

You must have heard of the adage ‘time is money.’ While this saying applies to almost all aspects of work and life, it rings very close to the truth in project management. It is either time or quality that defines the project’s monetary value.
Managing components of a project management triangle with overlaps of scope, time, and cost is a delicate balancing act. It requires conscious utilization of time and resources to deliver optimum value that matches expectations. At the heart of all this orchestration of deadlines and deliverables lies a schedule—the backbone of success.
A schedule is a meticulously crafted roadmap that directs activities from inception to project planning and execution. However, a project journey is complicated. Seasoned project managers employ schedule variance to handle such twists and turns.
Here is everything you need to know about it—from the schedule variance formula to how to apply it in real-world projects.
What is Schedule Variance?
We all know what a schedule means. It is a timeline that you wish to follow while achieving a set goal, which is the expected schedule.
However, unexpected events may cause you to veer off this charted course when executing the project. Your actual schedule will include these detours.
Schedule Variance (SV) measures the difference between the baseline schedule and the actual progress. It is a key performance indicator that denotes whether a project is ahead of schedule, on track, or behind schedule at a specific time.
Understanding Schedule Variance
There are two underlying elements of a rudimentary schedule variance formula. These are:
- Earned Value (EV): It denotes the actual budget used. To get the EV, multiply the total project budget by the percentage of the work completed so far. It is a window into the project’s schedule and performance
- Planned Value (PV): It depicts the project’s expected budget utilization by a specific date. It is calculated by multiplying the total project budget by the percentage of the work to be completed by that time. It helps assess whether the project is on time in terms of expected progress and whether resource leveling is required
Having an idea of these variables helps calculate schedule variance by applying the following formula:
SV = EV – PV
Where,
- SV = Schedule Variance
- EV = Earned Value
- PV = Planned Value
Some alternatives for calculating schedule variance use the following formula:
SV = BCWP – BCWS
Where,
- BCWP = Budgeted Cost of Work Performed
- BCWS = Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled
Once you get the value for schedule variance, you can interpret it in the following ways:
- SV > 0: Positive schedule variance means a project is ahead of its schedule, which means the project progress is better than what was planned
- SV = 0: No variation means that the project is on schedule and the actual progress aligns with the planned progress
- SV < 0: Negative schedule variance means the project is behind schedule. It indicates that the actual project progress is less than what was planned
Schedule Variance Percentage (SV%) shows the variance’s percentage value and offers an easier way to track a project.
SV% = (SV/PV)*100
Like schedule variance, a negative SV% indicates a project lagging, while a positive SV% suggests it is ahead of schedule.
Using this basic schedule variance formula, you can calculate other project management KPIs to track the project schedule and progress.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is the ratio of earned value to planned value. This performance indicator measures the efficiency of time utilization in a project.
SPI = EV/PV
Once you calculate the complete schedule performance index, you can interpret it as below:
- SPI > 1: The project is ahead of schedule
- SPI = 1: The project is on schedule
- SPI < 1: The project is behind schedule
When there’s number crunching involved, use project management software to run the numbers.
