RAID Logs for Project Management: Risk-Proof Your Projects

Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
Sorry, there were no results found for “”
A critical component of project management is managing or mitigating risk. Adjusting for risks and contingencies is critical with the multiple variables and moving parts in complex or long-term projects. ⭐
An equally crucial aspect of risk mitigation in project management is documenting it. Risks and issues seldom make themselves apparent in the initial project planning phase. It is only when a project undergoes execution that project managers and project teams encounter problems.
Along with forecasting potential problems and monitoring possible causes, documenting project issues keeps projects on track. Documenting project issues also eliminates similar difficulties likely to occur as the project progresses.
This is where a RAID log comes in handy.
A RAID log is an effective project management tool to streamline a project; it tracks risks, actions, issues, and decisions. The log tracks triggers, probabilities, issues, impacts, actions, owners, etc.
The jury’s out on the specifics of the acronym, but everyone agrees that RAID includes Risks, Assumptions or Actions, Issues, and Dependencies or Decisions.
Recording such details in a RAID log helps track and manage a project’s progress. RAID logs also provide a framework for proactive risk mitigation and issue resolution, keeping the project on track and meeting the project objective.
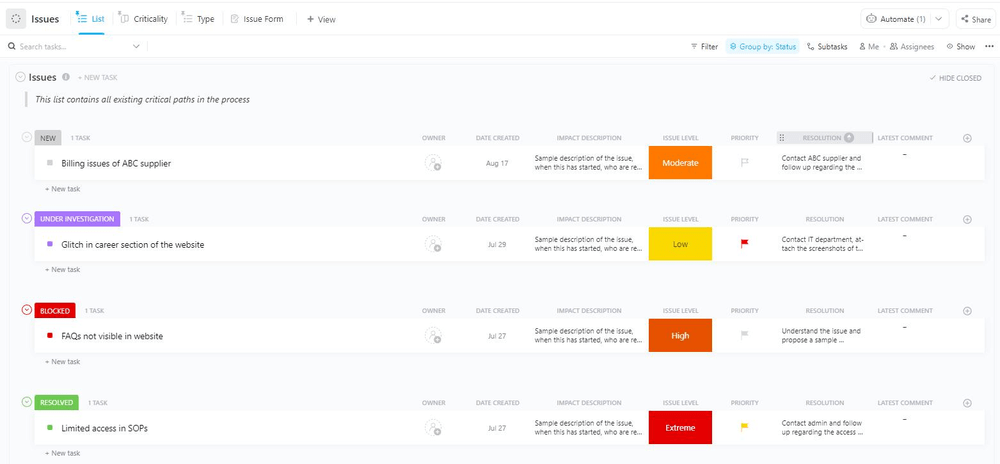
In the risks part of a RAID log, project managers record potential problems or circumstances likely to impact the project negatively. Early identification and assessment of project risks allows project teams to develop contingency plans and take proactive measures to minimize their impact, if not prevent them from occurring.
While you define risks comprehensively in the project planning stage, you must update and revise risks as the project progresses. This is an essential part of the log, and the project team uses the log along with the risk management software.
Project teams factor in certain circumstances or events they expect as the project progresses, with or without definitive proof.
While assumptions are often necessary to make project decisions, they introduce uncertainty and potential risks. Documenting assumptions ensures the project team validates and addresses them during execution.
Unlike risks you anticipate or assumptions based on project knowledge, you record issues based on actual events that threaten to hinder the project’s progress. Once you identify the risks, project teams prioritize and formulate plans to address them. The project team tracks these issues and their resolution in a RAID log.
Teams use the ‘action’ section in a RAID log to document issue resolution. Sometimes, you will find that certain teams club together risks and issues depending on their RAID log template. This helps establish the causal relationship between the risk and the extent of the associated issue.
A dependency is a task that is contingent on another being completed. Many times, the components of a project are connected in a way that they must follow a particular order.
Project teams must complete these interrelated tasks in a specific order or within a certain timeframe for the project to proceed.
Identifying and documenting significant dependencies at the project planning stage helps the project manager keep pivotal points of a project in view. That way, anticipating possible disruptions affecting the project’s progress is easy.
In the project execution stage, managing dependencies ensures that the team coordinates tasks well and promptly anticipates and addresses potential delays or bottlenecks.

