While Google Sheets is an excellent free tool for managing work data, its true power lies in its formulas.
Google Sheet formulas automate calculations, improve accuracy, and basically get the most out of the platform. So save this article, as we’ve curated a list of essential formulas to help you work faster and more efficiently.
We’ll look at Google Sheets formulas that are not just for advanced users but accessible to everyone, regardless of expertise level.
What Is a Google Sheets Formula?
Google Sheets is a cloud-based spreadsheet tool with features similar to Microsoft Excel or other tools that allow you to create, edit, and share your data, especially numerical information or charts.
Google Sheets formulas are sets of instructions used to perform calculations, manipulate data, or generate specific results based on the values in your spreadsheet. They include various elements, including functions, cell references, operators, and constants.
By entering a formula into a cell, you instruct the Google Sheets database to perform a specific calculation and display the result in the cell.
Formulas in Google Sheets are similar to those in Microsoft Excel, starting with an equal sign (=), followed by a function name and a range of cells to apply the function. These formulas can be as simple as adding two numbers or as complex as performing advanced statistical analyses.
Benefits of Using Formulas in Google Sheets
For simple mathematical calculations, entering new formulas may be an overkill. But when you have to analyze all the values in a cell range or perform complex calculations, using the Google Sheets formulas helps you save time and increase productivity.
It provides several advantages, such as:
- Automation: Formulas automate repetitive calculations and tasks, so you don’t have to recalculate each time there is a change in value. For an automation example, let’s consider that instead of manually summing up columns or calculating averages, you use formulas SUM() or AVERAGE() to get instant and accurate results
- Improve accuracy: Calculating numbers manually can always result in errors. However, Google Sheet formulas ensure that the answer is accurate, making it ideal for financial reports, statistical analysis, or other complex reporting
- Gain insights: Not all formulas are focused only on calculations. Some, like VLOOKUP(), INDEX(), and MATCH(), help you analyze large datasets, compare information across different sheets, and extract specific data points
- Flexibility: Formulas are easily adapted to changing data or requirements. Whether you need to create complex financial models, generate custom reports, or perform specialized calculations, there’s likely a formula—or a combination of formulas—to help you achieve your goals
- Teamwork: Google Sheet formulas ensure that your teams don’t unknowingly introduce errors in your final calculations. Just apply a formula to a shared sheet, and team members can add their data and get the required answers instantly or replicate the same formula in one or more columns if needed. This helps particularly for ongoing projects or reports that need real-time updates.
How to Use Google Sheets Formulas
We’ll now show you how to use Google Sheets formulas in a few simple steps:
Start with an equal sign (=)

To create formulas in Google Sheets, type an equal sign (=) in the cell where you want the result to appear. This signals Google Sheets that you are about to enter a formula.
Enter the function name

After the equal sign, type the name of the function you want to use. Google Sheets will offer suggestions as you type, making it easier to find the function you need. For example, to sum up a range of cells, you would use the SUM function.
Specify the cell range

Next, specify the range of cells you want the formula to act upon. Type the cell reference and column number (e.g., A1:A10) manually, or click and drag to select the cell address.
Close the formula

Most formulas require you to close the parentheses after specifying the cell range or any additional arguments. The complete sum function would be =SUM(A1:A10), ending with the brackets.
Press enter
Once you’ve entered the formula, press Enter, and the formula calculates and displays the result in the selected cell.
The best part about Google Sheets formulas is that you don’t have to use a single formula per cell. Combine multiple functions within a single formula. For example, use =SUM(A1:A10) * AVERAGE(B1:B10) to multiply the sum of one range by the average of another.
