Dealing with similar organizational problems repeatedly can be frustrating for working professionals like you.
They interrupt your workflow, your productivity suffers, and you miss critical deadlines and milestones.
To put an end to this, you must start looking for the root cause of the problems you’re dealing with as opposed to solving visible symptoms alone.
While temporary remedies offer quick relief, conducting a root cause analysis to identify critical causes of a problem saves you time, money, and frustration. It also ensures you don’t have to face the same problems again.
Finding the root cause of different organizational problems isn’t as complicated as it may seem because there’s a methodology behind it. Moreover, this method is reputed in fields that rely on continual improvement for success.
This article will discuss six steps for performing a root cause analysis (RCA), its effects, and some RCA methodologies.
Understanding Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a structured method that breaks down problems to identify their root causes and pinpoint relevant solutions. It takes an analytical approach by dissecting your problem until you uncover its underlying causes.
RCA works to resolve various problems, from malfunctioning software to low lead-to-conversion rates, automobile inefficiencies, poor customer service, healthcare cases, content marketing setbacks, and more.
So, instead of patching things up temporarily, you can dig deeper and figure out lasting solutions that boost the reliability and efficiency of your business operations.
Even better, RCA promotes a robust problem-solving culture and motivates your team to discover problem-free approaches to larger processes and tasks.
The principle behind root cause analysis
RCA runs on the principle that effective problem-solving demands more than fixing issues with short-term solutions. You must focus on finding the underlying issue contributing to or causing the problem.
Root cause analysis proves that most (if not all) problems have an underlying cause that can be traced through a structured analysis and investigation.
It involves a systematic problem-solving approach that identifies different layers of issues related to the core problem you’re dealing with, their impact, and causes to help you address them.
Above this, it prioritizes finding long-term solutions over temporary relief. Multiple root causes are often involved, and a methodical approach can help you gather evidence to support your case. Consider breaking the problem down to find cause-effect proof for each sub-problem.
By focusing on root causes rather than general problem indicators, you can prevent issues from recurring by implementing measures that address the underlying problems.
Since root cause analysis is an iterative process, multiple rounds of analysis may be necessary to identify the core issue. The goal is to resolve project management challenges related to inconsistent process outputs.
What is root cause analysis used for?
Here are some examples of how RCA helps in comprehensive problem-solving across different sectors:
- Project management: Diagnoses causes of delays, failures, or overruns, ensuring projects adhere to timelines, budgets, and quality standards
- IT and software development: Solves system outages, software bugs, and security breaches, improving system reliability and user experience
- Supply chain management: Analyzes system disruptions within the supply chain to optimize logistics, inventory management, and supplier relationships
- Healthcare: Investigates medical errors, patient safety incidents, and unexpected outcomes to improve patient care
- Manufacturing: Addresses production inefficiencies, equipment failures, and quality defects, aiming to improve productivity and reduce downtime
- Customer service: Identifies root reasons for customer complaints or dissatisfaction, improving service quality and increasing customer retention
Let’s look at some of the benefits and goals of RCA.
Benefits and goals of RCA
Implementing RCA tools within your organization often comes with the following benefits and goals:
- Prevents the recurrence of problems: Addressing the hidden causes of problems helps RCA resolve them entirely rather than treating their symptoms
- Cost efficiency: Solving the root cause often reduces long-term costs associated with quick fixes and repeated issues
- Improved quality and safety: Particularly in manufacturing and healthcare, RCA is a key tool to upgrade quality and overall safety
- Knowledge sharing: Digging deeper to spot sub-problems and their causes encourages a better understanding of processes and systems in your team.
Let’s now understand how effective root cause analysis benefits your teams’ overall output.
Effect of Performing Root Cause Analysis on Work Efficiency
Frequent root cause analysis of your organization’s processes improves your team’s work efficiency in the following ways.
Preventive culture
Regularly scheduled RCA (root cause analysis) cycles instill a preventive mindset within your team. You’ll observe a proactive approach when addressing potential issues before they manifest as recurring problems instead of doing cause analysis.
Furthermore, it reduces the frequency and impact of problems, allowing teams to maintain a steady workflow and enhance their performance. Notably, this enables you to optimize your resource allocation choices and achieve the project’s timely objectives.
By implementing RCA, teams can enhance their implementation of project management principles and effectively address problems, leading to long-term solutions instead of temporary fixes.