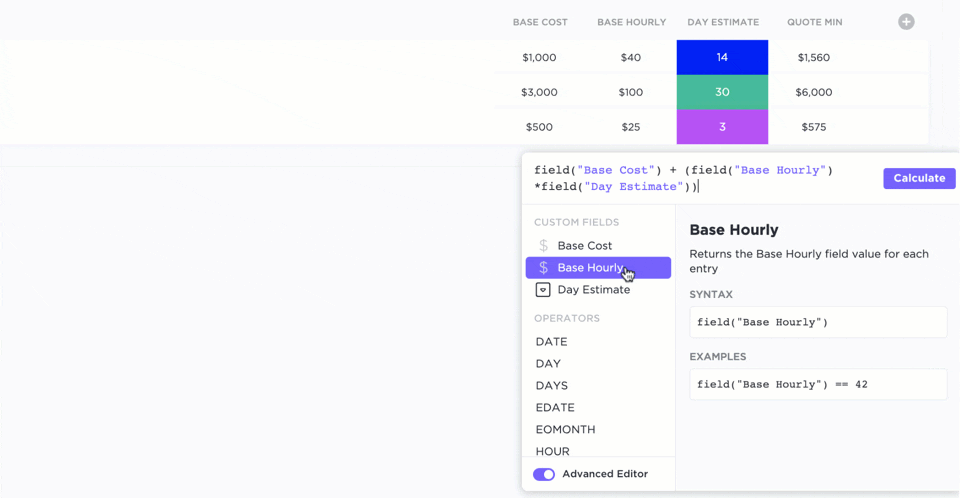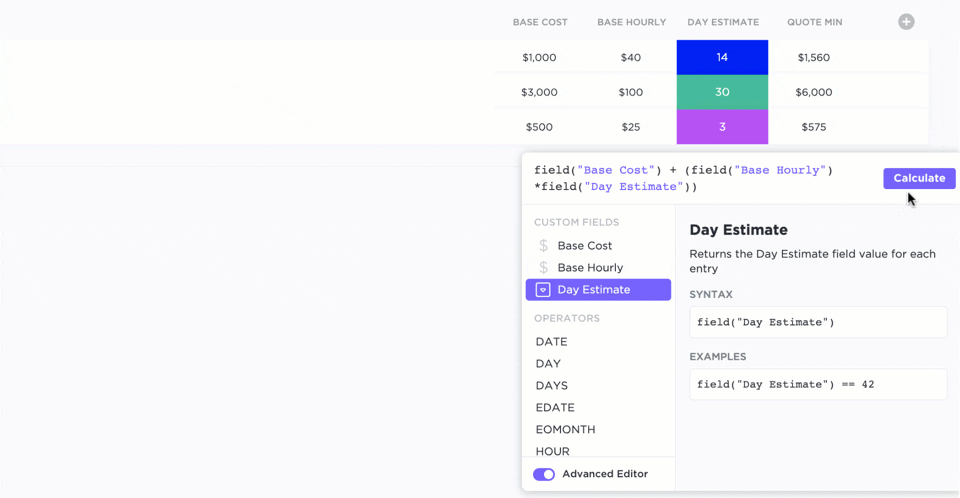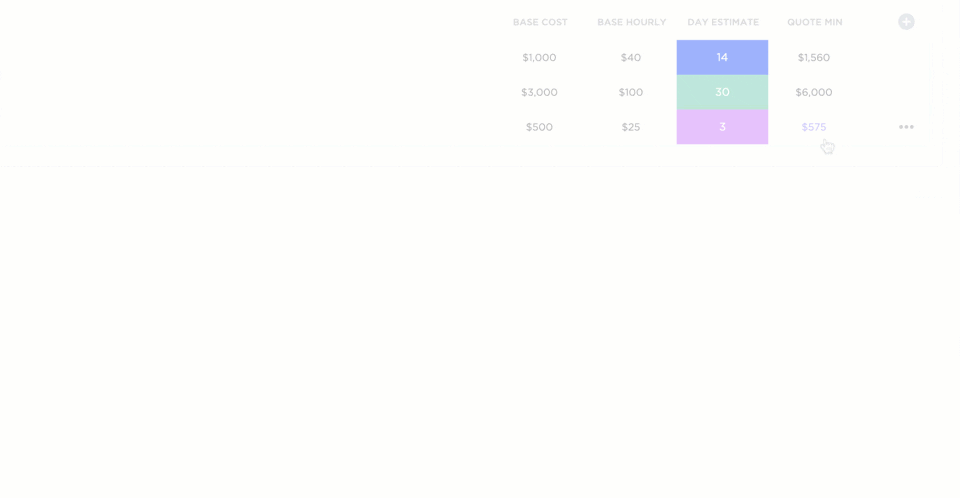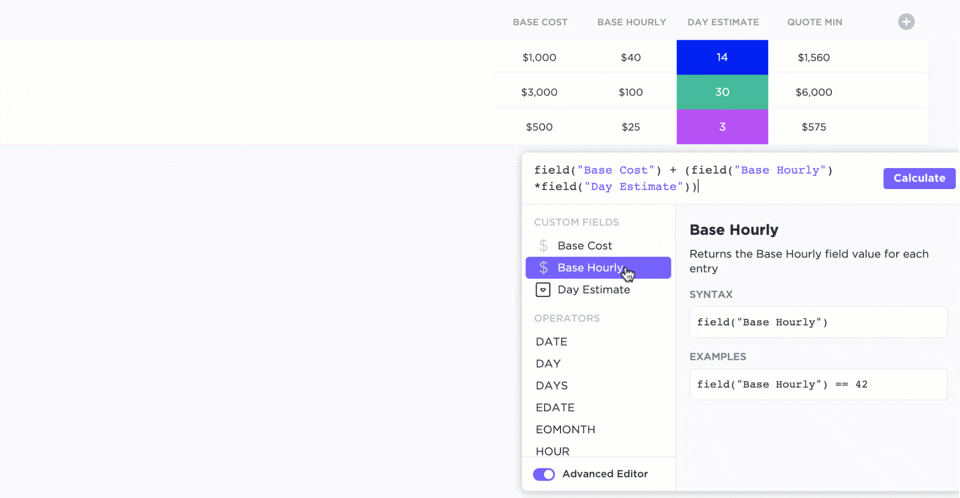
Tools like ClickUp offer configurable formula fields to simplify project-related calculations. By eliminating unnecessary heavy-duty computations without compromising accuracy, you can focus on project management.