Top 30 Google Sheets Formulas for Different Use Cases
Google Sheets offers many formulas to simplify your mathematical calculations. Here are 30 of the most commonly used Google Sheets formulas:
Basic calculations
Here are the basic mathematical Google Sheets formulas that you should know:
| Function formulae | What they do | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SUM() | The SUM() function allows you to add up a range of numbers, making it perfect for quick totals, whether you’re managing a budget or adding up sales figures. | SUM(value1, [value2, …]) |
| AVERAGE() | The AVERAGE() function calculates the mean of a range of numbers. This formula is useful for finding average values in data sets, such as the average test score or the average sales per week. | AVERAGE(value1, [value2, …]) |
| COUNT() | The COUNT() function calculates the number of numeric values in a range. This is particularly handy when you need to know how many entries exist in a list, such as the number of items sold or the number of times a certain value appears. | COUNT(value1, [value2, …]) |
| COUNTA() | The COUNTA() function counts the number of non-empty cells in a range, regardless of the data type. Use this formula when you need to count cells that contain text, numbers, or any other data. | COUNTA(value1, [value2, …]) |
| MAX() | The MAX function returns the largest number or maximum value from a given range of values. | MAX(value1, [value2, …]) |
| MIN() | The MIN function returns the smallest number or minimum value from a specified range. | MIN(value1, [value2, …]) |
Logical functions
Next come logical Google Sheets formulas, such as:
| Function formulae | What they do | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| IF() | The IF() function is a logical formula that returns one value if a logical expression is true and another if it is false. This formula is incredibly versatile and can be used for several decision-making tasks in your spreadsheet. | IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]) |
| AND() | The AND function evaluates multiple conditions and returns TRUE if all conditions are true; otherwise, it returns FALSE. | AND(logical1, [logical2, …]) |
| OR() | The OR function checks multiple conditions and returns TRUE if at least one condition is true and returns FALSE if all conditions are false. | OR(logical1, [logical2, …]) |
| NOT() | The NOT function returns the opposite of a logical value. If the input is TRUE, it returns FALSE, and vice versa. This is useful when you need to reverse a condition. | NOT(logical) |
Text function or manipulation
Google Sheets formulas are not just for numerical values but also text functions and cell manipulations like:
| Function Formulae | What they do | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| CONCATENATE() | The CONCATENATE() function joins multiple text strings together into one. This Google Sheets formula is perfect for combining first and last names, addresses, or any other text data that needs to be merged into a single cell. | CONCATENATE(string1, [string2, …]) |
| LEFT() | The LEFT() function extracts a specified several characters from the beginning of a text string. This is useful for removing a portion of text, such as the first few letters of a product code. | LEFT(text, [number_of_characters]) |
| RIGHT() | The RIGHT() function is similar to LEFT(), but it extracts characters from the end of a text string. Use this formula when you need to isolate the last few digits of a number or code. | RIGHT(text, [number_of_characters]) |
| MID() | The MID() function extracts a specific number of characters from the middle of a text string. This Google Sheets formula extracts a substring from within a longer text string, such as the middle part of an ID number. | MID(text, start_position, number_of_characters) |
| TRIM() | The TRIM() function removes any extra spaces from a text string, leaving only single spaces between words. This formula is great for cleaning up text data with irregular spacing. | TRIM(text) |
| SPLIT() | The SPLIT() function divides a text string into separate parts based on a specified delimiter. This formula is ideal for breaking up data like addresses or names into different columns. | SPLIT(text, delimiter, [split_by_each], [remove_empty_text]) |
| REPLACE() | The REPLACE() function replaces part of a text string with another text string based on the position you specify. This formula updates codes, names, or any other data where a part of the text needs to be changed. | REPLACE(old_text, start_position, number_of_characters, new_text) |
| SUBSTITUTE() | Similar to REPLACE(), the SUBSTITUTE() function replaces all instances of a specific text string with another. This corrects any errors and standardizes text in large datasets. | SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, [instance_number]) |
| UPPER() | The UPPER() function converts all characters in a text string to uppercase. Use this formula to standardize text to uppercase, such as for codes or identifiers. | UPPER(text) |