Improved quality of feedback
Effective root cause analysis collects continuous feedback from your team members and the problems they face in predetermined processes.
This collective feedback offers several perspectives on the problem, encouraging critical thinking and prompting better questions, motivating your team to improve on the feedback they deliver.
Ultimately, the ongoing feedback loop refines processes and aligns day-to-day tasks with organizational objectives.
Better problem-solving skills
Steering away from superficial fixes and preferring systematic problem-solving can help your team learn to resolve issues permanently by helping them identify causal factors.
RCA keeps your team engaged and motivated to achieve certain goals based on problem-solving, whether by analyzing the problem’s impact on the workforce or tech-related setbacks caused by the problem.
Remember that your entire team can be involved in this business process. To distribute the workflow and ensure each person’s views are acknowledged, you can allocate sections of larger problems to different members to determine possible causal factors.
This collective push to improve your team’s problem-solving skills gives them greater ownership and responsibility for their work ethics.
Importance of Communication and Team Work in RCA
Collecting opinions on the problem from various sources expands the knowledge pool, helping you analyze the issue comprehensively and identify the underlying root causes.
Effective communication and strategic teamwork are essential for successfully implementing root cause analysis (RCA) as they facilitate gathering comprehensive information.
This collaboration paints a full picture of the process and the issue at hand, making it easier to identify the problem’s causes.
Communication is invaluable in helping your team members share their perspectives and constructively challenge everyone’s assumptions. Such a diversity of thought avoids oversights and biases that creep in during a one-sided analysis.
After shortlisting potential root causes and confirming their priority, you must finalize the best corrective actions. Here, effective communication and teamwork are crucial for building consensus.
Open dialogue lets your teams discuss each proposed solution’s feasibility and potential impacts. This value-oriented collaboration ensures that the final decisions are well-supported and have buy-in from all stakeholders.
Let’s look at an example.
Problem: Your customer service team is failing to resolve queries related to your software subscription offers.
Solution: Offer your customer service team a ready script with sections for common subscription-related queries.
You can only find this solution after:
- Inquiring about the problem your customer service team is facing
- Identifying the common queries that often go unanswered
- Documenting answers for all possible subscription-related questions
- Understanding if there’s a specific target audience with similar questions
Executing RCA projects is only possible through tailored communication patterns between your team members.
Root Cause Analysis Methodologies
Here are four common root cause analysis methods with an explanation and example for each.
RCA methodology 1: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a systematic and structured RCA technique for identifying and documenting all potential failures within a process. It can be applied to design, product, service, or assembly processes.
It involves a comprehensive end-to-end study of prospective failures, where components, assemblies, and subsystems are reviewed. It ensures that all causal factors identified are further analyzed.
The primary objective of FMEA is to identify failure modes, determine their root causes, and assess their effects.
ClickUp’s FMEA Lean Sigma Template lets your team diagnose process problems and prepare safety guidelines and protocols for process variations.
You can design an action plan to study possible failures and their impact on your processes. This acts as reference documentation for your team to address in case of process malfunctions.
Example:
In automotive manufacturing, FMEA calculates the risks associated with different failures, such as airbags, sensors, or software failures.
Once these failures are identified, their severity is determined, and the likelihood of their occurrence is assessed.
Finally, based on this data, risk priority numbers (RPNs) are assigned, and improvements are made to the automobile’s features.
RCA methodology 2: Five whys
The five whys RCA technique focuses on identifying the root of an organization’s problems by asking ‘why’ five times.
Each question comes with a follow-up query to discover the causes of closely related problems.
You may ask ‘why?’ more than five times to determine the root cause.
ClickUp’s 5 Whys Template presents an easy-to-digest visual format for diagnosing and highlighting each sub-problem of a bigger issue.
You can use color codes, add notes as comments, and collaborate with other team members to gather collective perspectives on the problems.
