can break down AI workflows into clear steps, making it easier to iterate and refine content
Suppose you have a working AI prompt that occasionally produces extra limbs or distorted faces. ClickUp Brain suggests optimized negative prompts based on previous results, helping you refine the prompt into something more precise without excessive trial and error.
ClickUp Whiteboards: Visual planning for AI art projects
AI-generated art often requires experimentation with different styles, references, and iterations. ClickUp Whiteboards act as a visual planning tool, helping artists track their creative process, test results, and project workflows in one place.
With ClickUp Whiteboards, you can:
- Map out artistic styles and references: Use a visual layout to organize different artistic influences, themes, and styles
- Track prompt testing results: Compare AI-generated images, take notes on what works, and fine-tune future prompts accordingly
- Collaborate on AI projects: Share ideas with teams, clients, or fellow artists without losing track of revisions or feedback
💡 Pro Tip: Instead of manually keeping track of failed prompts and successful variations, use ClickUp Whiteboards to create interactive boards for version control. This eliminates the need for messy folders and documents scattered across different tools.
Manage AI Content Projects with ClickUp
Negative prompts are powerful tools for refining AI-generated images and text, whether you’re aiming for realistic portraits, short-form copy, formal reports, or stylized artwork. By strategically removing unwanted elements, you can save time, reduce errors, and gain more control over your creative outputs.
However, crafting the perfect negative prompt requires experimentation and refinement, so don’t be afraid to test and tweak your approach. Use the AI negative prompt examples we’ve shared as a reference to experiment further.
For those managing multiple AI projects, ClickUp Brain and ClickUp Whiteboards help streamline prompt tracking, brainstorming, and creative workflows. Whether you’re an AI artist, marketer, designer, or prompt engineer, ClickUp makes managing your AI-driven projects effortless.
Get started with ClickUp to supercharge your workflow. Try ClickUp for free!