| LOWER() | The LOWER() function converts all characters in a text string to lowercase. This formula is useful to standardize text to lowercase, such as for email addresses or usernames. | LOWER(text) |
| PROPER() | The PROPER() function converts the first letter of each word in a text string to uppercase, with all other letters in lowercase. This function is perfect for formatting names, titles, or addresses consistently. | PROPER(text) |
| ROUND() | The ROUND() function rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places. This formula is essential for financial calculations or the precision of your data. | ROUND(number, [number_of_digits]) |
| TEXT() | The TEXT() function allows you to format numbers, dates, and times as text, applying custom formats. For example, use TEXT() to display dates in a specific format or to add currency symbols to numbers. | TEXT(value, format) |
Data manipulation functions
Some Google Sheets formulas also sort and filter a spreadsheet, such as:
| Function Formulae | What they do | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| VLOOKUP() | The VLOOKUP() function, or vertical lookup, searches for a value in the first column of a range and returns a value in the same row from another column. This formula is ideal for searching information in a table or database. | VLOOKUP(search_key, range, index, [is_sorted]) |
| HLOOKUP() | Similar to VLOOKUP(), the HLOOKUP() function or horizontal lookup searches for a value in the first row and returns a value from a specified row within the same column. Use this formula when your data is organized horizontally rather than vertically. | HLOOKUP(search_key, range, index, [is_sorted]) |
| INDEX() | The INDEX() function returns the value of a cell in a given range based on the row and column numbers you specify. This formula retrieves specific data points from a large dataset, especially in the first column. | INDEX(reference, row, [column]) |
| MATCH() | The MATCH() function searches for a specified item in a range and returns its relative position. Often used with INDEX(), this formula is great for finding the location of specific data within a range. | MATCH(search_key, range, [search_type]) |
Date and time functions
Google Sheets formulas can also perform advanced numerical or respond with the current date and time values, like:
| Function Formulae | What they do | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| TODAY() | The TODAY() function returns the current date (according to your device’s date setting) without the time. It updates automatically every day, which is helpful for tracking deadlines or timestamps. | TODAY() |
| NOW() | The NOW() function returns both the current date and time. It’s useful when you need to log the exact date and time of an event. | NOW() |
| DATE() | The DATE() function allows you to create a specific date by inputting the year, month, and day as arguments. | DATE(year, month, day) |
Limitations of Using Google Sheets Formulas
Google Sheets formulas save time, and there are several Google Sheet hacks to help you get your job done. However, this tool also has several limitations, especially when compared to advanced data management and project automation tools.
Some of these limitations include:
- Performance issues with larger datasets: Google Sheets struggles with handling large datasets, especially when using complex formulas or functions like ARRAYFORMULA(), QUERY(), or IMPORTRANGE(). As the number of rows and formulas increases, you might experience lag, slow loading times, or even crashes
- Collaboration issues: While Google Sheets is known for its real-time collaboration features, it becomes challenging to manage when multiple users are editing the same Google Sheets file. Conflicts can arise if changes are made simultaneously, and tracking these changes is difficult
- Complexity in advanced formulas for beginners: For users unfamiliar with advanced formulas, creating and debugging complex Google Sheets formulas can be daunting. Errors in formula syntax or logic can lead to incorrect data analysis and decision-making
- Overly dependent on internet connectivity: Google Sheets is a cloud-based application, meaning it requires an internet connection to function fully. While you can work offline in some cases, the offline functionality is limited, and syncing issues may arise when you reconnect to the internet
- Lack of advanced visualization: Google Sheets includes basic charting and graphing tools, but these are limiting for advanced data visualization. For example, creating interactive dashboards, sophisticated charts, or complex data visualizations often requires additional tools like Looker, Power BI, or Tableau
Meet ClickUp: The Best Google Sheets Alternative
Google Sheets formulas are undoubtedly incredible for managing and analyzing data. However, Google Sheets has limitations, especially when handling large datasets, complex workflows, and advanced automation needs.
This is where ClickUp steps in as the perfect Google Sheets alternative, offering a range of features to enhance your data management and project tracking.