Connection Between Schedule Variance and Earned Value Management
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a project management methodology that combines project cost, schedule, and performance data to get a complete idea of the project’s progress.
Schedule variance (SV) is one underlying component of this broader framework. It is the difference between the planned value (PV) and earned value (EV).
Any variance in schedule represents the corresponding cost variance in the work planned to be done by a certain point. It is a complete schedule performance indicator, as any variation in this value may indicate whether a project is behind schedule, ahead of it, or on time.
The SV metric, combined with other KPIs such as cost performance index, remaining project time, project budget, etc., acts as a comprehensive toolset to analyze project health, manage project schedule, and balance resources throughout its lifecycle.
Importance of Calculating Schedule Variances
Schedule variance calculations highlight different variables impacting the project’s progress. Staying alert to these risks and opportunities allows project managers to intervene to meet deadlines. However, there’s more to it than assisting with project time management.
Here’s a list of reasons project managers must calculate schedule variance:
Performance assessment
Metrics like schedule variance and other performance indicators help with project efficiency ratings. They provide a clear and realistic assessment of project performance as a function of its schedule. For instance, a positive value for SV means that the project is ahead of its estimated schedule and vice versa.
The quantification of project health allows project managers to benchmark performance and take the necessary actions to ensure progress and minimize risks. It also enables project managers to identify areas where the project is excelling or falling short so that they can make informed decisions to keep the project on track and enhance its performance.
Problem identification
Schedule variance embodies proactive vigilance. By calculating actual progress and measuring it against planned progress, project managers can use it to detect potential project management challenges.
Even the slightest of deviations in the schedule acts as an early warning system, signaling potential problems or issues with a specific task or phase within a project.
Use these indicators to mitigate risks, implement corrective measures, and reallocate resources strategically. The early-stage intervention prevents problems from cascading and fosters a more resilient and successful project environment.
Effective decision-making
Calculating schedule variance is instrumental in facilitating effective decision-making while managing projects. By comparing project progress, project managers can understand whether a project is ahead of schedule.
Using such insights, they can judiciously decide how to schedule activities, allocate resources, adjust timelines, involve stakeholders, or implement corrective measures.
For example, the project management professional may redirect resources to teams with negative schedule variance from those delivering positive outcomes. Such tweaks enhance the overall project performance through strategic decision-making for successful project delivery.
Stakeholder communication

Project managers can utilize schedule variance to get a realistic idea of the project schedule. Once apprised of the facts, they can convey the project’s present status to the stakeholders. Staying ahead of schedule will instill confidence and satisfaction among the stakeholders.
On the other hand, proactively disclosing any potential delays or setbacks in the agreed-upon schedule will promote transparency and accountability. In case of any setbacks or delays, project managers can also meaningfully engage stakeholders to recalibrate project expectations regarding scope, deliverables, and timelines. They can also raise requisitions for additional resources for successful project completion if required.
