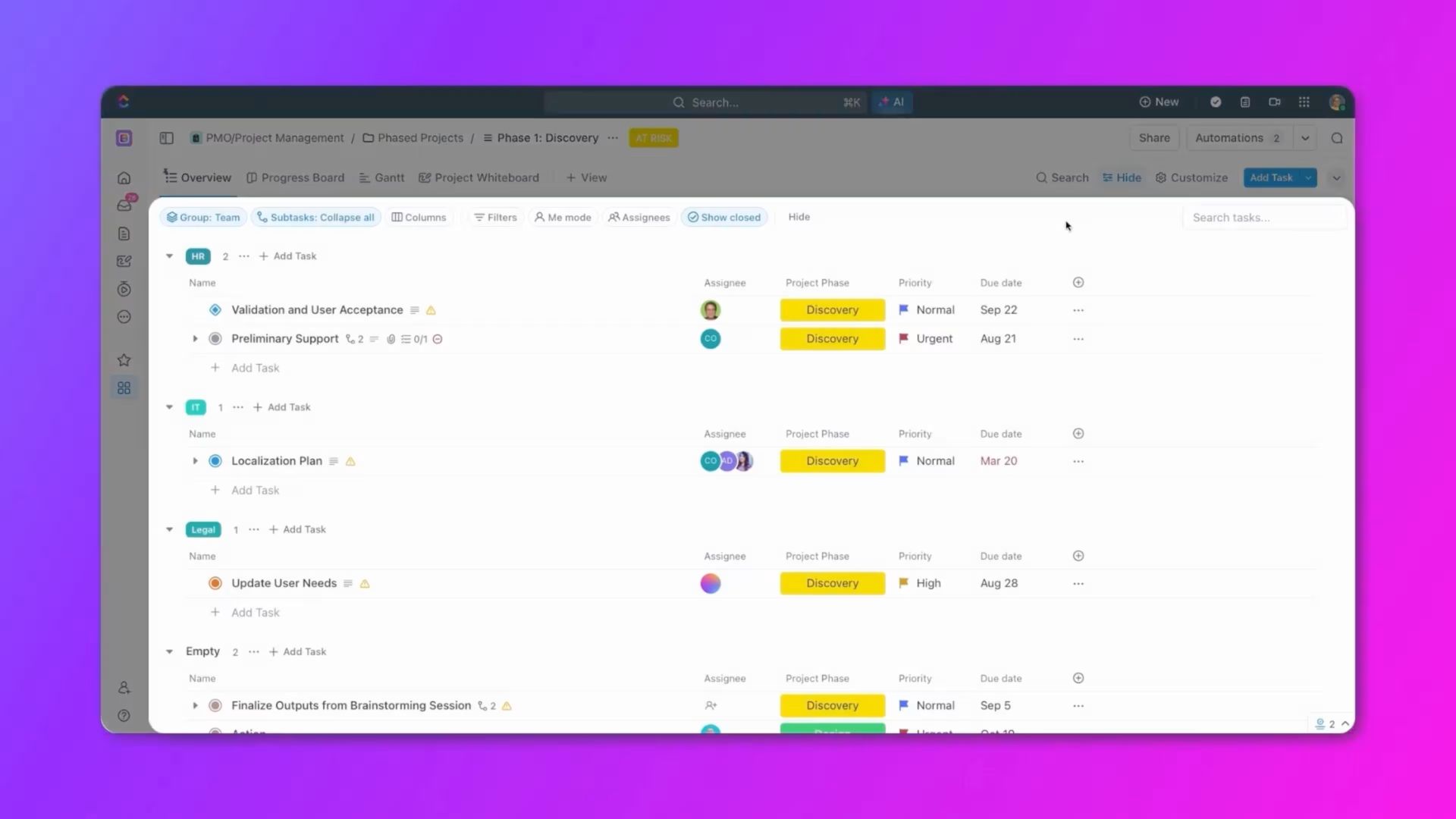
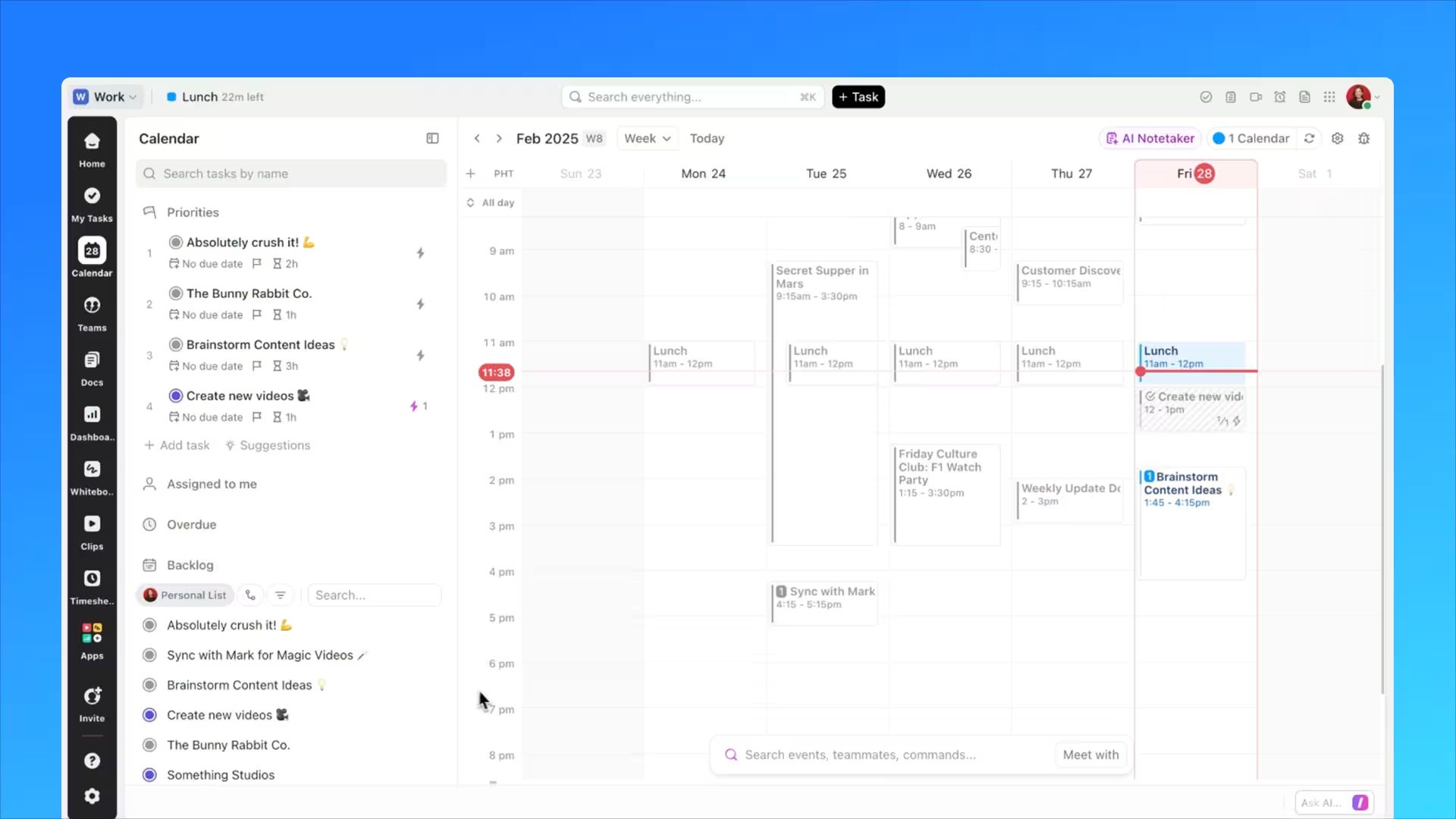
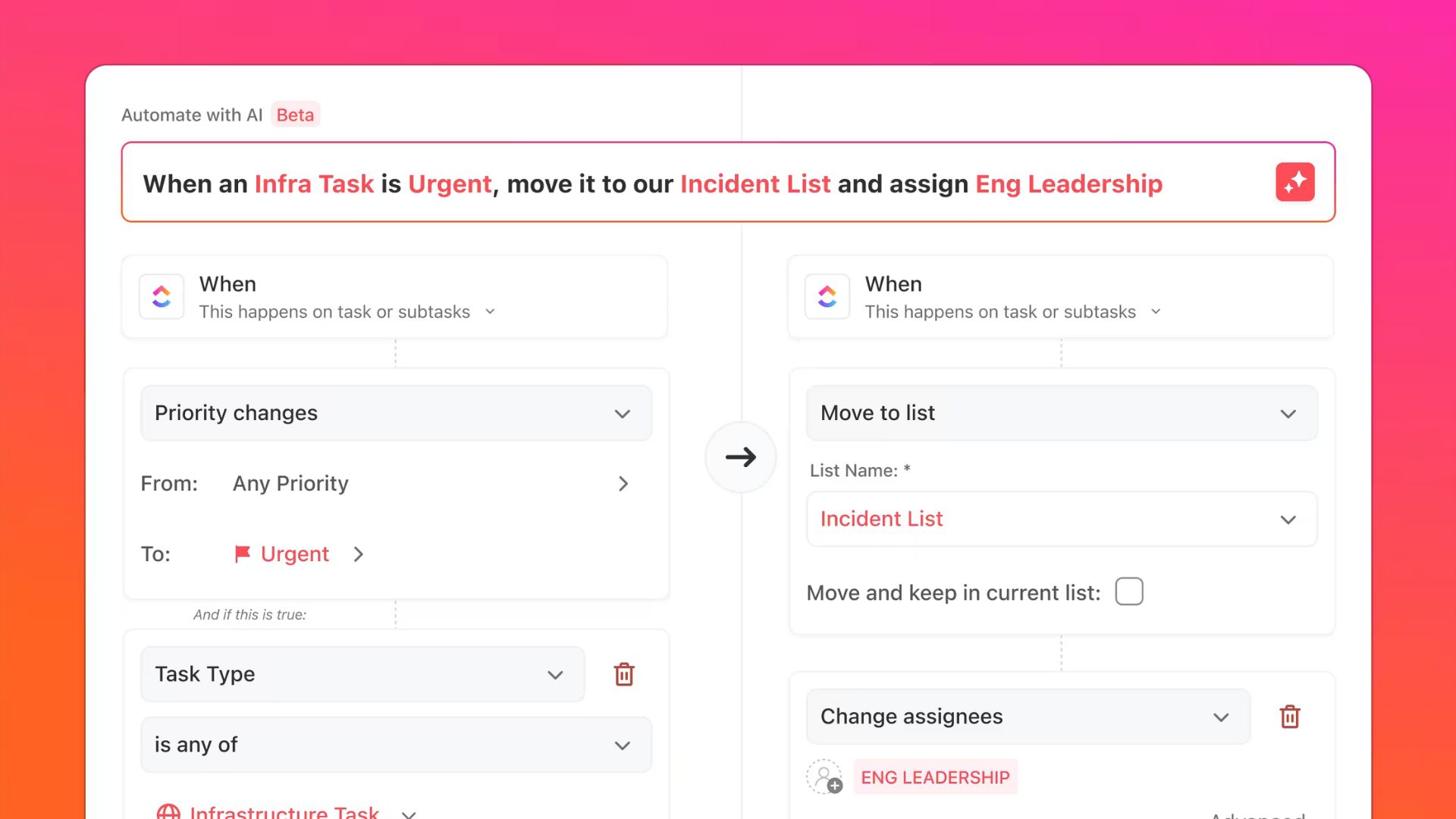
What is Project Management?
Project management is the disciplined practice of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring, and closing projects to achieve specific goals within defined constraints of time, budget, and resources.

Project management has evolved from traditional methods to embrace digital transformation and collaborative technologies. Today's project managers leverage integrated platforms that combine task management, communication, documentation, and analytics in unified workspaces.
This convergence allows teams to work more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and adapt quickly to changing requirements.
At its core, successful project management follows a structured project management life cycle that guides teams through five distinct phases. Each phase builds on the previous one, creating a roadmap from initial concept to final delivery.
The Five Phases of Project Management
Understanding this lifecycle helps project managers anticipate challenges, allocate resources appropriately, and maintain momentum throughout the journey.
Initiation establishes the foundation by defining project objectives, scope, and stakeholders. This is where teams ask critical questions like:
- What problem are we solving
- Who needs to be involved
- Is this project feasible?
Clear project requirements emerge from this phase, defining what needs to be accomplished and why.
Planning transforms those requirements into actionable roadmaps. Teams create detailed project plans and project roadmaps that outline timelines, budgets, resources, and dependencies.
This phase also involves risk assessment and contingency planning to prepare for potential obstacles.