Example:
- If a machine stops working, the first ‘why’ may reveal that a fuse blew
- The second ‘why’ indicates the fuse blew due to an overload
- The third ‘why’ answers that the electrical engineer wasn’t verifying the sustainability or circuit designs
- The fourth ‘why’ mentions this was because of irregular machine maintenance schedules
- The fifth ‘why’ highlights that there was a shortage of junior electrical engineers
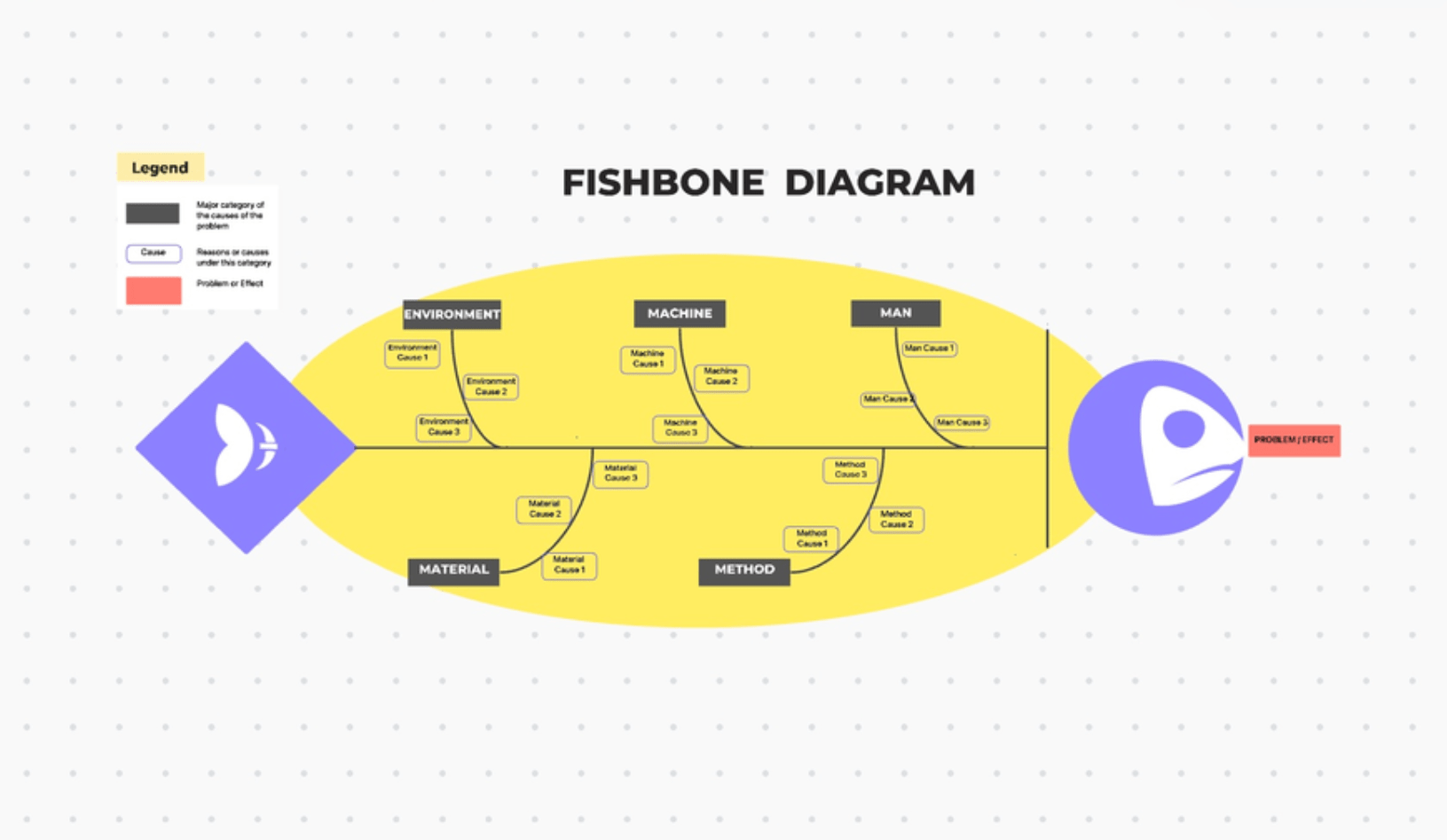
RCA methodology 3: Ishikawa diagram (fishbone diagram)
The Fishbone Diagram is a tool that helps teams visually map the causes of a problem. It sorts causes into major categories to identify and organize possible sources of variation.
This segmentation highlights related factors and sub-factors, placing the causes of issues in context. You can use common categories like Methods, Machines, People, Materials, Measurements, and Environment.