Let us look at how ClickUp helps overcome the limitations of Google Sheets:
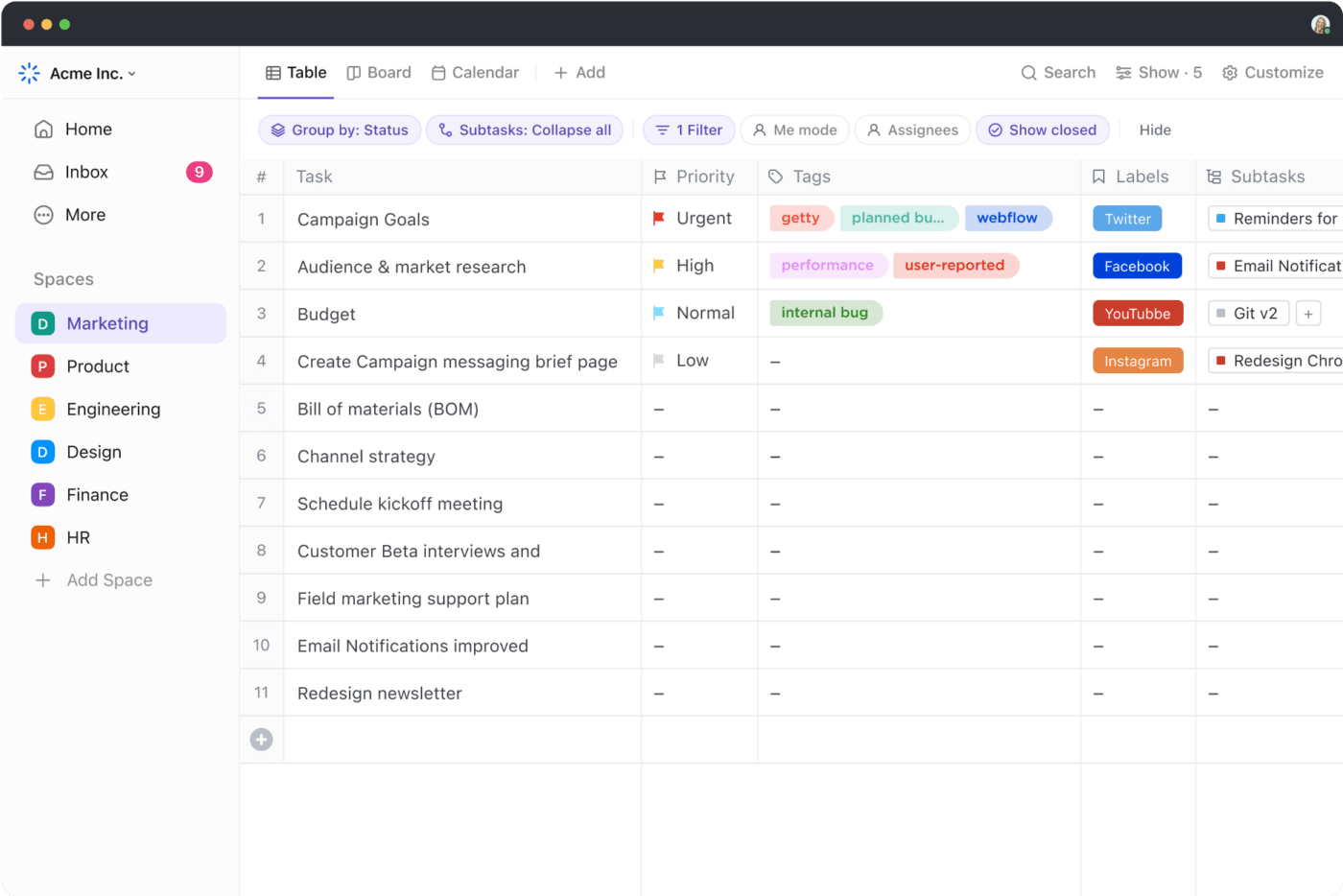
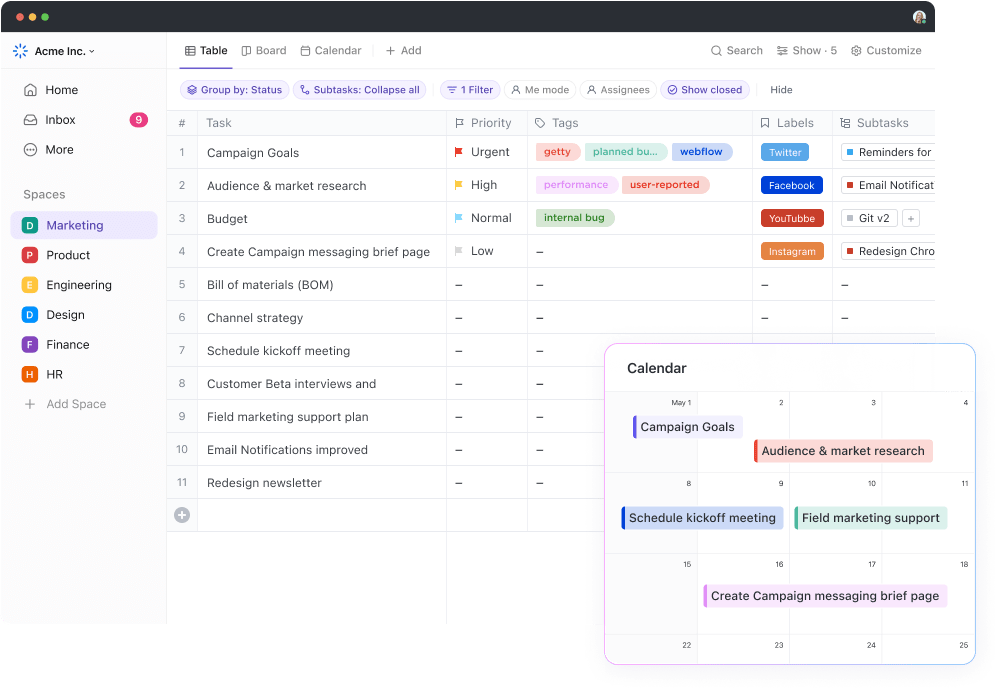
ClickUp Table view
ClickUp Table View is a powerful feature that allows you to organize and view your tasks in a structured, spreadsheet-like format. Focused on ease-of-use and powerful formatting options, it brings excellent features like:
- Intuitive no-code interface: Create and customize tables to fit your specific needs, making it easy to link tasks, documents, and dependencies