Execution is where plans become reality. Teams implement strategies, complete deliverables, and keep everyone aligned on progress.
This phase requires strong communication, coordination, and the ability to address blockers quickly as they arise.
Monitoring runs parallel to execution, providing ongoing oversight of progress and performance. Project managers track whether the work stays on schedule, within budget, and aligned with original objectives.
This continuous feedback loop allows teams to spot issues early and make course corrections before small problems become major setbacks.
Closure finalizes deliverables, ensures stakeholder acceptance, and captures lessons learned. This often-overlooked phase is critical for building institutional knowledge and improving future project outcomes.
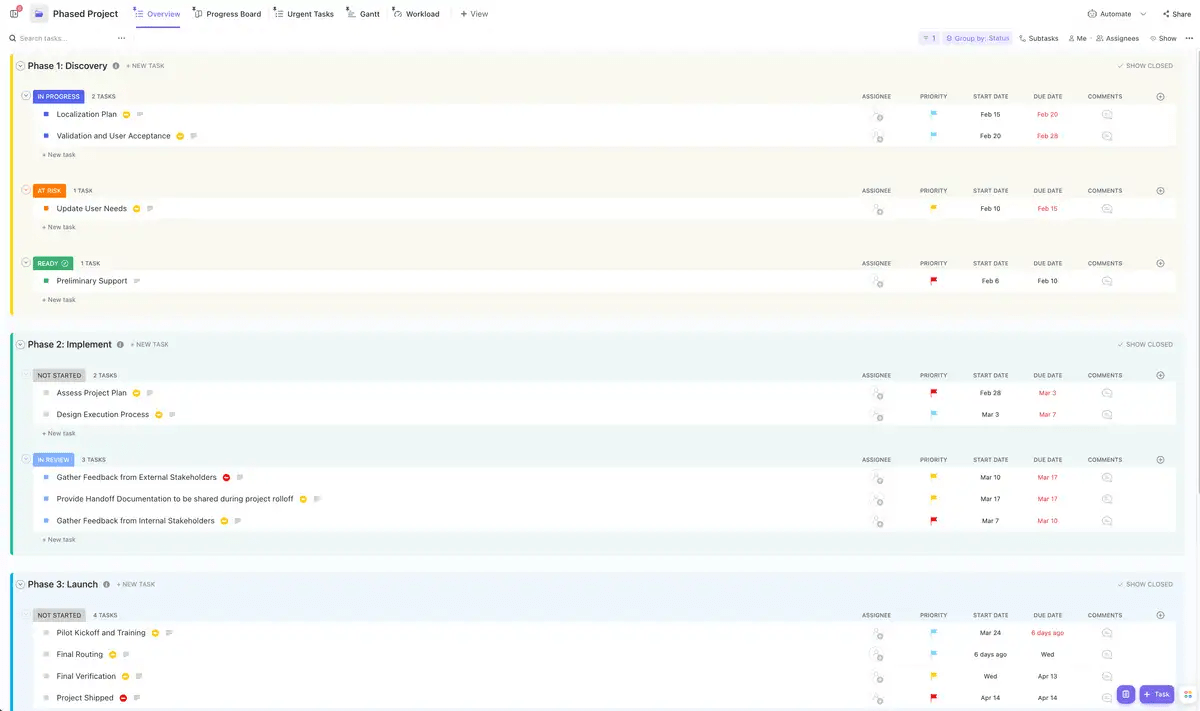
Managing Resources and Performance
Successfully navigating these phases requires mastering several key disciplines. We suggest every new project manager learn them inside and out.
Resource allocation involves strategically distributing people, budget, time, and materials to maximize impact without overextending the team. This connects directly to project time management and ensures deliverables arrive on schedule while maintaining sustainable work practices that prevent burnout.
Throughout the project lifecycle, teams measure success using project management KPIs that track performance against objectives. These metrics provide objective data about what's working and what needs adjustment.
Many organizations take this further by implementing OKR software to align individual contributions with broader strategic goals, creating transparency and accountability from individual tasks all the way up to company-wide initiatives.
And let's not forget that communication is the glue that holds everything together. Regular project reports keep stakeholders informed about progress, challenges, and upcoming milestones while building institutional knowledge for future initiatives.
By establishing clear project management goals and mastering project prioritization, teams ensure high-impact work receives appropriate attention while lower-value activities don't consume disproportionate resources.