This variety encourages teams to think outside their routine problem-solving paradigms, promoting more comprehensive analysis and allowing them to implement solutions.
ClickUp’s Fishbone Diagram Template allows your team to visualize linkages between problems, sub-problems, causes, and their lasting effects.
From creatively presenting the RCA breakdown method to categorizing causes to spot patterns, this template permits end-to-end modification to suit your RCA style.
Example:
Consider a scenario where a car manufacturer notices a spike in assembly line defects, especially in indoor installation.
The fishbone diagram can categorize potential causes under:
- People (skills and fatigue)
- Methods (installation procedures)
- Machine (tools and equipment calibration)
- Materials (quality of doors)
The diagram works well to pinpoint specific areas for further investigation.
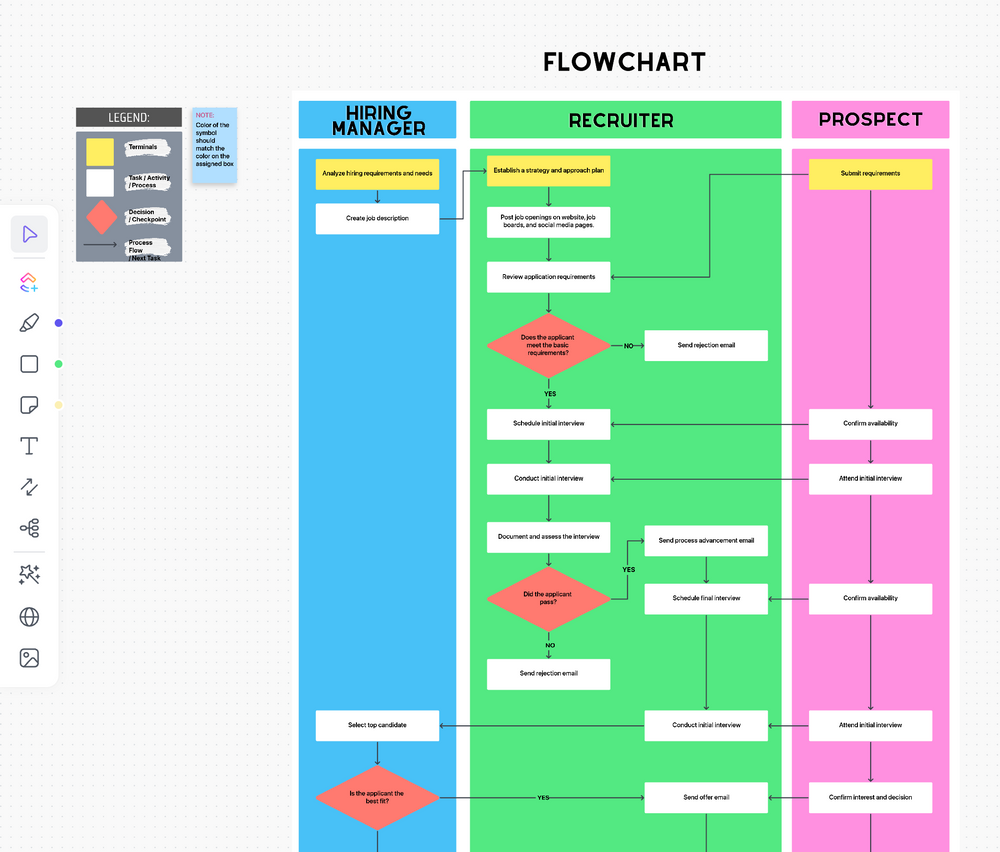
RCA methodology 4: Flowchart method
The Flowchart Method creates a detailed diagram showing a process’s step-by-step workflow. This visual analysis tool tracks the progression of inputs and outputs through various stages, simplifying the identification of bottlenecks and errors.
Remember that flowcharts are best for complex processes where multiple variables and decisions affect your process’s outcomes.
ClickUp’s Flowchart Template offers an organized mapping style for diagnosing problems in your everyday processes. You can streamline RCA workflows and keep all team members up-to-date on typical protocols when solving troubleshooting issues.
Insert symbols and other shapes into this template to customize the process maps according to your team’s preferences.
Example:
A logistics company can use a flowchart to trace the steps in their package handling process. This can pinpoint where delays occur, possibly at check-in, sorting, or dispatch stages.