- Rich-formatting options: Format cells, rows, and columns with robust filter and grouping options, making it easy to attach files, add links, color-code your fields, and more
- Access controls for sharing files: Share your table view with anyone, be it internal team members or those outside your organization. With access controls, manage people and permissions and create a view-only public link for external sharing, ensuring that your organization’s data is always protected
The best part about ClickUp is the ability to use customizable ClickUp spreadsheet templates to get an organized, easy-to-edit spreadsheet setup with your organizational data.
ClickUp Automations
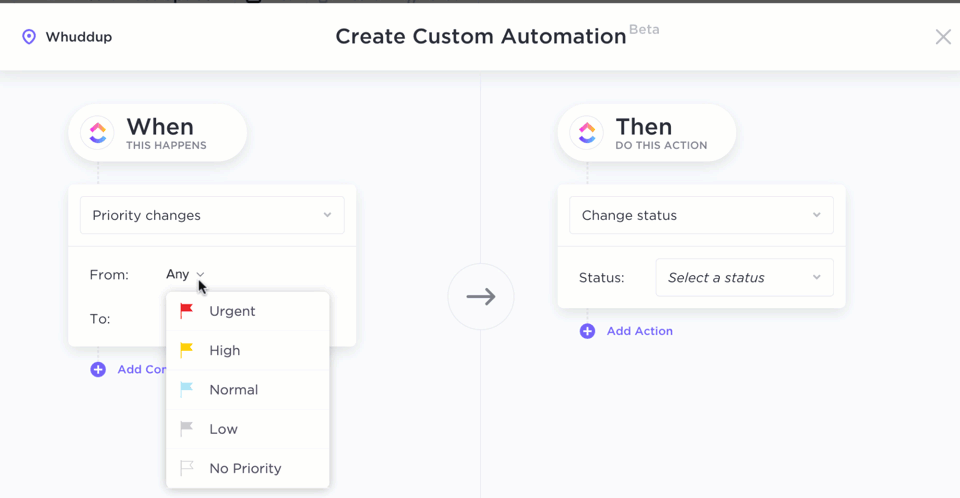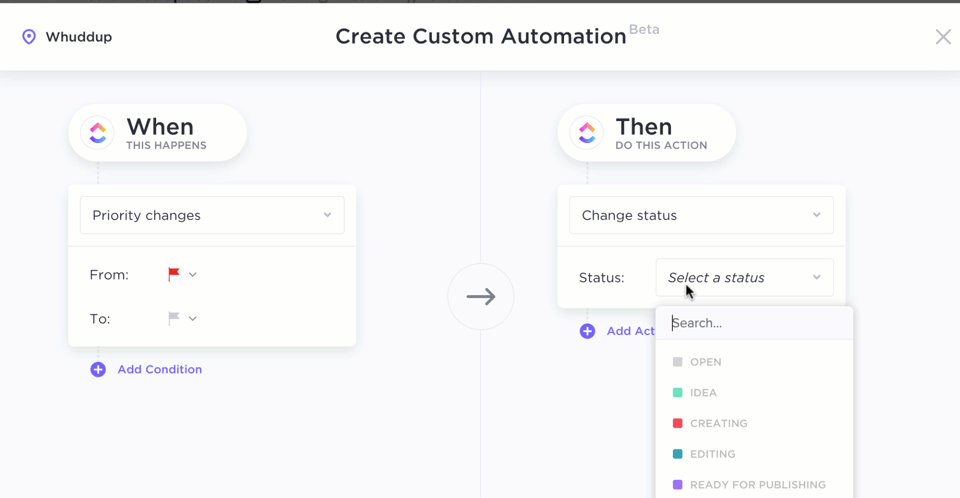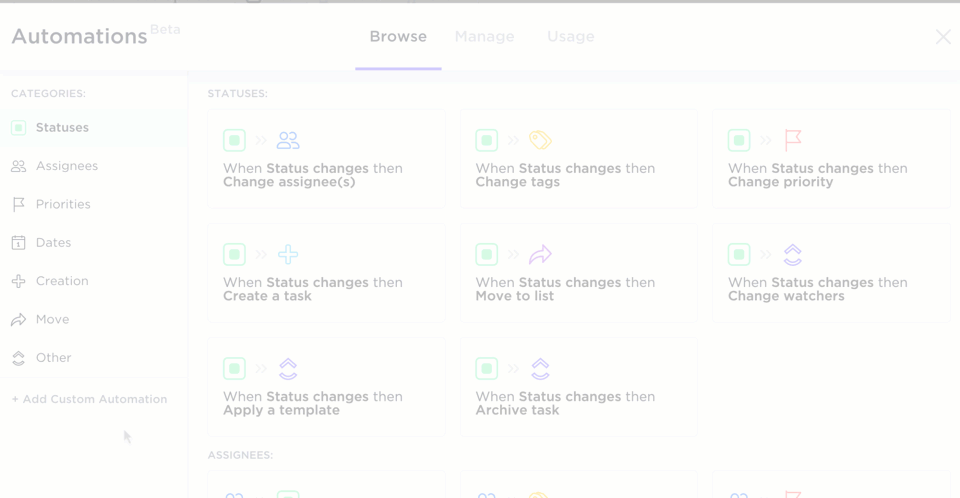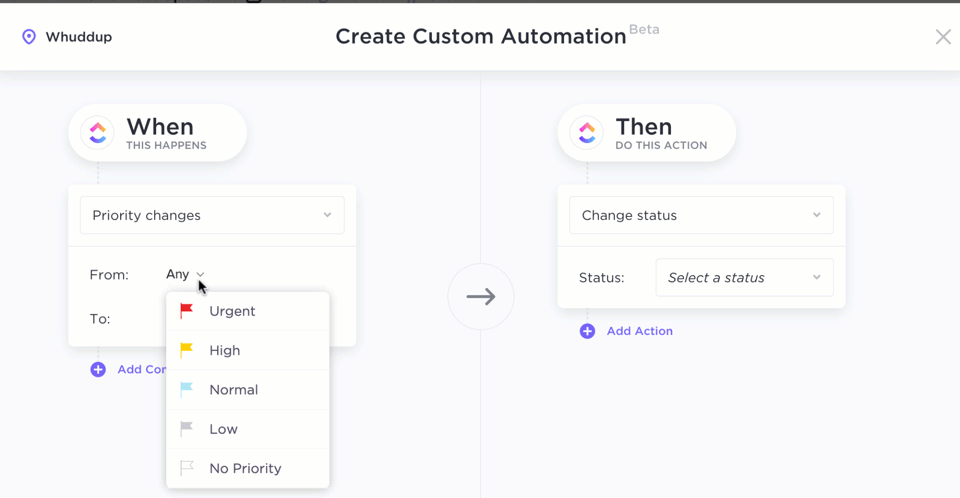
Google Sheets formulas are excellent for organizations working with large and periodically fluctuating data volumes. But ClickUp Automations takes it up a notch.