Resource optimization
As we’ve broadly discussed, a project’s schedule variance can help with effective resource management. Projects ahead of schedule may feature underutilized resources that may add to the project cost. These remaining resources can also be reallocated to other projects or critical areas to expedite project development.
On the other hand, when a project is behind schedule, it may be due to resource restraints or inefficiencies. In this case, the project manager may optimize resource allocation to address bottlenecks promptly.
Schedule variance ties up directly with cost variance, as resources typically comprise the largest component of any project cost. Unsurprisingly, an alternative to schedule variance features the difference between actual and scheduled costs (BCWP—BCWS)!
Risk management
We’ve seen how schedule variance links directly to cost variance, which, in turn, highlights the importance of managing project cost risks. Similarly, we’ve also seen how schedule variance enables project managers to detect potential issues early and nip the problem in the bud. However, risk doesn’t always show up in the form of delays.
Accelerated timelines where parts of a project may be ahead of schedule can also pose a risk, specifically when dependencies are involved—and schedule variance can help address these.
With such tangible benefits, the role of schedule variance in detecting and managing risk becomes evident. Anticipating possible risks allows project managers to implement effective risk management and mitigation strategies.
Continuous improvement
Project managers can use variance analysis to gain visibility into the different trends, patterns, and insights that emerge as the project progresses. For example, positive schedule variance reveals effective practices that they can replicate. In contrast, negative schedule variance highlights inefficiencies.
Such systematic evaluation allows them to learn from their experience and refine project planning processes and best management practices in future endeavors. It evaluates the project manager’s capabilities and assesses the performance of the project team. Regular performance variance analyses will iteratively refine project outcomes.
Real-World Examples of Schedule Variance
Let’s use real-world examples to illustrate how to run schedule variance calculations.
Example #1: Construction project
Suppose you are managing a construction project with a total budget of $1,000,000. The project is scheduled to be completed within the next 12 months.
You calculate schedule variance after six months. To do this, you must first calculate the planned and earned values.
- Planned Value: This is the budgeted cost of the work planned to be performed by the six-month mark. For the sake of simplicity, we’ll assume that 50% of the work should have been completed by month six. Using this data, calculate the PV as:
- PV = 50% ✕ $1,000,000 = $500,000
- Earned Value: This is the actual cost of work done so far. Assume that only 40% of the work has been completed by the sixth month. With this, you can calculate the EV as follows:
- EV = 40% ✕ $1,000,000 = $400,000
Now, let’s calculate the Schedule Variance:
SV = EV – PV
SV = $400,000 – $500,000
SV = -$100,000
The negative value denotes that the project is behind schedule after six months. Project managers will take note of this and execute corrective actions to bring the project back on track.
Example #2: Software development project
Suppose your team is developing a software application within eight months. You have a budget value of $600,000 to complete the task.
You decide to evaluate the project schedule variance after two months. Once again, start by calculating the planned and earned values.
- Planned Value: Typically, you should have completed 25% of the work by the second month. Based on this, the value would be:
- PV = 25% ✕ $600,000 = $150,000
- Earned Value: Due to the efficient performance of the project team, you complete 40% of the planned work by the second month. Accordingly, it would be:
- EV = 40% ✕ $600,000 = $240,000
Now, let’s calculate the Schedule Variance:
SV = EV – PV
SV = $240,000 – $150,000
SV = $90,000
The positive variance indicates that the project is ahead of schedule by $90,000 in the second month. Based on this performance, managers can reallocate resources and expedite interlinked tasks to stick to the project timeline.
The above examples are relatively straightforward and simplistic. They work with the assumption that projects flow linearly. However, real-world projects are slightly more complex, with several interdependencies that can delay or accelerate project timelines. Use advanced digital tools like ClickUp for Project Management to get a complete view of the project and its interdependencies.
While ClickUp is a comprehensive project management platform that does not strictly perform schedule variance or earned value management calculations, you can leverage it to track and manage schedules. We’ll be talking about it at length in the subsequent sections.