How to Perform a Root Cause Analysis: Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s walk you through how to do a root cause analysis.
Let’s consider an example of a web application that frequently experiences downtime during peak hours. We need to identify the root cause of this issue, as user complaints are leading to revenue loss.
Here are six steps you can use to do a root cause analysis process:
Step 1: Define the problem
First, clearly define the specific issue affecting your software’s performance.
For example, your web application may experience delays lasting about 30 minutes.
User satisfaction can suffer when high-activity periods occur due to increased traffic, leading to decreased business revenue.
This straightforward definition lays the groundwork for a focused investigation and alerts your team members to the targeted business threat.
Step 2: Collect data about the problem
To effectively address your system issues, involve your team members and customers in identifying and documenting all the problems they face.
Your agenda should be to gather detailed information and analyze downtime incidents. This involves examining various data points that may contribute to the issue, from backend code to frontend content. Here are some examples:
- Server logs: Review for errors or unusual activity preceding the downtimes
- User reports: Collect feedback from users about their in-application activity before the lag occurs
- Performance metrics: Analyze data from monitoring tools for CPU usage, memory usage, and network activity
- Change logs: Examine any recent updates or changes made to the application that correlate with the problem’s onset
This data collection step provides the factual groundwork for further RCA. Furthermore, you may find data categories to set project management KPIs for your RCA objectives.
Step 3: Determine potential causal factors
Study the data gathered in the previous step to identify and list possible causes for the web application’s downtime.
This step is critical for setting the direction for further investigation and eventual problem resolution. Some possible causes include:
- Server capacity: Study server performance logs to check if the hardware resources are adequate during peak loads. This could be a key factor if the servers are consistently reaching capacity
- Memory leaks: Identify patterns in memory usage that indicate memory isn’t being released back to the system. This may cause system crashes. You can use memory profiling tools to track any leaks
- Database issues: Review database metrics and logs for slow queries, locking issues, or timeouts that cause delays or shutdowns in your application
- External dependencies: Examine the reliability of third-party services and APIs that your application depends on
Step 4: Determine the root cause of the problem
Now that you’ve completed the foundational research for your RCA, it’s time to identify the actual root cause(s) from this potential list. Here are some tips to follow:
- Data assessment: Use statistical tools to assess the collected data for correlations between potential causes and downtime incidents. For example, if memory usage spikes precede every downtime event, this points to a memory leak
- Hypothesis testing: Formulate a hypothesis based on the data analysis. For instance, if you suspect a memory leak, you might recreate the peak conditions in a controlled environment to test if the issue can be reproduced
- Consultation: Sometimes, complex issues require consultations with experts like database administrators or senior developers
- Validation: Validate the identified root cause by temporarily addressing the cause and monitoring to see if the problem persists
Step 5: Prioritize causes
Narrowing down to potential causes is only half the battle won. You must prioritize them based on what best impacts the lowering of your web application’s downtime.
Account for these factors when prioritizing causes:
- Likelihood of occurrence: Some issues may be more likely than others. For example, memory leaks in a specific poorly maintained legacy module might be more probable than server hardware inadequacies
- Resource allocation: Calculate the resources (time, cost, and expertise) needed to address each cause. Prioritizing issues that can be resolved quickly and with fewer resources may provide quick wins, but this should be balanced against the impact
- Risk assessment: Assess the risks associated with each cause. For instance, if your choice of not addressing a database locking issue can lead to data loss, it should be prioritized over less critical issues
Your goal must prioritize potential causes contributing largely to the problem.
Step 6: Solution, recommendation, and implementation
Now that the root causes are prioritized, you can develop actionable solutions. In the case of a memory leak, you can do:
- Code refactoring: Update and optimize the code where the memory leak occurs
- Increase resources temporarily: Enhance server capacity to handle increased loads while the code is being fixed
- Improve monitoring tools: Implement better monitoring to alert your team immediately when memory usage patterns point to a potential leak
You must prepare a detailed action plan and document the process for future reference. In this step, consider using the critical path method to schedule the order of implementation tasks accurately.