Using its advanced logic and trigger-based automation builder, you can:
- Create advanced workflows: Instantly build advanced workflows with over 100 pre-built automation options, customized to fit your specific needs
- Build automation with Formula Fields: Use Formula Fields in ClickUp to automate workflows based on specific events or conditions, allowing for more sophisticated data handling and decision-making
- Access advanced functions: Perform various calculations and automate routine tasks with access to over 70 different functions in ClickUp. Whether you’re calculating project costs, tracking hours, or analyzing performance metrics, ClickUp’s robust functionality has you covered.
For more advanced calculations and frameworks, ClickUp’s advanced formulas allow you to sort, filter, and group formulas to simplify complex workflows and automate data functions.
For example, if you want to use formulas to calculate project timelines based on start and due dates or to create conditional logic to trigger actions based on task completion percentages, do this in ClickUp by:
Setting up automation triggers: Determine the conditions under which your formula should be evaluated
Creating a formula field: Add a new Formula Field in your Table View. This field will act as the container for your formula
In our example, you can set up automation triggers this way:
- Calculate due dates based on task priority: Create a formula that calculates the due date for a task based on its priority level
- Automatically assign tasks based on criteria: Use formulas to assign tasks to specific team members based on their skills or availability
By combining the power of ClickUp’s Table View and Automations, create highly customized and efficient workflows that automate complex tasks and provide valuable insights into your data.
ClickUp Brain
ClickUp Brain, the AI-powered assistant, makes it incredibly easy to build workflows and instantly configure automation on a folder, file, or data set. With AI technology, you get:
- Intelligent recommendations: Receive smart recommendations for tasks, projects, and workflows based on your team’s data and patterns
- Natural language interactions: Communicate with the advanced AI assistant using everyday language, simplifying your workflow and eliminating the need for complex commands or formulas, making automations and data management more intuitive and convenient
- Valuable data insights: Use the power of AI to gain deeper insights into your data and identify opportunities for further trigger-based automations, simplifying the entire process of workflow management and decision-making
For instance, to merge two Google Sheets files into one spreadsheet, you will need to use the QUERY, IMPORTRANGE, or Google Sheet add-ons.
With ClickUp, you can use the drag-and-drop automation builder to combine data from multiple sheets or Google Sheets files and even fetch AI summaries, updates, and more.
When it comes to managing your daily tasks, collaborating with your team, and tracking project timelines, ClickUp offers everything you need in one intuitive platform.
Savitree Cheaisang, AVP of Bubblely, mentions why she loves using ClickUp for calculations and data management:
An Easier Way To Use Google Sheets Formulas
While Google Sheets formulas can certainly help you manage and analyze data, there’s an easier and more efficient way to handle your tasks and projects—ClickUp!
It is a powerful collaboration platform that offers a superior alternative to spreadsheets. With its intuitive Table View and powerful automation capabilities, ClickUp helps you get the best of a spreadsheet app while providing the analytical and visualization features of an advanced data management tool.
But that’s just the beginning! ClickUp is also easy to use, allowing you to easily drag and drop tasks, resize columns, and even share your tables with a unique link for seamless collaboration.
Ready to make the switch? Create your Table View in ClickUp for free today and see how much easier data management can be.