Top Tips for Working With Project Schedule Variance
Now that you understand what constitutes schedule variance and its different aspects let’s look at how to use it to improve efficiency and stay on schedule. Here are a few tips and tricks to help:
- Calculate schedule variance value periodically. Track this value throughout the project lifecycle, from the project planning process to completion, for early detection of deviations and corresponding timely interventions
- Rather than viewing SV values in a vacuum, compare them to other metrics like cost variance, schedule performance index, work completed, etc., to gain a holistic idea of the project performance
- Establish predetermined values for SV threshold and tolerances to quickly identify when the variance exceeds the acceptable limits to trigger prompt action
- While corrective action is vital, you must also perform root-cause analysis to identify what caused the variance in the first place. Understanding this aspect helps prevent similar occurrences in the future
- Exploit SV data for scenario planning. Exploring the different ‘what-if’ scenarios sheds light on the potential impact of change in resource allocation or project scope to understand the interplay of different project triangle elements
- Pay close attention to the tasks involved in the critical path of a project, as any changes to these will affect the project outcomes and timelines
- Leverage automation tools to automate the calculation and benchmarking of SV values to track and analyze them more effectively
- Compare SV values against historical data and map them against industry standards to gain a relative perspective of the project’s performance
- Use customizable project schedule templates to manage project timelines and schedules while keeping an eye on dependencies
Stay On Track With ClickUp
As mentioned, ClickUp is conventionally not an EVM platform. However, ClickUp offers Custom Project Management, which can be appropriately modified to meet this objective.
You can use ClickUp for schedule variance tracking and management in the following ways:
- Create, assign, and track tasks to project team members. Set due dates for these tasks to ensure that they keep to schedule. By tracking the work completed and progress percentages, you can manually calculate EV, PV, and SV or export data sets onto spreadsheet tools like Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel for in-depth analysis

- If manual calculation is too complicated, input these values into custom formula fields and directly get the computations. Accessing such a feature right on the platform itself prevents context switching and keeps you hyper-focused
- Integrate with time-tracking tools to capture data about the time spent on a task and the effort involved. Even though it does not directly affect EV, it can help with effective resource management and provide data for task completion assessments, which indirectly features in variance management
- Set up automated workflows that trigger when SV values touch critical levels. From optimizing resources to conducting detailed analyses of the root cause, ClickUp can help you orchestrate the next course of action
Add collaboration to the blend of such desirable features, and ClickUp emerges as the best scheduling app that minimizes variations. Sign up to know more.
FAQs
1. How is schedule variance calculated in project management?
Schedule Variance (SV) is calculated using the formula: SV = EV – PV
Here, EV is the earned value (value of the work performed), and PV is the planned value (the value of the work to be done). It offers a quantitative measure of the variance between the planned and actual progress regarding the schedule.
2. What does it mean if schedule variance is negative?
A negative SV indicates that the project is behind schedule, and it is time to investigate and find the root cause of the delay. The next step is to take corrective action.
3. What does it mean if schedule variance is positive?
A positive SV stands for a project that is ahead of its schedule. In this case, you can look at all the factors that contributed to the positive outcome and emulate this for other projects in the future.
4. How can project managers efficiently monitor schedule variance?
Project managers can efficiently monitor schedule variance using a project management tool in the following ways:
- Regularly updating task progress and completion
- Leveraging built-in reporting and analytics features
- Defining thresholds or tolerances for SV values to display notifications or alerts
- Setting up trigger-based risk management plans to minimize variances
- Conducting a regular review of cumulative schedule variance trends
5. What is the importance of schedule variance in project management?
Schedule variance quantitatively assesses how well a project adheres to its prescribed timeline. Upon conducting such an assessment, project managers can use it for:
- Gauging project performance and health
- Making informed decisions based on actual work completed
- Identifying areas where a project excels or falls short
- Implementing reparative measures to keep the project on track
- Communicating with internal and external stakeholders regarding the project status
6. How can schedule variance assist in project risk management strategy?
Schedule variance can assist in project risk management in the following ways:
- Helps with early detection of potential risks or delays for prompt problem resolution
- Performs comprehensive root-cause analysis to probe into the primary cause behind the deviation
- Reinforces contingency planning as insights related to schedule variances can trigger proactive resource optimization, risk management, etc.
- Simulates different scenarios and conditions to help assess the impact of other variables and potential risks on the project schedule