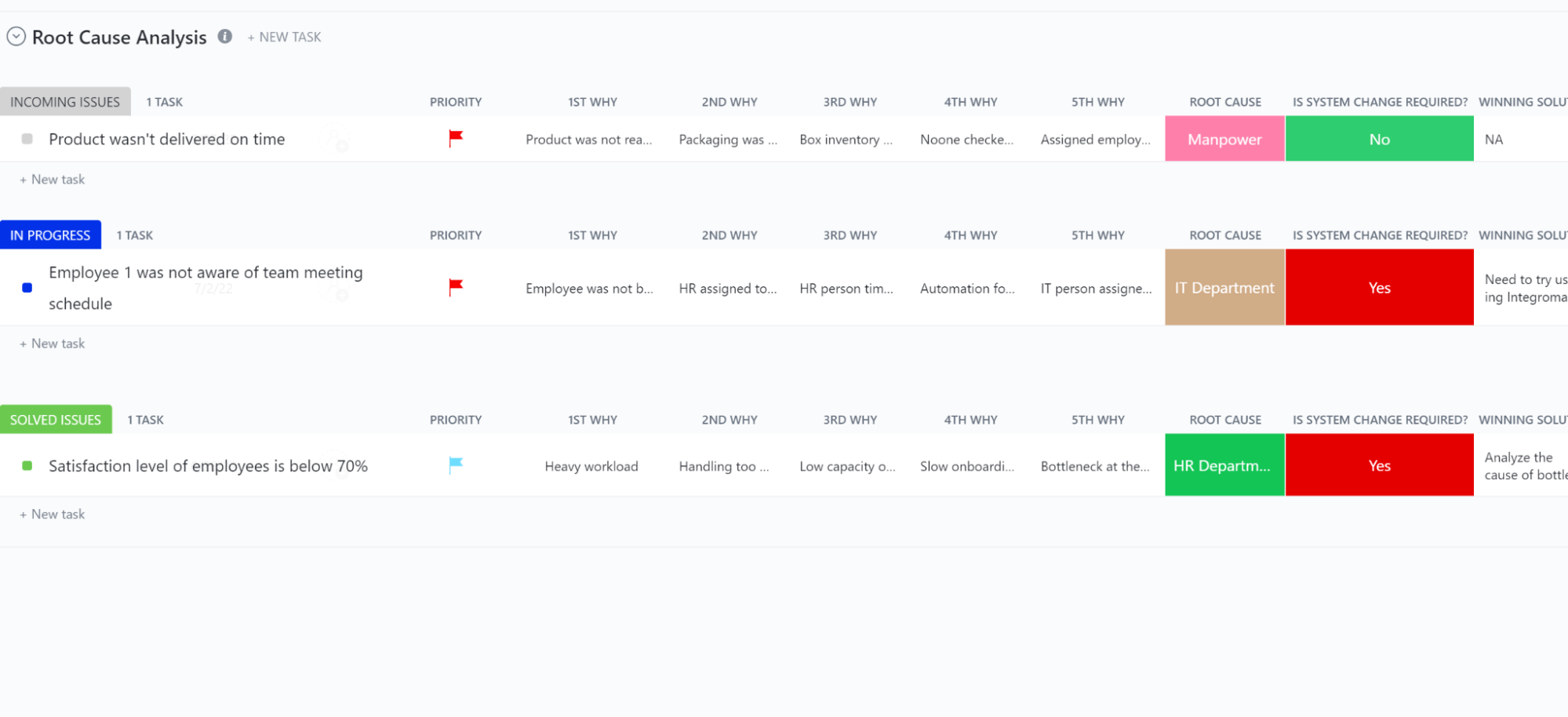
ClickUp’s Root Cause Analysis Template helps you understand how to do a root cause analysis. It simplifies these six steps with an all-in-one project management and visualization tool to find the originating source of your organization’s problems.
By brainstorming potential causes and analyzing everyone’s opinions before repairing the root cause, you can increase in-team collaboration.
Move from Reactive to Proactive with RCA’s Problem-Solving Style
RCA’s strategic approach empowers organizations to examine recurring problems and develop long-term solutions. When gathering data on potential causes, it’s essential to clearly define the problem and involve all team members and project collaborators.
RCA templates can fortify your department’s processes against future vulnerabilities. This proactive approach also improves your operational reliability in the long term.
Try ClickUp to explore a wide range of continuous improvement RCA techniques within a fully customizable dashboard. Within minutes, you can customize fields and template views and allocate smaller cause-effect identification to your teams.
Sign up to use ClickUp for free today.