In addition to the first four, certain projects demand the project team document actions and project managers’ decisions.
Project managers closely control a project’s progress by documenting and regularly reviewing critical elements that contribute to a project.
Logs also help project teams gain valuable insights into the project’s potential challenges. They proactively develop priorities and strategies to counter them, eventually contributing to project success.
Moreover, RAID logs serve as a valuable communication tool to foster transparency and collaboration among the project’s resources, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
RAID logs and risk registers are essential project management tools to identify and manage risks. However, they differ in their scope and purpose.
A RAID log is used throughout the project lifecycle, while a risk register focuses solely on comprehensive risk assessment and prioritization at the beginning of the project.

It is clear that a RAID log is a vital tool for project leaders, but project managers must understand its limitations, too. This will equip you to address the tool’s constraints and optimize its effectiveness.
RAID logs store crucial information centrally and are accessible to all project stakeholders. And since they contain project-related information, the logs provide a high-level overview of the project’s progress.
As the project progresses, RAID logs help you make informed decisions and evaluate their effectiveness based on your documented decisions and actions.
RAID logs usually have a defined structure with set components, and creating templatized RAID logs helps project teams quickly jump into action. Also, templatized logs allow for consistency across projects, simplify onboarding new project resources, and facilitate training on essential processes within the team.
The RAID log encourages an organized and strategic project management approach and efficiently collects and disseminates vital information. Communication improves, increasing your chances of identifying risks earlier.
You then reduce the time spent while minimizing or preventing risks altogether.
RAID logs assign responsibilities to individuals responsible for resolving issues and challenges. Ultimately, the logs empower project managers to prepare solutions, proactively improving adherence to deadlines and budgets.
RAID logs alone may not suffice for risk management as they only focus on identifying and tracking the R-A-I-D components. A project plan is more appropriate for documenting the specifics of a project in detail.
Additionally, alongside a RAID log, a centralized project management software ensures that project information is accessible to all team members, regardless of their department or function.
The effectiveness of this tool depends on whether the project team consistently updates the log. This will only distract from active project management tasks unless the team balances documentation and project execution.
Also, going too deep may lead to information overload, while being too cursory defeats the purpose of the RAID log.
On the flip side, failing to update the log in real-time renders the log obsolete, potentially leading to confusion among stakeholders.
On larger projects, RAID logs may require frequent reviews, creating a sense of constant scrutiny among the project team members.
RAID logs rely on manually identifying and documenting risks and issues by project team members. Hence, human judgment and awareness play a crucial role in the effectiveness of the RAID log.
Some specific examples of using a RAID log include the following instances.
Selecting a suitable format is the first step. Start a RAID log on paper, through spreadsheets, or with risk management software. Whatever the format, ensure it aligns with the project objectives and accounts for its complexity.
Involve your team and stakeholders in choosing a format, as they will be the end users of the tool and should be comfortable with it.
The next step is to discuss and record each component in detail. For this, team collaboration is paramount. The project team will help you identify potential risks based on their experience and areas of specialization
Collaboration in the creation stage will also help your team members identify their roles and responsibilities for managing projects.
Regular real-time updates to the log are essential for tracking progress and documenting responses to challenges. External stakeholders, including managers and clients, will use the log to understand risk mitigation and issue resolution. These updates will ensure seamless communication within the team and with external partners.
With its comprehensive view of your project’s information, a RAID log also contributes to the decision-making process in future projects, effectively turning experience into valuable insights.
Rather than creating RAID log outlines from scratch, creating a template will make it easier to initiate project planning quickly. A RAID log template is a customized framework for documenting and tracking the individual components: risks, assumptions or actions, issues, and decisions and dependencies.
Below is a sample of a RAID log template:
RAID logs are an indispensable tool in your kitty. You no longer have to sift through prior meeting notes or worry about missing documentation for assumptions—a RAID log is your remedy.
Creating a RAID log for the first time is challenging, but It helps to have the right tools. For instance, ClickUp’s RAID log template will get you started, enabling you to efficiently organize and handle project-related information from the get-go.
While a RAID log is helpful, it is essential to note that it’s much narrower in scope than a project management software offering a more comprehensive approach.
ClickUp, for instance, is a versatile software that helps with project management, team collaboration, customer relationship management (CRM), communication, and much more. Look at ClickUp Tasks and Clickup Features to understand how we can help you.
© 2025 ClickUp